Split Phase Induction Motor: Working & Best Applications
Read More About
Introduction
A split phase induction motor is a type of AC motor that is commonly used in various applications, including household appliances, fans, and pumps. It is called a “split phase” motor because it uses a special starting winding and a main (running) winding to generate a rotating magnetic field.
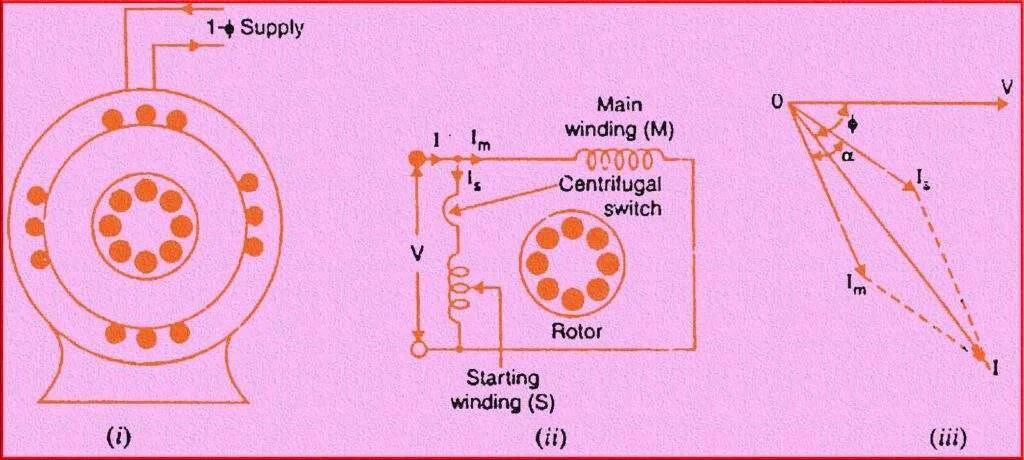
The construction of a split phase induction motor typically includes two windings: the main winding and the auxiliary (starting) winding. The main winding is made of heavy-gauge wire and is responsible for the motor’s normal operation. The auxiliary winding is made of finer-gauge wire and is positioned at an electrical angle to the main winding.
When power is supplied to the split phase motor, the current flows through both windings. However, due to the difference in wire gauge and positioning, the starting winding creates a magnetic field that is out of phase with the magnetic field generated by the main winding. This phase difference creates a rotating magnetic field, which causes the motor to start rotating.
Once the motor reaches a certain speed, a centrifugal switch or a current relay disconnects the starting winding from the power source. At this point, the motor relies solely on the main winding to generate the rotating magnetic field required for continuous operation.
Split phase induction motors are relatively simple and cost-effective compared to other types of AC motors. However, they have limitations in terms of their starting torque, efficiency, and speed control. They are typically used in applications that don’t require high starting torque, such as small appliances, fans, and light loads.
It’s worth noting that split phase induction motors are different from capacitor start induction motors and capacitor start capacitor run induction motors, which use capacitors in addition to the starting winding to improve the motor’s starting characteristics and overall performance.
Split Phase Induction Motor construction
The construction of a split phase induction motor consists of several key components that work together to enable its operation. Here is a breakdown of the typical construction elements:
Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the motor and is primarily responsible for generating the rotating magnetic field. It is typically made of laminated iron cores stacked together to minimize eddy current losses. The stator includes slots where the motor windings are placed.
Main Winding: The main winding, also known as the running winding, is made of relatively heavy-gauge wire and is connected directly to the power supply. It is positioned in the stator slots and carries the majority of the current during motor operation.
Auxiliary Winding: The auxiliary winding, also known as the starting winding, is made of finer-gauge wire and is connected in series with a starting capacitor. It is also placed in the stator slots but is positioned at an electrical angle to the main winding. The auxiliary winding creates a phase shift in the magnetic field during startup to induce rotation.
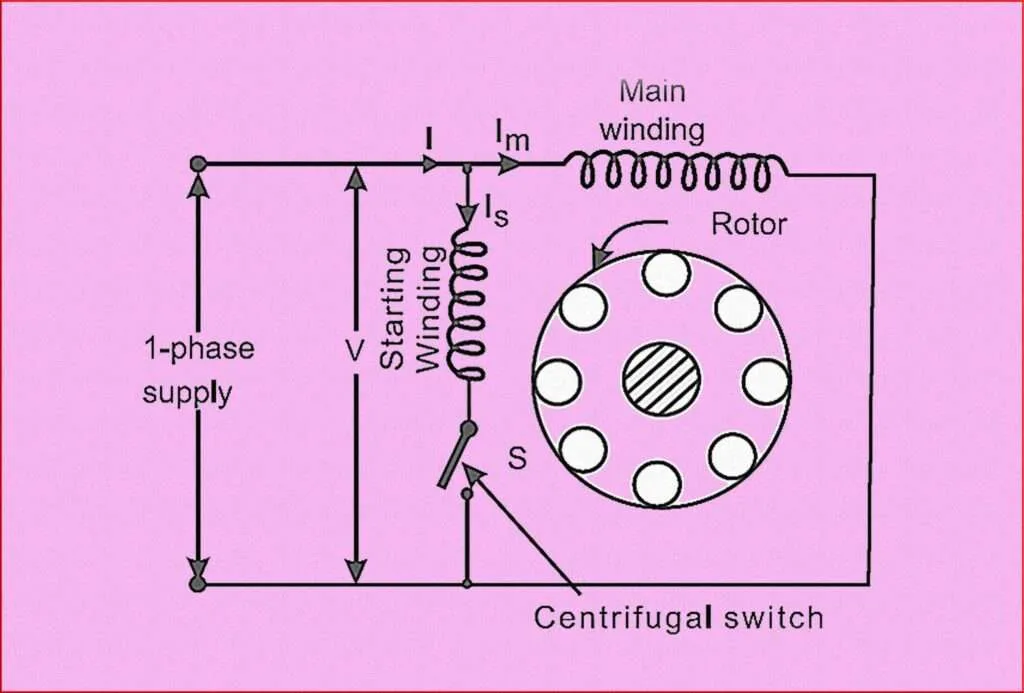
Capacitor: The starting winding is connected to a capacitor, which provides a phase shift to the auxiliary winding’s current. The capacitor is typically an electrolytic or motor-run capacitor and helps create the necessary torque during motor startup.
Centrifugal Switch or Current Relay: To disconnect the auxiliary winding and capacitor from the power supply once the motor reaches a certain speed, a centrifugal switch or a current relay is often employed. These devices are activated by the rotational speed of the motor and open the circuit of the auxiliary winding to ensure that only the main winding remains connected during normal operation.
Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the motor. In a split phase induction motor, the rotor typically consists of a squirrel cage rotor. It is made of laminated iron cores and conductive bars or shorted copper/aluminum segments. The rotating magnetic field generated by the stator induces currents in the rotor, creating the torque necessary for rotation.
Bearings: The motor includes bearings that support the rotor shaft and enable smooth rotation. These bearings are typically made of high-quality materials, such as ball bearings or sleeve bearings, to reduce friction and ensure longevity.
Motor Housing: The motor housing encloses and protects the internal components of the motor. It is typically made of a durable material, such as aluminum or cast iron, and helps dissipate heat generated during operation.
These are the basic components of a split phase induction motor. The specific design and arrangement of these components may vary depending on the motor’s size, power rating, and intended application.
Torque Speed Characteristic of Split Phase Induction Motor
The torque-speed characteristic of a split phase induction motor is an important parameter that describes the relationship between the motor’s torque output and its rotational speed. The characteristic curve typically consists of two distinct regions: the starting region and the running region.
Starting Region: In the starting region, the motor is initially at rest, and both the main winding and the auxiliary winding are energized. The starting winding, in combination with the capacitor, creates a rotating magnetic field that induces a starting torque. The starting torque is relatively high but gradually decreases as the motor accelerates. The motor accelerates until it reaches a certain speed, at which point the centrifugal switch or current relay disconnects the auxiliary winding.
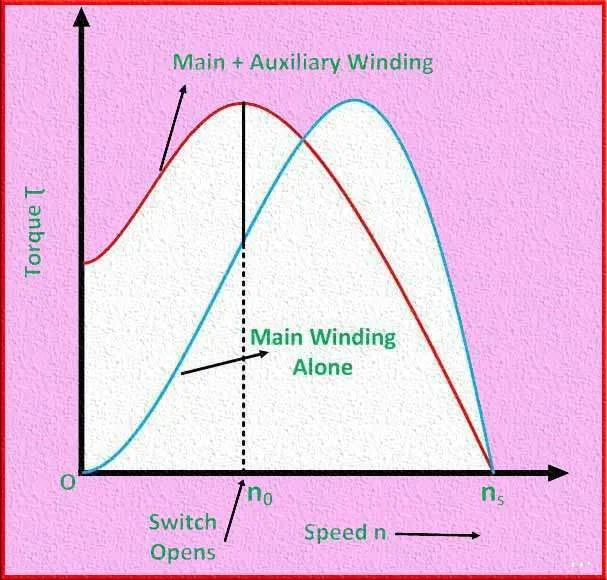
Running Region: Once the motor enters the running region, it continues to operate with only the main winding. The running region represents the stable operation of the motor. The torque in this region is lower than the starting torque but remains relatively constant with slight variations due to load changes. The motor achieves its maximum torque in the running region at a specific speed called the “synchronous speed.” The synchronous speed is determined by the motor’s design and the frequency of the power supply.
It’s important to note that the torque-speed characteristic of a split phase induction motor exhibits limitations compared to other motor types. Split phase motors generally have lower torque compared to other motor types, and the starting torque is typically lower than the running torque. Additionally, the motor’s efficiency decreases as the speed decreases, resulting in reduced overall performance.
Applications of Split Phase Induction Motor
Split phase induction motors find applications in various devices and systems where moderate starting torque and simple construction are sufficient. Here are some common applications of split phase induction motors:
Household Appliances: Split phase motors are extensively used in household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and fans. They are ideal for powering the rotating mechanisms in these appliances.
HVAC Systems: Split phase motors are employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to drive blowers, fans, and pumps. They provide the necessary air circulation and cooling in these systems.
Compressors: Split phase motors are utilized in small air compressors for applications such as inflating tires, powering pneumatic tools, and operating small-scale air systems.
Water Pumps: Split phase motors are commonly employed in water pumps for residential and light commercial applications. They power the impeller that circulates water in systems such as wells, swimming pools, and irrigation systems.
Office Equipment: Split phase motors can be found in various office equipment, including printers, scanners, shredders, and photocopiers, where they drive the mechanical components of these devices.
Vending Machines: Split phase motors are used in vending machines to power the motors that dispense products, rotate spiral dispensers, and operate cooling systems.
Small Industrial Machinery: Split phase motors are suitable for driving small-scale industrial machinery, such as conveyor belts, mixers, small-scale manufacturing equipment, and pumps.
It’s important to note that split phase motors are generally not suitable for applications that require high starting torque or precise speed control. In such cases, other types of motors, such as capacitor start induction motors or three-phase induction motors, may be more appropriate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the split phase induction motor is a commonly used type of AC motor in various applications. Its construction includes a stator, main winding, auxiliary winding, capacitor, centrifugal switch or current relay, rotor, bearings, and motor housing.
The split phase motor operates by using a phase difference between the main winding and auxiliary winding to create a rotating magnetic field, which initiates motor rotation. The starting winding and capacitor provide the necessary starting torque, and once the motor reaches a certain speed, the auxiliary winding is disconnected, leaving the main winding to generate the rotating magnetic field for continuous operation.
Split phase induction motors are known for their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability. They are commonly used in household appliances, HVAC systems, water pumps, office equipment, vending machines, and small industrial machinery.
However, split phase motors have limitations in terms of starting torque, efficiency, and speed control compared to other motor types. They are most suitable for applications that do not require high starting torque or precise speed regulation.
Overall, split phase induction motors provide a practical and economical solution for a wide range of applications where moderate starting torque and simple construction are sufficient.
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn to see our latest posts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a split phase induction motor?
A split phase induction motor is a type of AC motor that uses a secondary winding with a phase shift to create a rotating magnetic field necessary for motor operation.
Is a split phase motor AC or DC?
A split phase motor is an AC (alternating current) motor, meaning it operates with an AC power supply.
What is the objective of a split phase induction motor?
The objective of a split-phase induction motor is to provide a simple and cost-effective solution for applications requiring low to moderate starting torque, such as household appliances and small machinery.
Which type of rotor is used in a split phase induction motor?
A split phase induction motor typically uses a squirrel cage rotor, which consists of conductive bars shorted at the ends by conducting rings.
What is the difference between a single-phase and a split phase motor?
The main difference between a single-phase motor and a split phase motor is the presence of an additional auxiliary winding in the split phase motor. This auxiliary winding creates a phase shift and assists with motor starting.
What is an example of a split phase motor?
Is a split phase motor single-phase?
Yes, a split phase motor is a type of single-phase motor. It utilizes a single-phase power supply but incorporates an additional winding to enable starting torque.
Which motor can run on both AC and DC?
A universal motor is capable of running on both AC and DC power sources. It is designed with a series-wound rotor and can be used in applications where flexibility between AC and DC operation is required.
What are the two types of split phase motors?
The two main types of split phase motors are the resistance-start induction motor and the capacitor-start induction motor. These variations differ in their methods of achieving the phase shift required for starting.
Which motor is stronger, AC or DC?
The strength or power output of a motor depends on various factors such as design, size, and application. Both AC and DC motors can be designed for high power output, so it is not accurate to categorically state that one type is stronger than the other.
Why is it called a universal motor?
It is called a universal motor because it can operate on both AC and DC power sources. This versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications where the power source may vary.
Which motor is a universal motor?
The universal motor is a type of motor that can run on both AC and DC power sources. It is commonly used in appliances like vacuum cleaners, power tools, and kitchen appliances.
What are three applications of a split phase motor?
Three common applications of split phase motors include household appliances (e.g., fans, air conditioners, refrigerators), small machinery (e.g., pumps, compressors), and tools (e.g., drills, saws).
What are the two main types of motors?
The two main types of motors are AC (alternating current) motors and DC (direct current) motors. AC motors operate on an AC power supply, while DC motors operate on a DC power supply.

2 Comments