Types of Pumps: Important Types, Working & Applications
Introduction
In different sectors of industries, we see various types of pumps. Do all types of pumps work in the same manner? The answer to this question is yes as the basic phenomenon behind these different types of pumps is the basic operation of pumps.
A pump rotates and moves different types of fluids in a variety of reactions or processes. It’s a device that uses its electrical energy at one end and mechanical energy on the other end to move the fluids in pipes or ducts.
Read More About
In the operation of all types of pumps, the electrical energy converts into mechanical or hydraulic energy as it serves the purpose of moving fluids through them. Depending upon the pumping mechanism, a pump may contain more than one pump attached in series on the same shaft.
So, these types of pumps come in categories of muti-stage pumps while a single-stage pump has only one stage. We will try to cover the main types of pumps, their construction, and their applications in this article.
Types of Pumps
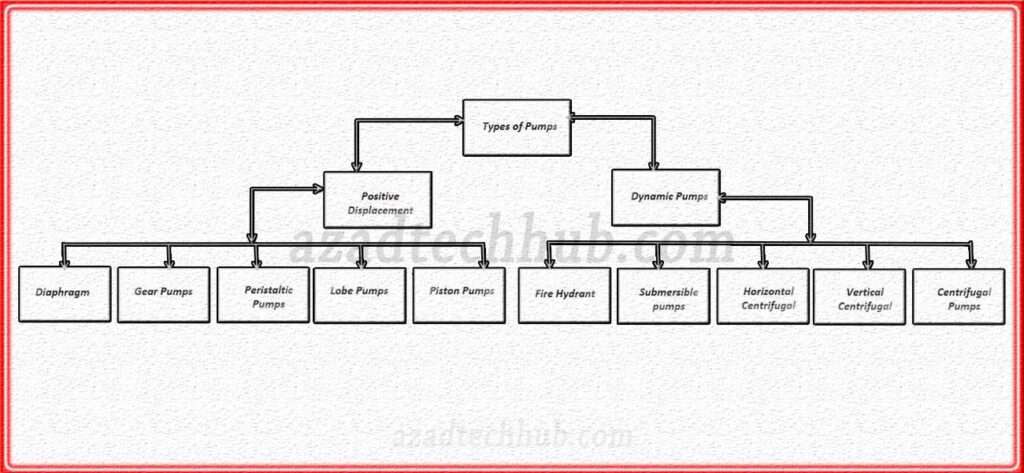
We can classify types of pumps into two main categories depending on the direction of fluids that pumps pass through. These types include positive displacement and dynamic pumps.
We can submerge the pumps into fluids that they need to pass through. On the other hand, we can also make them work by placing them externally. So, a general tree structure is shown below figure,
Positive Displacement Types Pumps
A positive displacement pump gives an extra displacement to the contained fluid inside the pump cavity. Normally, the suction and discharge cavities are different in size. A positive displacement pump encloses a fixed volume of fluid and then displaces it out through a narrow discharge side.
There are numerous types of pumps but we will discuss here the main five types of positive displacement pumps.
Diaphragm Pumps
This is a positive displacement type of pump where the fluid is pumped through the combined effort of a membrane or diaphragm and different types of valves. These valves may include flap valves, butterfly valves, shut-off valves, and some types of check valves.
These valves are located on the sides of the diaphragm. As the pump functions, the valves on the opposite side of the diaphragm open and close with the movement of the fluid.
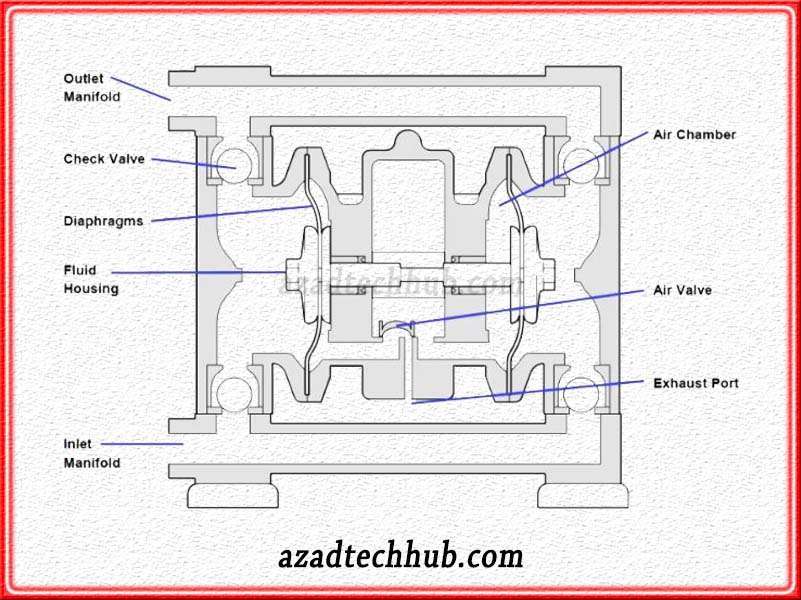
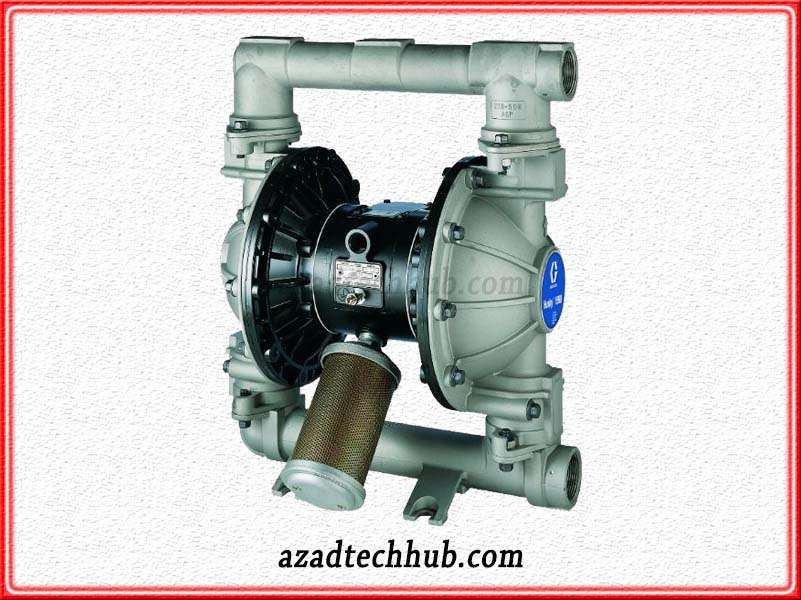
The diaphragm in these pumps operates with a hydraulic or pneumatic system. Due to operation with air, we call these types of pumps AOD pumps or air-operated pumps. These pumps can discharge pressure up to 1200 bar.
Depending upon flow rates, these pumps include both types and can be utilized to handle slurries and sludges. These types of pumps are around 97% efficient. Some of the major applications include food processing, coal extraction, slurry transfer, industrial chemical transfer, etc.

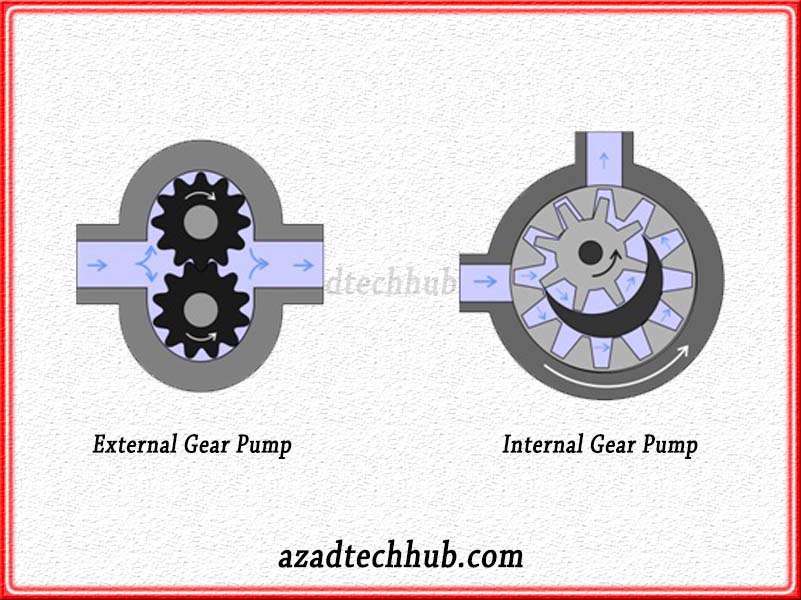
Gear Pumps
These types of pumps contain meshing gears that displace the fluid by their clockwise or anti-wise movement. With each revolution these pumps push a stable amount of fluid therefore we normally refer to these types of pumps as positive dislocation pumps. Heavy and thick fluids can easily be surpassed by the movement of the meshing gears inside.
The impeller velocities are high because these positive displacement pumps do not contain any valves to open or close. Therefore, resultantly friction losses are reduced and the movement of the fluid becomes an easy task for the pump. Depending upon low friction and the movement of meshing gears, thick fluids like greases, fuels, and lubricants can be tackled easily by these pumps.
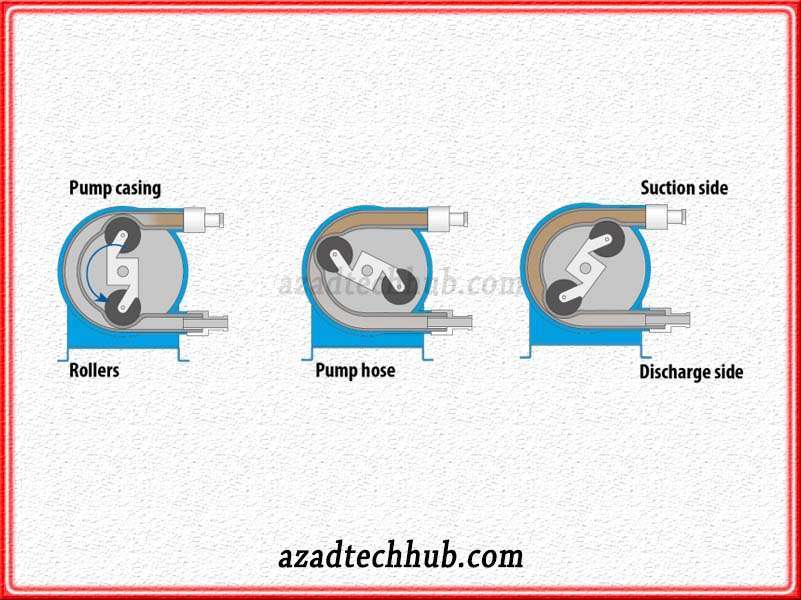
Peristaltic Pumps
This is a positive displacement pump which is commonly referred to as the roller pump due to its movement. The Peristaltic pump has a circular outer pump casing where there is a flexible tube containing liquid fitted inside. Some sort of rollers are also attached to the rotor.
As the pump functions, with the rotatory motion of the rotor, these rollers or wipers compress the tubing liquid or fluid and thus give easiness in flow. Due to fitted tubing, these types of pumps are also known as tube pumps. These types of pumps find applications in the processing industry, food, and chemical transfer. These pumps find applications in the filling industry like toothpaste, medical tubes, ointments, etc.
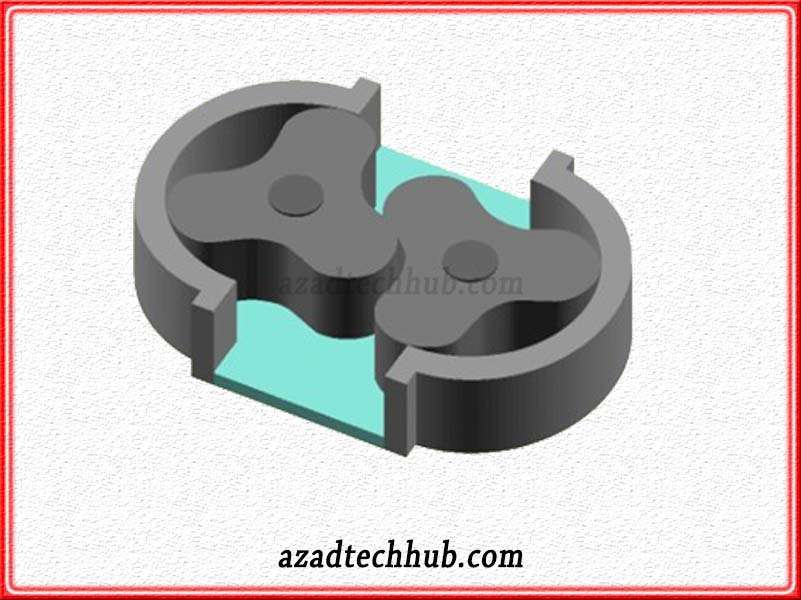
Lobe Pumps
Lobe pumps are very similar to gear pumps in terms of operation. The main difference is unlike gear pumps where meshing gears join and force each to turn the other, here in lobe pumps just join together. Beverage, food, chemical, biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and pulp and paper industries are common examples of applications of these types of pumps.
These pumps have clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) characteristics. These types of pumps have very high corrosion restive and good sanitary qualities. These pumps can easily handle very thick fluids without damaging their properties. In comparison with gear pumps these pumps seem superior to moving slurries & sludges.
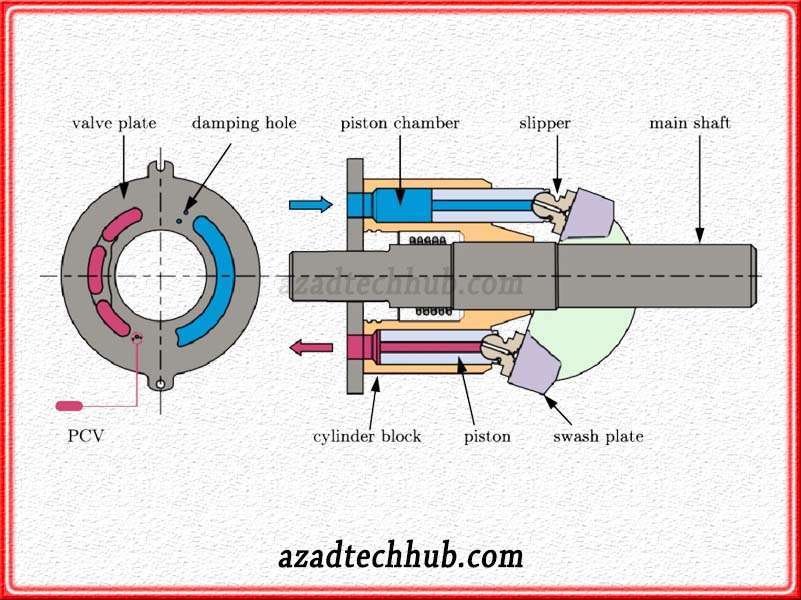
Piston Pumps
Piston pumps are the types of positive displacement pumps where the piston incorporates a a high-pressure seal. The operating pressure range is very wide for piston pumps and the flow rate does not disturb with high pressures.
High-viscosity compounds can be handled by piston pumps very easily. There are mainly two types of piston pumps including force pumps and lift pumps. Piston pumps find applications where there is a requirement for high pressure with consistency. These pumps we normally find in irrigation systems.
Dynamic Types Pumps
Dynamic pumps are the pumps that are mostly eemployedwater applications. Major types include fire hydrants, centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, vertical centrifugal systems, and horizontal centrifugal systems. Let’s look at different types of dynamic pumps one by one.
Centrifugal Types Pumps
Centrifugal force is the main ingredient in the operation of centrifugal pumps. In this type of dynamic pump, electrical energy from the coupled motor converts into hydraulic type. The impeller and the curved casing are the two important and main components of a centrifugal pump.
The curved casing collects the fluid, leaving the impeller, and then surpasses with high pressure through the discharge tube.
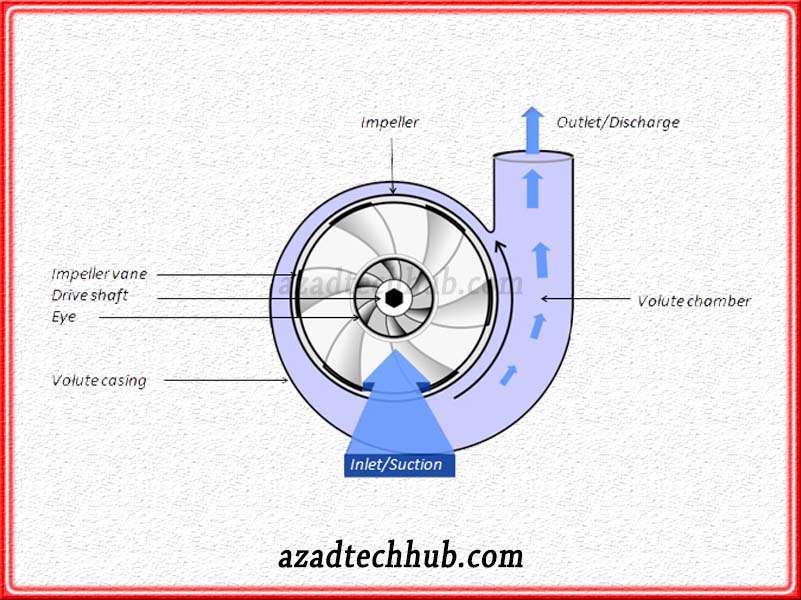
These pumps are the most common type of pumps and are comparatively cheap to manufacture. These types of pumps mmore tly stilloyed in solar systems of irrigation and fishing farms. The liquid surpasses the pump’s high pressure at the end due to the pressure difference.
Additionally, when the liquid leaves the impeller, the velocity of the liquid is very high. Therefore, centrifugal force increases which in the end increasing the momentum of the liquid leaving the discharge tube. Normally, these types of dynamic pumps find applications in septic tanks, pharmaceuticals, mining, agriculture, power plants, and petroleum sectors.
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
Vertical centrifugal pumps have vertical turbines inside and are mainly eemployed applications where there is a requirement of transferring water from deep wells. These pumps due to their vertical turbine refer to as line shaft pumps or vertical pumps.
They are sometimes also termed cantilever pumps. These types of pumps normally use throttle bushing instead of filling containers for covering shafts. These types of pumps coare coupled directly operated motors which have a maximum of 3000 rpm. Due to a flow rate of around 6 to 75m3/h and a head of around 5 to 38m, these types of pumps have higher performance.
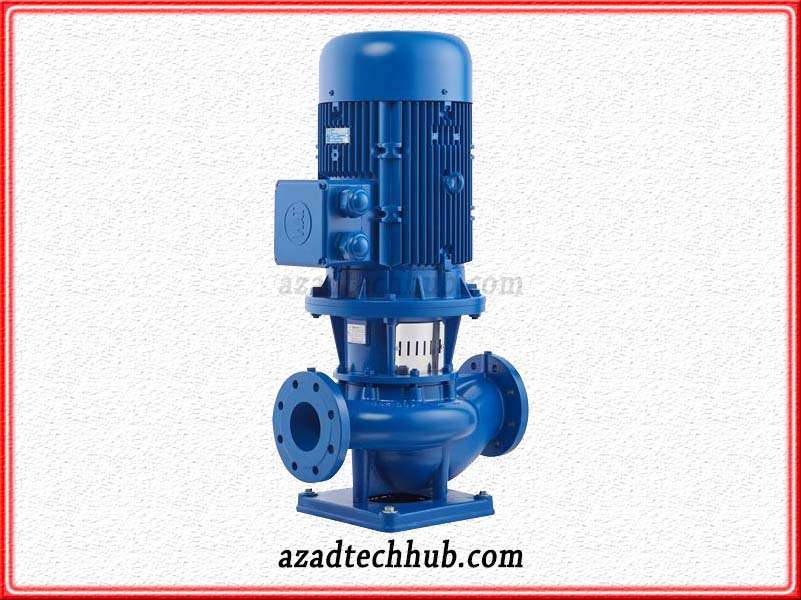

Horizontal Centrifugal Pumps
Horizontal centrifugal pumps are same as the vertical centrifugal pumps, just the shaft location is horizonhorizontaler, the placement of the shaft is in between overhthe ung and the bearings. While as discussed above the vertical centrifugal pump has a shaft vertically oriented. The pumps used in the solar systems are horizontal centrifugal pumps.
These pumps can run well on solar panels and they can deliver maximum flow rate when connected with variable frequency drives. These drives run in such a way that these pumps even start in the morning with little sunshine. The same scenario happens in the evening when the sunshine is decreasing.
These pumps are best suitable for domestic needs as well as fulfill requirements in irrigation, air conditioning, drinking water supply, and for boosting pressures of watering pipes. In solar systems these pu,mps refer to are referredrface pumps as they install on the surface to get the water out of bore wells.
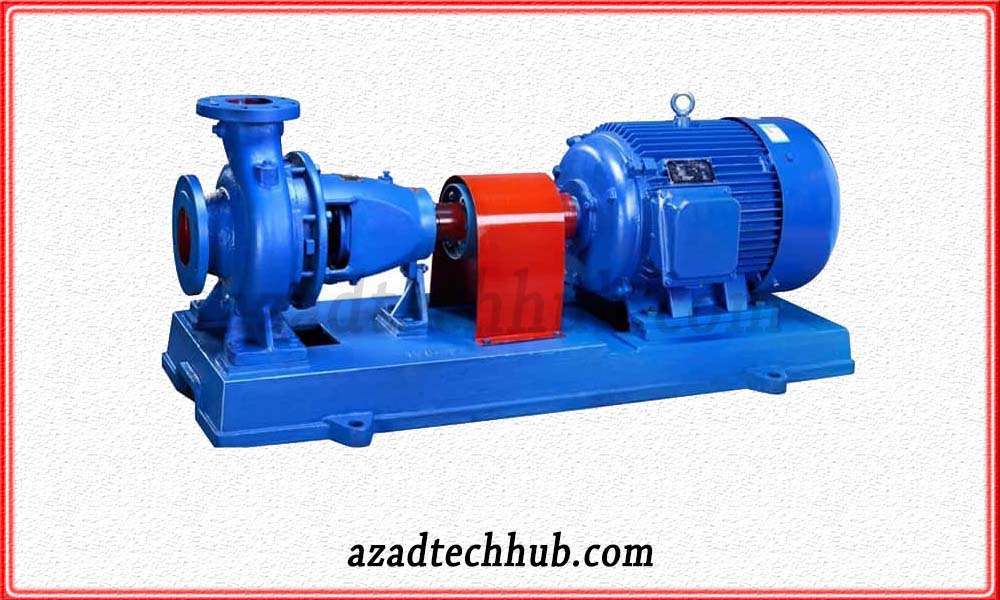

Submersible pumps
These types of pumps are widely becoming prominent in solar systems as they are installed or submerged inside the water. Apart from the solar system, these pumps are entirely capable of submerging in any liquid. These pumps have a hermetically sealed motor which is coupled with the main pump and sealed in such a way that the whole body can be submerged inside the liquid.
The impeller inside is connected to the diffuser. The impeller drives liquids and transfers their kinetic energy. In the diffuser section, the liquids convert their kinetic energy into pressure energy.
These pumps are also term to sewage putermedptic pumps or stormwater pu,mps due to their compact and sealed design or submerged property. These pumps have different ratings according to the head and the flow rate.
As the pumps are becoming increasingly popular due to their best suit in solar system design, these pumps are expensive as compared to the surface pumps. Submersible pumps work very well with variable frequency drives where they operate along with solar panels in morning to evening with full efficiency. Learn more about working solar system design by following this link.

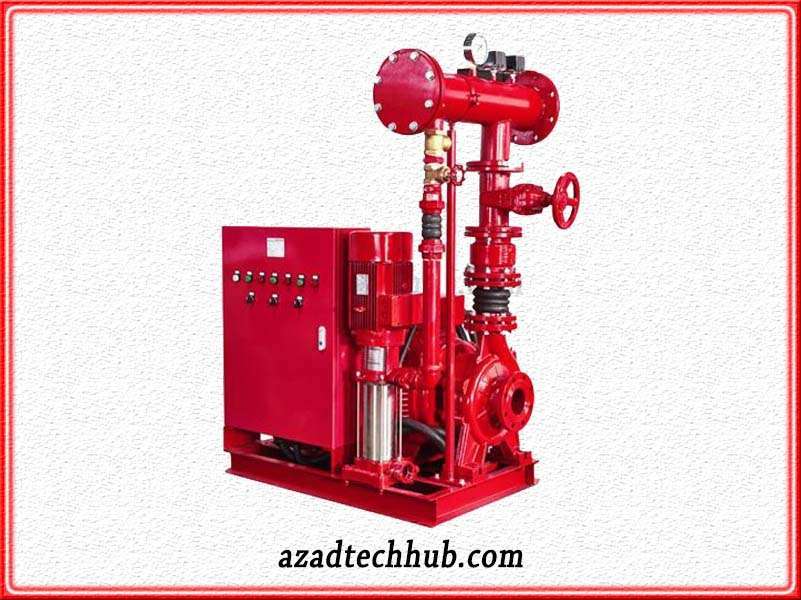
Fire Hydrant Pumps
Fire water pumps, hydrant boosters, or fire pumps are the reciprocal names of fire hydrant pumps. These pumps are mainly employed to increase the firefighting capacity of any premises or building residential or commercial area. These pumps increassure of the fire hydrant service especially when the hydrant service is connected to the water tank.
These types of pumps are also used in irrigation and the transmission of water. In a fire sprinkler system, fire pumps increase the water’s flow rate. Fire hydrant pumps are installed in high-rise buildings where there is a requirement for water pressure and the flow of water flow is not as high without fire pumps. Wherever flow and pressure are not sufficient, fire hydrant pumps are installed to cope with fire safety needs.

What is a pump?
A pump is a mechanical device that is used to move fluids (liquids or gases) from one place to another by applying mechanical force.
What are the main types of pumps?
The main types of pumps include:
Centrifugal Pumps: Work on the principle of centrifugal force to move fluids.
Positive Displacement Pumps: Displace a fixed volume of fluid with each cycle of operation. Examples include piston pumps and diaphragm pumps.
How do centrifugal pumps work?
Centrifugal pumps work by converting rotational kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy, creating a flow of fluid. The pump has an impeller that spins, generating centrifugal force to move the fluid radially outward.
What are the advantages of centrifugal pumps?
Centrifugal pumps are known for their simplicity, high flow rates, and suitability for handling liquids with low viscosity. They are commonly used in water supply, irrigation, and industrial applications.
What are positive displacement pumps?
Positive displacement pumps move a fixed volume of fluid with each cycle, ensuring a constant and steady flow. Examples include gear pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
What is the working principle of reciprocating pumps?
Reciprocating pumps use a piston or plunger to create a reciprocating (back-and-forth) motion. During the suction stroke, fluid is drawn into the pump, and during the discharge stroke, it is expelled.
What are some common applications of reciprocating pumps?
Reciprocating pumps are used in applications where a precise and controlled flow is required, such as in high-pressure water systems, hydraulic systems, and metering applications.
What is a gear pump?
A gear pump is a type of positive displacement pump that uses intermeshing gears to move fluid. As the gears rotate, they create a suction and discharge action, pushing the fluid through the pump.
How do diaphragm pumps work?
Diaphragm pumps use a flexible diaphragm to create a reciprocating action that moves fluid through the pump. This design allows for the pumping of viscous or abrasive fluids.
What are the advantages of diaphragm pumps?
Diaphragm pumps are suitable for handling corrosive, abrasive, and viscous fluids. They are commonly used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment.
What is the role of a submersible pump?
A submersible pump is designed to be submerged in the fluid it is pumping, such as water. They are often used in wells, boreholes, and sewage pumping applications.
How are centrifugal pumps different from positive displacement pumps?
Centrifugal pumps generate flow through rotational kinetic energy, while positive displacement pumps move a fixed volume of fluid with each cycle. Centrifugal pumps are suitable for high-flow, low-viscosity applications, while positive displacement pumps are used for precise and controlled flows.
Worth Read Posts
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
