Ultrasonic Motor: A Comprehensive Overview with PDF
An ultrasonic motor, often referred to as a USM, is a unique type of electric motor that utilizes the phenomenon of ultrasonic vibrations to generate mechanical motion. These motors have gained significant attention in various industries due to their exceptional characteristics and applications.
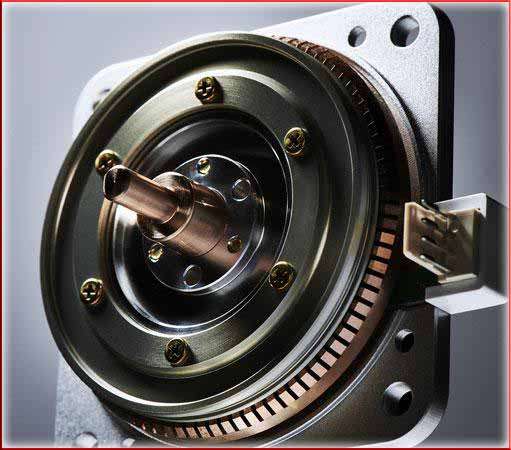

The development of ultrasonic motors represents a remarkable achievement in the field of electromechanical systems.
Read More About
The history of these types of motors development can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring the potential of ultrasonic vibrations for motor applications. The first practical ultrasonic motor was developed in the 1980s, marking a significant milestone in the field. Since then, continuous research and advancements have led to the widespread adoption of these motors in various industrial sectors.
The importance of these types of motors in today’s industries cannot be overstated. These motors have revolutionized automation and precision control systems. They offer numerous advantages, making them indispensable in applications where high precision, low noise, compact size, and lightweight components are crucial.
Working Principle of Ultrasonic Motor
The working principle of an ultrasonic types of motors is based on the piezoelectric effect, which is the ability of certain materials to generate mechanical motion when subjected to high-frequency electrical signals. In an ultrasonic motor, a piezoelectric element, often a piezoceramic crystal, is used as the primary actuator.
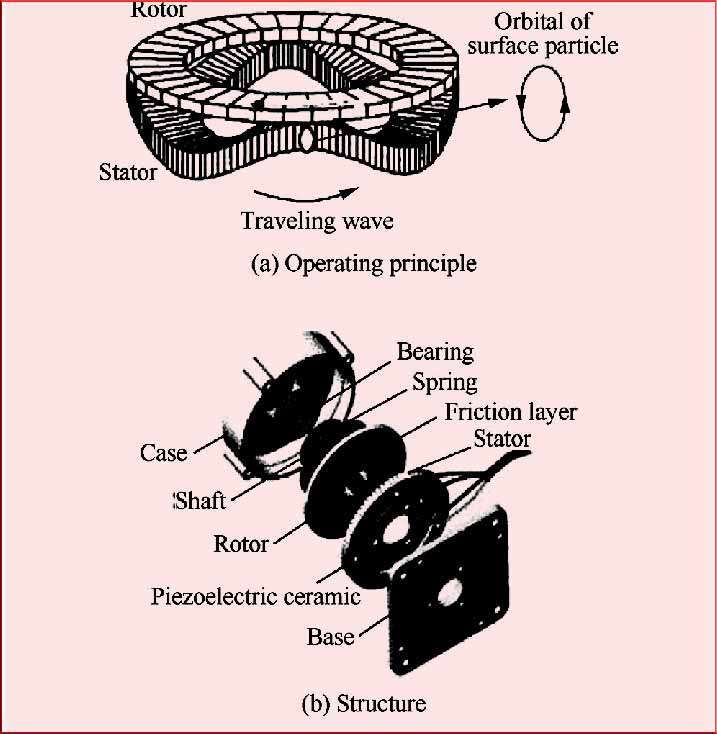
When an ultrasonic electrical signal is applied to the piezoelectric element, it generates ultrasonic vibrations at a frequency above the audible range (typically in the tens of kilohertz to megahertz range). These ultrasonic vibrations are then translated into mechanical motion through various mechanisms, depending on the specific design of the motor.
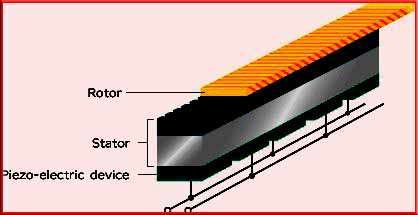
Types of Ultrasonic Motor
Ultrasonic motors can be categorized into contact and non-contact types. Contact-type motors rely on the frictional force between the vibrating element and a rotor to generate motion.
Non-contact-type ultrasonic motors, on the other hand, utilize standing waves or traveling waves to create a nodal motion, allowing for contactless operation. Each type has its advantages and is chosen based on the application’s requirements.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Motor
High Precision and Accuracy: These are known for their exceptional precision and accuracy, making them ideal for applications requiring fine control and positioning, such as semiconductor manufacturing and medical equipment.
Low Noise and Vibration: these types of motors produce minimal noise and vibration, making them suitable for applications where a quiet operation is essential, such as in optical systems and camera lens focusing mechanisms.
Compact Size and Lightweight: These motors have a compact form factor and are lightweight compared to traditional electromagnetic motors, making them ideal for portable and space-constrained applications.
No Electromagnetic Interference: Since these motors do not rely on electromagnetic fields for operation, they are immune to electromagnetic interference, which is crucial in sensitive environments like medical devices and aerospace equipment.
Applications of Ultrasonic Motor
Robotics and Automation: Ultrasonic types of motors are widely used in robotic systems for precise and rapid motion control, enabling robots to perform delicate tasks with high accuracy.
Medical Equipment: They find applications in medical devices like ultrasound scanners, where precise positioning of transducers is critical for imaging quality.
Aerospace and Defense: In aerospace and defense industries, ultrasonic motors are used in camera gimbals, antenna positioning systems, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for their reliability and accuracy.
Consumer Electronics: These motors are used in consumer electronics such as digital cameras, camera phones, and camcorders for autofocus and zoom functions.
Future Prospects of Ultrasonic Motor

The future of these types of motors holds exciting prospects:
Advancements in Technology: Ongoing research and development are expected to lead to even more efficient and powerful motors, expanding their range of applications.
Potential for New Applications: As technology evolves, new applications for ultrasonic types of motors are likely to emerge, especially in emerging fields like nanotechnology and 3D printing.
Challenges and Limitations: While ultrasonic ones offer numerous advantages, they also face challenges, such as heat generation at high frequencies and limited torque output. Future research will focus on addressing these limitations.
In conclusion, ultrasonic types of motors represent a remarkable fusion of physics and engineering, offering precision, reliability, and versatility across various industries. With ongoing advancements in technology and a growing understanding of their potential, these motors are poised to continue transforming the way we approach automation and precision control systems in the future.
Their significance in industries such as robotics, medical equipment, aerospace, and consumer electronics is undeniable, and their role is expected to expand further as technology advances.
Subscribe to our Newsletter “Electrical Insights Daily” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
- Servo Motors: High-Precision Control in Modern Technology
- Arduino Stepper Motor Projects: A Quick Guide
- Induction Motor: Important Types, Construction & Working
- Wound Rotor Induction Motor: Working & Important Applications
- Squirrel Cage Induction Motor: Working and Best Applications
- Brushless Motor(BLDC): Construction, Types & Applications
- Split Phase Induction Motor: Working & Best Applications
- Stepper Motor Position Control with Arduino: A Quick Guide
