Amoled, OLED, IPS, LCD, TFT, and Super AMOLED Display: Best Guide
What is an AMOLED display?
An AMOLED display (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a type of screen technology used in electronic devices like smartphones, TVs, and smartwatches. It’s known for its vibrant colors, high contrast levels, and energy efficiency.
Table of Contents
In simpler terms, an AMOLED display is a type of screen that’s really good at showing colors and uses less power compared to other screens, making it popular in many devices today. It works by lighting up tiny colored pixels when electricity passes through them, creating the images and videos you see on your device.
AMOLED Display vs LCD
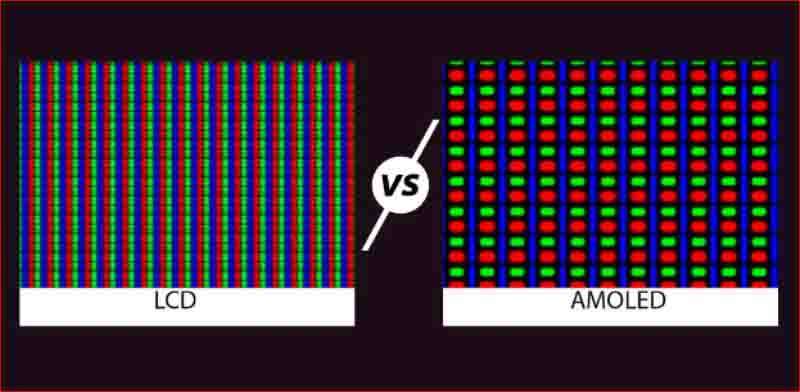
Here’s a comparison table between AMOLED display and LCDs:
| Feature | AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) | LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) |
| Display Type | Uses organic compounds that emit light when a current passes through them. | Relies on a backlight to illuminate liquid crystals. |
| Contrast Ratio | High contrast ratio, producing deeper blacks and better color contrast. | Typically lower contrast ratio compared to AMOLED. |
| Power Efficiency | More power-efficient because individual pixels emit their own light, allowing for power savings when displaying darker content. | Consumes more power as the backlight is constantly on regardless of displayed content. |
| Viewing Angles | Offers better viewing angles and maintains color accuracy even when viewed from different angles. | Viewing angles can be limited, and colors might shift when viewed from extreme angles. |
| Response Time | Generally has faster response times, resulting in smoother motion and better performance for activities like gaming. | Slightly slower response times compared to AMOLED. |
| Image Quality | Known for vibrant colors, high saturation, and true blacks, providing a more vivid visual experience. | Offers good color accuracy, but may not achieve the same depth of blacks or vibrancy as AMOLED. |
These differences often influence the user experience and preferences when choosing between devices with AMOLED or LCD displays.
AMOLED vs IPS
Here’s a comparison between AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays:
| Feature | AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) | IPS (In-Plane Switching) |
| Display Type | Uses organic compounds that emit light when a current passes through them, enabling individual pixel illumination. | Employs a liquid crystal technology with better color reproduction and viewing angles than traditional TFT LCD screens. |
| Contrast Ratio | High contrast ratio, offering deeper blacks and more vibrant colors due to its ability to turn off individual pixels. | Good contrast ratio, but typically not as high as AMOLED, resulting in slightly less vivid colors and blacks. |
| Power Efficiency | More power-efficient when displaying darker content as it can turn off pixels entirely, consuming less power. | Consumes more consistent power because the backlight is always on, regardless of displayed content. |
| Viewing Angles | Provides excellent viewing angles and maintains color accuracy even when viewed from extreme angles. | Offers good viewing angles, but may not match the same level of color accuracy at extreme angles as AMOLED. |
| Response Time | Generally has faster response times, contributing to smoother motion and better performance, especially in gaming and fast-paced activities. | Offers good response times but might be slightly slower than AMOLED, impacting motion smoothness marginally. |
| Image Quality | Known for vivid colors, high saturation, true blacks, and excellent visual contrast. | Offers good color accuracy and viewing angles but might not achieve the same depth of blacks or vibrant colors as AMOLED. |
Both AMOLED display and IPS technologies have their strengths, influencing factors like power consumption, visual experience, and display performance. Choosing between them often depends on individual preferences regarding color accuracy, contrast, and viewing angles.
AMOLED vs super AMOLED
AMOLED and Super AMOLED are both display technologies, but Super AMOLED is an enhanced version of the original AMOLED technology. Here’s a comparison between the two:
| Feature | AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) | Super AMOLED |
| Display Type | Uses organic compounds that emit light when a current passes through them, enabling individual pixel illumination. | An improved version of AMOLED with integrated touch sensors directly into the screen, eliminating the need for an additional touch-sensitive layer. |
| Touch Layer | Requires a separate touch-sensitive layer above the display, which can slightly reduce image quality and increase screen thickness. | Integrates touch sensors directly into the screen, improving image quality and making the display thinner. |
| Visibility | Might have slight visibility issues in direct sunlight due to the presence of a separate touch layer. | Improved visibility in direct sunlight because there’s no additional layer between the display and the touch sensors. |
| Power Efficiency | Generally power-efficient but may consume slightly more power due to the additional touch-sensitive layer. | Offers better power efficiency because of the integrated touch sensors, reducing power consumption. |
| Image Quality | Provides excellent image quality with vibrant colors, high contrast, and deep blacks typical of AMOLED displays. | Maintains the qualities of AMOLED while enhancing visibility and overall display quality by integrating touch sensors into the screen. |
| Durability | May be marginally less durable due to the separate touch-sensitive layer, which might be prone to damage. | Potentially more durable as the touch sensors are integrated into the display, reducing the risk of damage to an additional layer. |
Super AMOLED improves upon AMOLED technology by integrating touch sensors directly into the screen, enhancing display quality, visibility, and power efficiency while reducing screen thickness. It’s an advancement aimed at providing better user experience and display performance.
AMOLED vs TFT
here’s a comparison between AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays:
| Feature | AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) | TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) |
| Display Type | Uses organic compounds that emit light when a current passes through them, enabling individual pixel illumination. | Utilizes a transistor for each pixel to control the amount of light passing through, commonly used in LCD screens. |
| Contrast Ratio | High contrast ratio, offering deeper blacks and more vibrant colors due to its ability to turn off individual pixels. | Contrast ratio can vary but generally not as high as AMOLED, resulting in slightly less vivid colors and blacks. |
| Power Efficiency | More power-efficient when displaying darker content as it can turn off pixels entirely, consuming less power. | Consumes more consistent power because the backlight is always on, regardless of displayed content. |
| Viewing Angles | Provides excellent viewing angles and maintains color accuracy even when viewed from extreme angles. | Viewing angles can be good but might not match the same level of color accuracy at extreme angles as AMOLED. |
| Response Time | Generally has faster response times, contributing to smoother motion and better performance, especially in gaming and fast-paced activities. | Offers good response times, but might not be as fast as AMOLED, affecting motion smoothness marginally. |
| Image Quality | Known for vivid colors, high saturation, true blacks, and excellent visual contrast. | Offers good color reproduction, but might not achieve the same depth of blacks or vibrant colors as AMOLED. |
AMOLED typically provides better contrast, deeper blacks, and more vibrant colors compared to TFT displays. Additionally, it tends to be more power-efficient when displaying darker content. TFT displays, on the other hand, are commonly used in LCD screens and provide decent image quality but might not match the same level of visual excellence as AMOLED displays.
AMOLED DDIC
The AMOLED display DDIC (Display Driver Integrated Circuit) refers to the specialized integrated circuit responsible for controlling and driving the individual pixels in an AMOLED display. This component is crucial as it manages the voltage and current to each pixel, ensuring proper illumination and color accuracy across the screen.
The DDIC serves several functions:
Pixel Control: It manages the activation and deactivation of each pixel in response to the incoming signals from the device’s processor or graphics unit.
Color Accuracy: The DDIC ensures that the correct voltage is applied to each pixel to accurately represent the desired color.
Power Management: It plays a role in power efficiency by regulating the power supplied to the pixels, especially in scenarios where darker content is displayed. This contributes to the overall energy efficiency of the display.
Refresh Rates: DDICs also influence the refresh rate and response time of the display, impacting the display’s ability to render fast-moving content smoothly.
In essence, the AMOLED DDIC is a vital component in the functionality and performance of an AMOLED display, influencing its quality, power efficiency, and overall visual experience.
AMOLED LTPO
AMOLED LTPO stands for Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide, a technology used in AMOLED displays that enhances power efficiency by dynamically adjusting the refresh rate based on the content being displayed.
LTPO technology allows for a variable refresh rate, meaning the display can switch between different refresh rates on the fly, ranging from high refresh rates (like 120Hz) down to as low as 1Hz when the content displayed doesn’t require a high refresh rate.
This technology is particularly beneficial for devices like smartphones and smartwatches as it optimizes power consumption. When the device is displaying static content or something that doesn’t require a high refresh rate, LTPO can lower the refresh rate, conserving battery life.
Conversely, when interacting with content that benefits from a high refresh rate, such as gaming or scrolling through apps, the display can ramp up to a higher refresh rate for a smoother experience.
In essence, AMOLED LTPO technology combines the advantages of AMOLED displays with the power-saving benefits of dynamic refresh rate adjustment, providing an improved balance between performance and battery efficiency in devices.
AMOLED vs OLED display
AMOLED and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) are closely related display technologies, but there are some differences between the two:
| Feature | AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) | OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) |
| Structure | Utilizes an active matrix to control each pixel individually, offering better control and potentially faster response times. | Uses a simpler passive matrix, which might result in slightly slower response times compared to AMOLED. |
| Efficiency | Generally more power-efficient as it can turn off individual pixels completely, conserving energy when displaying darker content. | Offers good power efficiency but might consume more power than AMOLED when displaying darker scenes due to fewer control capabilities. |
| Manufacture | More complex to manufacture due to the active matrix design, which can potentially make AMOLED displays more expensive. | Simpler manufacturing process compared to AMOLED, which could make OLED displays relatively more cost-effective. |
| Performance | Known for vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and potentially faster response times, contributing to a better visual experience. | Offers good color reproduction and contrast, but might not match the same level of performance as AMOLED displays in terms of response times and control. |
In essence, both AMOLED and OLED display technologies utilize organic compounds to emit light, resulting in vibrant colors and high contrast ratios. However, the key difference lies in the way pixels are controlled, with AMOLED employing an active matrix for better control and potentially improved performance compared to the passive matrix used in traditional OLED displays.
AMOLED display tends to offer more precise control over individual pixels, contributing to better power efficiency and potentially enhanced visual performance.
lTPO oLED vs AMOLED
LTPO OLED (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide Organic Light Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) are related yet distinct technologies used in displays.
LTPO OLED incorporates the benefits of both LTPO technology (which allows for variable refresh rates, thus optimizing power consumption) and OLED technology (utilizing organic compounds that emit light for vibrant colors and high contrast).
This combination enables OLED displays to dynamically adjust refresh rates, conserving power by lowering the refresh rate during static or less demanding content and ramping it up for more dynamic content, like video or gaming.
AMOLED, on the other hand, is a type of OLED display that uses an active matrix to control each pixel individually, offering better control and potentially faster response times compared to standard OLED displays. AMOLED technology allows for more precise control over pixels, resulting in vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and potentially improved visual performance.
In summary, LTPO OLED combines the power efficiency of LTPO technology with the visual benefits of OLED displays, while AMOLED technology focuses on the active matrix control for enhanced performance and visual quality in OLED displays. Both technologies aim to optimize power consumption and improve the visual experience but achieve this through slightly different approaches.
In the world of display technology, both LTPO OLED and AMOLED bring their unique strengths to the table. LTPO OLED merges the power-saving prowess of variable refresh rates with the vibrant colors and contrast of OLED displays, offering a balanced mix of efficiency and visual quality. On the other hand, AMOLED showcases its superiority in precise pixel control, resulting in stunning visuals and potentially faster response times.
Ultimately, LTPO OLED shines in its ability to intelligently adjust refresh rates for optimal power usage, while AMOLED stands out for its exceptional control over individual pixels, delivering impressive color accuracy and contrast.
Choosing between the two comes down to preferences—whether prioritizing energy efficiency with variable refresh rates or aiming for top-notch visual performance with AMOLED’s pixel-level control. Both pave the way for captivating displays, each with its own remarkable features catering to diverse user needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between AMOLED and OLED displays?
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a type of OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). The main difference lies in the active matrix used in AMOLED, which allows for better pixel control and improved performance compared to traditional OLED displays.
What are the advantages of AMOLED displays?
AMOLED displays offer advantages such as high contrast ratios, vibrant colors, faster refresh rates, and the ability to achieve true blacks since each pixel emits its own light. Additionally, AMOLED displays can be flexible, allowing for curved and foldable screens.
Is there a risk of burn-in with AMOLED displays?
Yes, AMOLED displays are susceptible to burn-in, where prolonged display of static images or patterns may cause permanent retention of those images on the screen. However, manufacturers implement various technologies like pixel shifting to mitigate this risk.
How do IPS displays differ from OLED and AMOLED displays?
IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays use a different technology involving liquid crystals and polarized light. They are known for wider viewing angles and accurate color reproduction. Unlike OLED and AMOLED, IPS displays require a backlight.
What is the key feature of Super AMOLED displays?
Super AMOLED is a term used by Samsung for its AMOLED displays that integrate touch sensors directly into the screen, eliminating the need for a separate touch-sensitive layer. This results in thinner and lighter displays with improved visibility in direct sunlight.
Do OLED displays have better energy efficiency compared to LCD displays?
OLED displays can be more energy-efficient than LCD displays because they do not require a backlight. In OLED, each pixel emits its own light, and power is consumed only for illuminated pixels. This contrasts with LCD, where a constant backlight is needed.
Which display type is best for gaming?
Both OLED and AMOLED displays are popular choices for gaming due to their fast refresh rates, vibrant colors, and high contrast ratios. However, personal preferences may vary, and some gamers also appreciate the wide viewing angles of IPS displays.
Can AMOLED displays be used in outdoor settings?
Yes, AMOLED displays, including Super AMOLED, can be used in outdoor settings. They often have high brightness levels, which, combined with their ability to achieve true blacks, contributes to good visibility even in bright sunlight.
Worth Read Posts
- Touch Sensors
- ESP8266 Pinout
- Hysteresis Loss Formula
- ESP32 Pinout
- Work Function Formula
- Power Triangle
- BC547 Pinout
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.






