Methods of Electrical Earthing: Important Concepts
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to ensuring electrical safety and preventing potential hazards, understanding the methods of electrical earthing is crucial. Electrical earthing, also known as grounding, is a crucial aspect of electrical systems that ensures safety and protects against electrical faults.
It involves establishing a connection between electrical equipment and the Earth’s surface, enabling the safe dissipation of electrical currents.
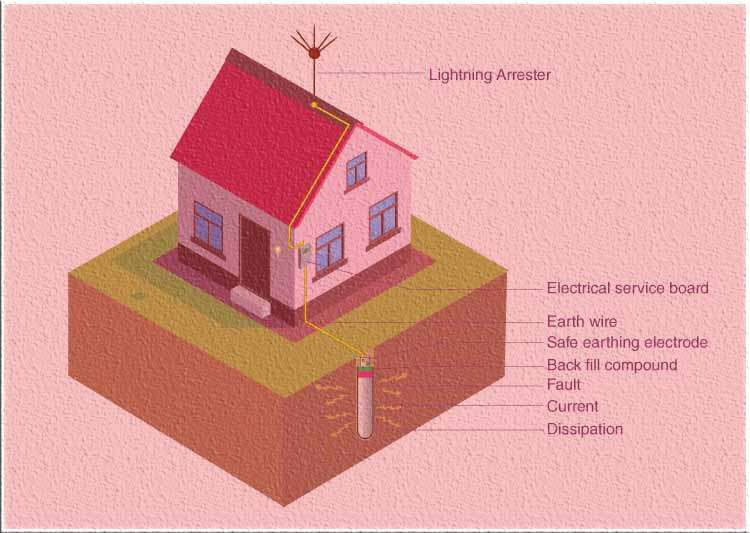
Methods of Electrical Earthing
Various methods of electrical earthing exist, each designed to address specific requirements and cater to different types of installations. These methods include Wire or strip earthing, Rod earthing, Pipe earthing and the plate earthing which are implemented based on the specific needs of the electrical system. Understanding the different methods of electrical earthing is essential for maintaining electrical safety and preventing potential hazards.
Electrical appliances are connected to the grounding/earthing system or electrodes positioned close to the soil or below ground level in order to assure safety. To make connections with all of the equipment’s metallic non-current-carrying components, a structure known as the flat iron riser-equipped electrode or earthing mat is buried beneath the surface of the ground.
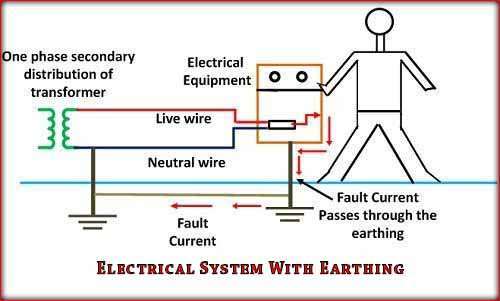
When an overload current or system fault occurs, the fault current from the equipment flows through the earthing system. The earth mat conductors play a role in increasing the voltage by the resistance of the earth mat multiplied by the ground fault, providing protection against overload or fault currents. In a building, there are three different types of wires: live, neutral, and earth. The ground is connected to a buried metal plate, while the live and neutral wires carry electric current from the power plant.
Devices such as TVs, iron boxes, and refrigerators are all connected to the ground wire, ensuring they are protected from shocks or poor electrical supplies. Local earthing is typically conducted near the home’s electrical meter.
Pipe Earthing
Pipe earthing is an efficient and cost-effective method used to establish a connection between electrical conductors and the Earth. It involves utilizing a steel pipe as an earth electrode, typically a galvanized steel pipe with a diameter of 38 mm and a length of 2 meters.
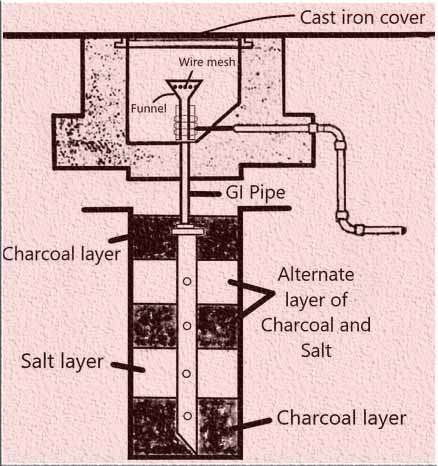
This pipe is installed vertically in the ground to ensure a reliable grounding system. The size of the iron pipe required for pipe earthing depends on factors such as the moisture content in the soil and the strength of the current. The level of moisture in the soil determines the maximum depth at which the steel pipe can be installed for optimal effectiveness. Overall, pipe earthing is considered one of the finest and most efficient methods of earthing, offering both reliability and affordability.
Plate Earthing
Plate earthing is a popular method among methods of electrical earthing. It provides effective electrical grounding by utilizing a vertical plate made of copper or galvanized iron. The plate is securely placed in a ground pit that is situated at a depth of less than three meters above the ground level. To ensure optimal performance of the plate earthing system, it is crucial to maintain suitable moisture levels in the surrounding earth.
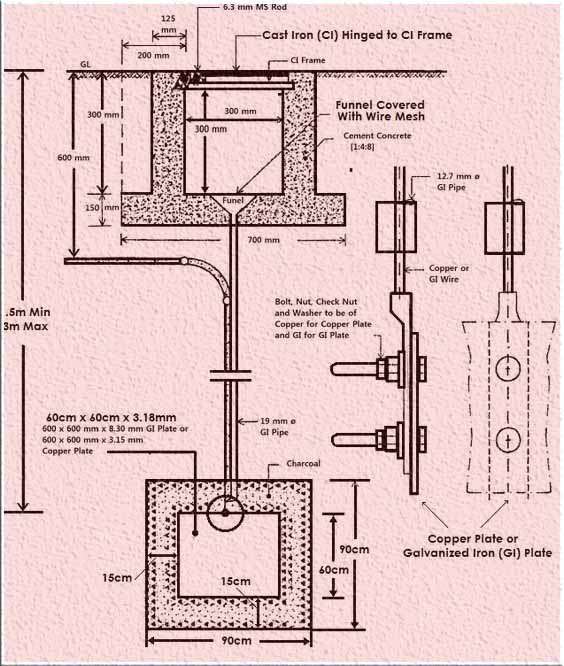
By connecting the plate to electrical wires, the electric charge can be efficiently redirected within the earth, resulting in a safe and reliable grounding setup. Plate earthing offers an effective solution for achieving proper electrical grounding and ensuring the smooth flow of electric current.
Rod earthing
Rod earthing is a widely used and cost-effective method to establish reliable electrical grounding. It involves inserting a copper rod with a galvanized steel pipe vertically into the ground, either manually or using a hammer. By adjusting the length of the implanted electrodes, the earth’s resistance can be minimized, ensuring efficient grounding. It is most common among methods of electrical earthing.
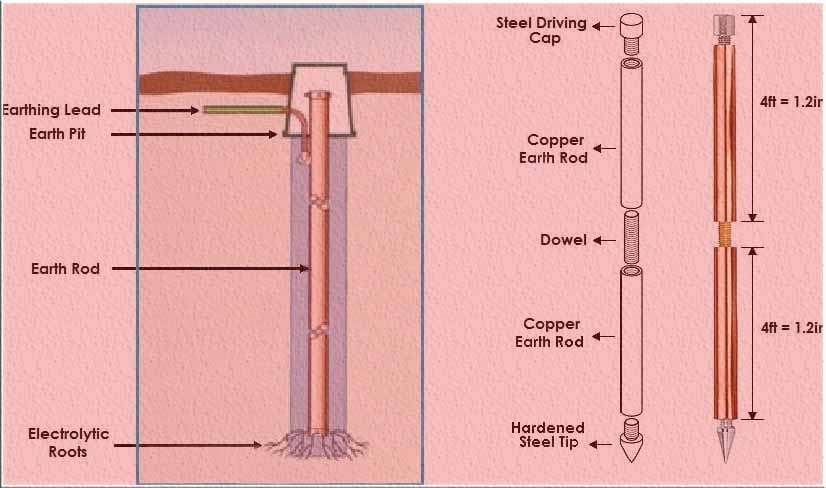
This technique effectively diverts short-circuit electricity to the ground, enhancing electrical safety. Rod earthing is particularly suitable for sandy areas, where it can deliver optimal results.
Not only is this method highly efficient, but it is also budget-friendly, making it a practical choice for various applications. Implementing rod earthing ensures a secure and reliable electrical grounding system that meets industry standards.
Strip or Wire Earthing
Strip or wire earthing is a highly effective method used to establish reliable electrical grounding. This technique involves burying strip electrodes or wires in horizontal trenches in the ground.
The strip electrodes should be at least 0.5 m deep and have a minimum cross-sectional area of 6.0 mm2. The cross-sectional area of the electrodes made of galvanized iron or steel shouldn’t be any smaller than 25 mm x 1.6 mm.
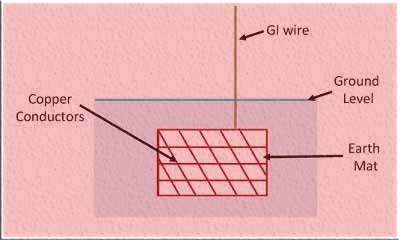
To ensure optimal earth resistance, a conductor with a minimum length of 15m is typically buried in the ground. Strip or wire earthing provides a robust grounding system, ensuring the safe dissipation of electrical currents. By implementing this method, you can achieve effective electrical grounding that meets industry standards.
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn to see our latest posts.
Worth Read Posts
- IEC Standard for Instrument Earthing
- Electrical Earthing Important Types
- Earthing Cable Size as Per IEC
- Plant Factor, Plant Capacity Factor, and Load Factor
- Difference Between Demand Factor and Diversity Factor
- Buck Converter Interview Questions
- DC DC Converter Interview Questions
- Transformer Electrical Interview
- Top 30 Op Amp Interview Questions
- Power Electronics Interview Questions
