Temperature Sensors: A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic world of sensing technology, Temperature Sensors stand as vital instruments, providing insights into the thermal characteristics of the environment. This exploration delves into the intricacies of Temperature Sensors, covering various types, and applications, and weighing the advantages and disadvantages of this crucial technology.
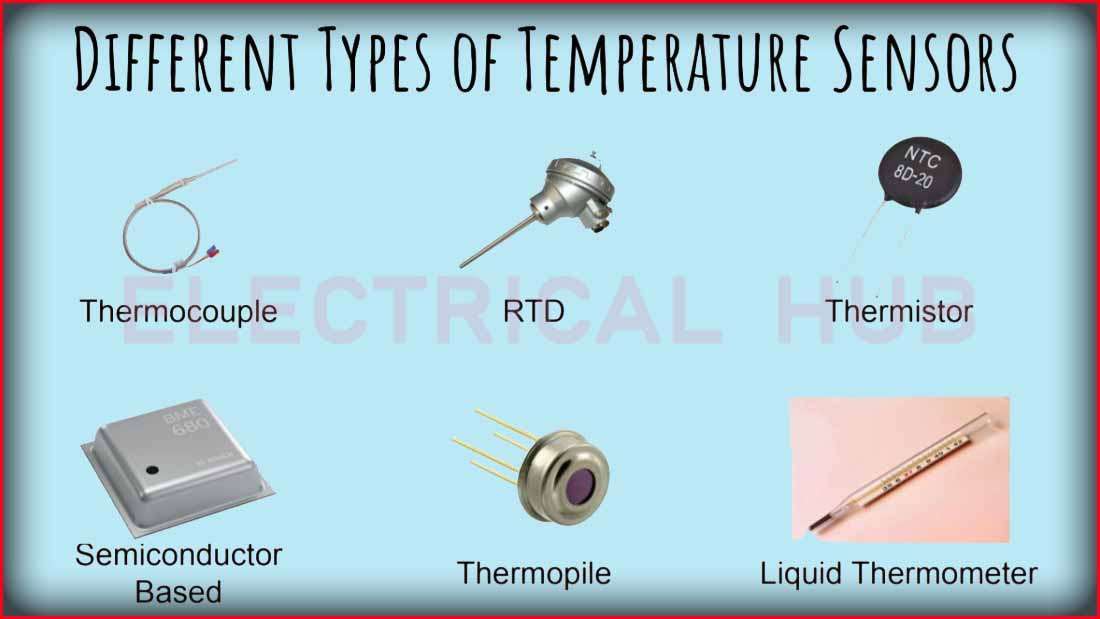
Table of Contents
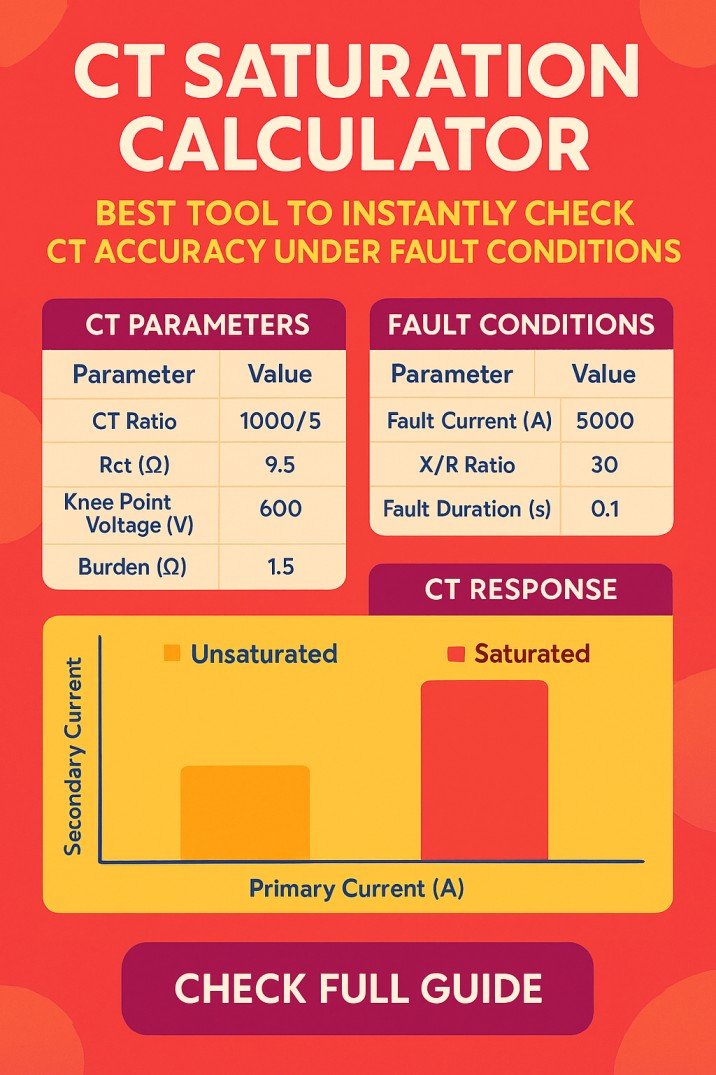
Types of Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors work by measuring physical or electrical changes in response to temperature variations. There are various types of temperature sensors, each employing different principles to achieve temperature measurement. Here’s an overview of the working principles of some common types:
1. Thermocouples:
Principle: Thermocouples are based on the Seebeck effect, where two different metals generate a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between their junctions.
Working: When the temperature changes at the junction of the two metals, it induces a voltage that can be measured and correlated to the temperature.
2. RTDs (Resistive Temperature Devices):
Principle: RTDs operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain materials, like platinum, changes predictably with temperature.
Working: As temperature changes, the electrical resistance of the RTD element changes, and this change is measured to determine the temperature.
3. Thermistors:
Principle: Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors with resistance that changes significantly with temperature.
Working: The resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases, and vice versa. Measuring the resistance allows for temperature determination.
You May Want to Read
4. Infrared (IR) Temperature Sensors:
Principle: These sensors detect the infrared radiation emitted by an object and convert it into an electrical signal.
Working: The amount of infrared radiation emitted by an object is directly proportional to its temperature. The sensor measures this radiation and converts it into a temperature reading.
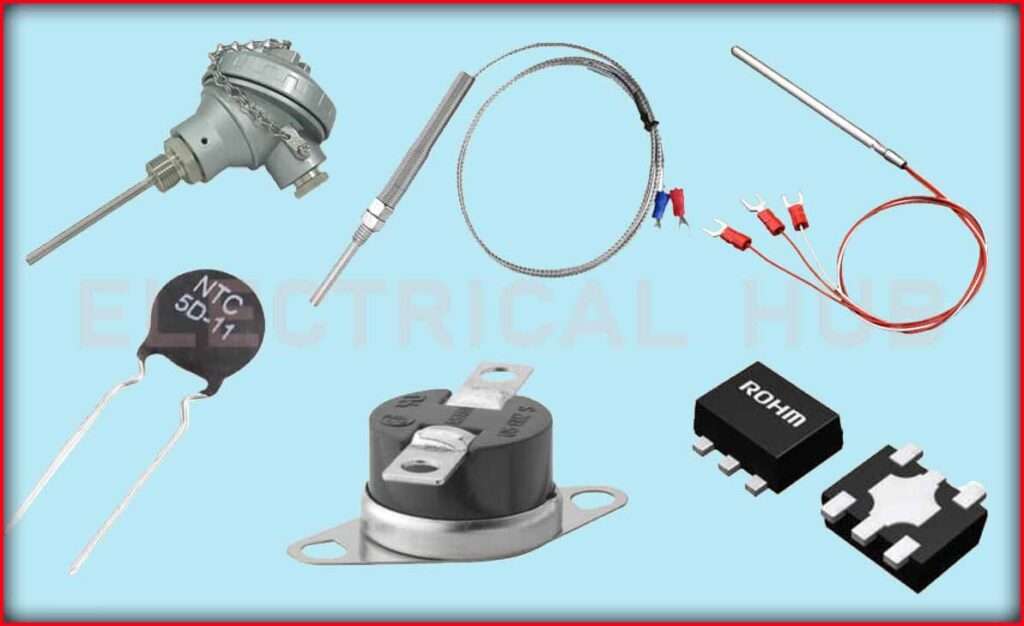

5. Bimetallic Temperature Sensors:
Principle: Bimetallic strips consist of two different metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion.
Working: When temperature changes, the bimetallic strip bends due to the different rates at which the metals expand or contract. This bending can be translated into a temperature reading.
6. IC Temperature Sensors:
Principle: Integrated circuit (IC) sensors use the temperature-dependent voltage across a diode or transistor.
Working: The voltage across the diode or transistor changes with temperature. The sensor circuitry amplifies this change, and the output is used to determine the temperature.
7. Gas Thermometers:
Principle: Gas thermometers utilize the change in pressure or volume of a gas with temperature.
Working: As the gas temperature changes, the pressure or volume changes accordingly. This change is calibrated to provide an accurate temperature measurement.
8. Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers:
Principle: These traditional thermometers use the expansion or contraction of a liquid (like mercury) with temperature changes.
Working: The liquid level in a calibrated tube rises or falls as the temperature changes, providing a visual indication of the temperature.
These sensors play crucial roles in a variety of applications, from industrial processes and environmental monitoring to consumer electronics and medical devices. The choice of sensor depends on factors such as accuracy, range, and the specific requirements of the application.
Applications of Temperature Sensors
Industrial Processes: These sensors are indispensable in industries such as manufacturing, where precise temperature control is crucial for quality and efficiency.
Healthcare: In medical applications, These sensors are used for patient monitoring, fever detection, and maintaining the temperature of medical equipment.
Environmental Monitoring: Temperature sensors contribute to environmental monitoring by measuring ambient temperatures, aiding in climate studies and weather forecasting.
Consumer Electronics: These sensors play a role in consumer electronics, regulating the temperature of devices to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating.
Advantages of Temperature Sensors
Accuracy: Many temperature sensors, such as RTDs and thermistors, provide high accuracy, making them suitable for applications where precision is critical.
Versatility: These sensors come in various types, allowing for application versatility. From extreme industrial environments to delicate medical settings, there’s a suitable sensor type.
Non-Contact Measurement: Infrared sensors enable non-contact temperature measurement, making them valuable in situations where physical contact is impractical or unsafe.
Disadvantages of Temperature Sensors:
Calibration Requirements: Some temperature sensors, especially thermocouples, may require frequent calibration to maintain accuracy, adding to maintenance efforts.
Limited Temperature Range: Certain types of temperature sensors have limited temperature ranges, and using them outside their specified range can result in inaccurate readings.
Cost: High-precision sensors can be expensive, and the cost may be a factor in certain budget-sensitive applications.
Conclusion
Temperature sensors play a pivotal role in a wide array of applications, providing the necessary data to make informed decisions and maintain optimal conditions. From the demanding industrial sector to the intricacies of healthcare, the adaptability and precision of temperature sensors continue to be indispensable.
While each type of temperature sensor has its advantages and disadvantages, the key lies in selecting the right sensor for the specific application, ensuring accurate and reliable temperature measurements in diverse environments. As technology advances, the capabilities of these sensors are likely to evolve, opening new possibilities for improved thermal management across industries.
1. What is a temperature sensor?
A temperature sensor is a device designed to measure the temperature of a substance or environment and convert it into a readable output, often in the form of an electrical signal.
2. How does a temperature sensor work?
The working principle depends on the type of temperature sensor. For example, thermocouples generate a voltage based on the Seebeck effect, while RTDs and thermistors rely on changes in electrical resistance with temperature.
3. What are the common types of temperature sensors?
Common types include thermocouples, RTDs (Resistive Temperature Devices), thermistors, infrared (IR) sensors, bimetallic temperature sensors, IC temperature sensors, gas thermometers, and liquid-in-glass thermometers.
4. Which temperature sensor is most accurate?
The accuracy of a temperature sensor depends on the application. RTDs are often known for high accuracy in industrial settings, while thermocouples are widely used for their versatility.
5. Where are temperature sensors used?
These sensors are used in various applications, including industrial processes, environmental monitoring, HVAC systems, medical devices, consumer electronics, and automotive systems.
6. Can temperature sensors measure extreme temperatures?
The ability to measure extreme temperatures depends on the type of sensor. Some sensors, like thermocouples and infrared sensors, are suitable for measuring both high and low temperatures.
7. How do infrared temperature sensors work?
Infrared sensors detect the infrared radiation emitted by an object. The amount of radiation is proportional to the object’s temperature, allowing the sensor to provide a non-contact temperature measurement.
8. Are temperature sensors affected by environmental conditions?
Some sensors may be influenced by environmental factors like humidity. However, proper calibration and sensor selection can mitigate these effects.
9. Can I use a temperature sensor for liquid measurements?
Yes, certain temperature sensors, such as thermocouples or RTDs, are suitable for measuring the temperature of liquids. However, considerations like the sensor’s material compatibility and the liquid’s properties are important.
10. How do I calibrate a temperature sensor?
Calibration procedures vary depending on the type of temperature sensor. Generally, it involves comparing the sensor’s readings to known temperature standards and adjusting the output accordingly.
11. Can I use a temperature sensor for medical applications?
Yes, These sensors are commonly used in medical devices like thermometers and fever monitoring systems. Contact and non-contact sensors cater to different medical applications.
Worth Read Posts
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.