Polarization Index (PI): Importance, Calculation, and Testing Procedures
Introduction to Polarization Index (PI)
The Polarization Index (PI) is a diagnostic test used to assess the condition of insulation in electrical equipment, particularly in motors, generators, and transformers. The PI test is a time-resistance test that provides insight into the insulation’s cleanliness, moisture level, and overall health by evaluating how the insulation resistance changes over time.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
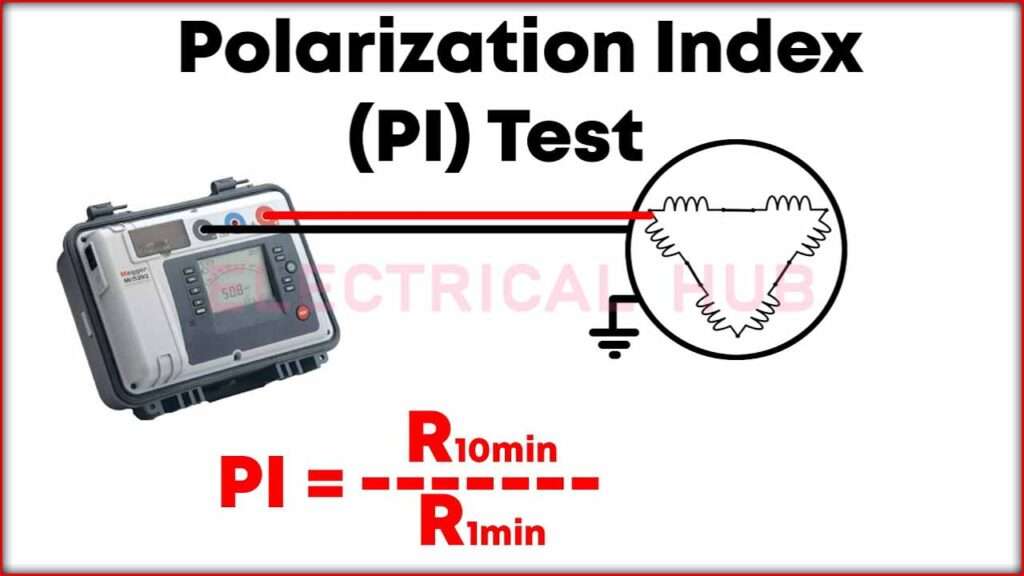
Significance of Polarization Index
The significance of the Polarization Index lies in its ability to detect problems in insulation that might not be apparent through simple resistance measurements. It is particularly useful because:
Aging Detection: Insulation resistance decreases over time due to aging, moisture absorption, and contamination. PI provides a way to quantify the extent of these effects.
Maintenance Planning: A low PI value can indicate that the insulation is deteriorating, helping to plan maintenance before a failure occurs.
Moisture Detection: Insulation exposed to moisture tends to have lower resistance. PI helps in identifying the presence of moisture, which can lead to insulation failure.
How to Find Polarization Index (PI)
The PI is calculated by measuring the insulation resistance over a period of 10 minutes and 1 minute. The PI is the ratio of the 10-minute insulation resistance to the 1-minute insulation resistance.
3.1 Steps to Measure PI
Preparation:
- Ensure that the equipment to be tested is de-energized and properly isolated.
- Connect a megohmmeter (insulation resistance tester) to the insulation to be tested.
Initial Resistance Measurement:
- Apply a DC voltage (typically 500V, 1000V, or higher depending on the equipment’s voltage rating) using the megohmmeter.
- Measure the insulation resistance after 1 minute of applied voltage.
Final Resistance Measurement:
- Continue applying the voltage and measure the insulation resistance after 10 minutes.
- 3.2 Formula for Polarization Index
The PI is calculated using the following formula:
- PI= Insulation Resistance at 10 Minutes (R10)/ Insulation Resistance at 1 Minute (R1)
- R10 = Insulation resistance measured at 10 minutes.
- R1 = Insulation resistance measured at 1 minute.
Interpretation of PI Values
PI > 2.0: Indicates good insulation. The equipment is likely to be in good condition.
PI between 1.0 and 2.0: Marginal insulation quality. Closer inspection or preventative maintenance might be required.
PI < 1.0: Indicates poor insulation. The equipment is at a high risk of failure and should be addressed immediately.
Equipment Tested with Polarization Index (PI)
The PI test is primarily used for assessing the condition of insulation in the following types of electrical equipment:
Rotating Machines (Motors and Generators)
AC and DC Motors: Regular PI testing helps ensure that the insulation in the windings remains intact, preventing potential failures due to insulation breakdown.
Generators: Insulation in generators is critical for reliable operation, and PI tests are often used during maintenance checks to assess insulation health.
Transformers
Power Transformers: Insulation in power transformers is essential for their safe operation. PI testing helps detect any degradation in the insulation material, which could lead to transformer failure.
Distribution Transformers: Similar to power transformers, distribution transformers also undergo PI testing to ensure the integrity of their insulation.
Cables
High-Voltage Cables: PI testing can be applied to the insulation of high-voltage cables to check for moisture ingress or contamination, which could lead to insulation failure.
Bushings
Transformer and Circuit Breaker Bushings: The PI test can help identify insulation problems in bushings, which are critical components in high-voltage systems.
When to Perform PI Testing
PI testing is typically performed during the following scenarios:
Pre-commissioning: Before new equipment is put into service, PI testing is conducted to ensure that the insulation is in good condition.
Routine Maintenance: Regular PI testing is part of a preventive maintenance schedule to monitor insulation health over time.
Post-Repair: After repairs involving insulation (such as rewinding a motor), PI testing is performed to ensure the insulation’s integrity.
Post-Moisture Exposure: If equipment has been exposed to moisture, PI testing is used to assess the extent of the impact on insulation.
Factors Affecting PI Test Results
Several factors can influence the results of a PI test:
Temperature: Higher temperatures can lower the insulation resistance, leading to lower PI values.
Humidity: High humidity can introduce moisture into the insulation, lowering resistance and PI values.
Contamination: Dirt, oil, or other contaminants on the insulation surface can affect PI results by lowering resistance.
Conclusion
The Polarization Index (PI) test is a valuable tool in the maintenance and monitoring of electrical equipment. By measuring the insulation resistance over time, PI provides critical insights into the condition of the insulation, helping to prevent unexpected failures and extend the life of the equipment. Understanding and interpreting PI results allow for proactive maintenance, ensuring the reliability and safety of motors, generators, transformers, and other critical electrical assets.
References
- IEEE Std 43-2013 – “IEEE Recommended Practice for Testing Insulation Resistance of Rotating Machinery”:
- This IEEE standard outlines the recommended practices for measuring insulation resistance, including detailed procedures for the Polarization Index test.
- IEEE Xplore Digital Library
- NEMA MG 1-2016 – “Motors and Generators”:
- The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) provides guidelines for the design, testing, and operation of motors and generators, including insulation resistance testing and PI.
- NEMA Standards
- Megger Handbook of Electrical Testing:
- This handbook by Megger, a leading manufacturer of electrical testing equipment, offers practical insights into various testing methods, including the Polarization Index test.
- Megger Official Website
- IEC 60034-1 – “Rotating Electrical Machines – Part 1: Rating and Performance”:
- The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard provides guidelines for the testing of rotating machines, including insulation resistance and PI testing.
- IEC Standards
- Electrical Power Equipment Maintenance and Testing by Paul Gill:
- This book covers various aspects of electrical equipment maintenance, including detailed explanations of insulation resistance testing and the significance of the Polarization Index.
- “Transformer Maintenance Guide” by ABB:
- ABB, a leading technology company, offers a guide specifically on transformer maintenance, which includes PI testing as part of routine diagnostics.
- ABB Official Website
Worth Read Posts
- Power Transformer Testing
- Power Transformer Parts
- Hysteresis Loss
- Derivation of Hysteresis Losses
- Transformer Tests Before Commissioning
- Transformer Electrical Interview
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering.
#PolarizationIndex, #InsulationResistance, #ElectricalTesting, #MotorMaintenance, #TransformerTesting, #PredictiveMaintenance, #InsulationTest, #ElectricalSafety, #PItest, #ElectricalEngineering, #MotorInsulation, #PowerSystemTesting, #DielectricTesting, #PreventiveMaintenance, #IndustrialElectrical
