BC547B Transistor: Comprehensive Overview
The BC547B transistor is a widely used NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) known for its versatility and numerous applications in electronics. Let’s take an in-depth look at the BC547B transistor, its specifications, features, and typical applications.
Read More About
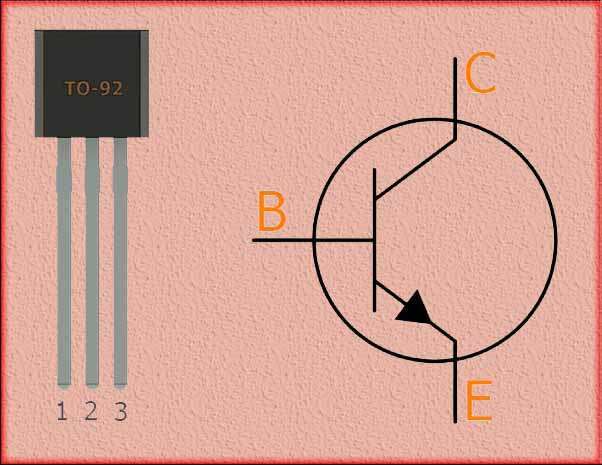
BC547B Transistor Overview
The BC547B is an NPN transistor commonly available in a TO-92 package. It is an improved version of the BC547 transistor with enhanced performance characteristics.
Package Type: The BC547B is typically encapsulated in a TO-92 package, which is a popular through-hole package with three leads for easy PCB mounting.
Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The maximum voltage that can be applied between the collector and emitter of the BC547B transistor without causing damage is 45V.
Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): The BC547B has a maximum collector-base voltage rating of 50V, which specifies the maximum voltage between the collector and base.
Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): The maximum voltage that can be applied between the emitter and base of the BC547B transistor is typically 6V.
Collector Current (IC): The BC547B can handle a maximum continuous collector current of 100mA, which defines its current-carrying capacity.
Power Dissipation (Ptot): The maximum power the BC547B transistor can dissipate without exceeding its temperature limits is 500mW.
Transition Frequency (fT): The BC547B typically has a transition frequency of 150MHz, indicating its high-frequency performance for amplifier applications.
Collector-Emitter Saturation Voltage (VCE(sat)): The VCE(sat) for the BC547B transistor is the voltage drop across the collector-emitter junction when the transistor is fully saturated. It exhibits a low VCE(sat), making it efficient in switching applications.
Base-Emitter Voltage (VBE): The voltage drop between the base and emitter of the BC547B when a current flows through the base terminal is around 0.65V at a base current of 10mA.
Features of BC547B transistor
The BC547B boasts several key features, including its NPN configuration, low saturation voltage, high transition frequency, and a maximum collector current of 100mA.
Characteristics: The BC547B exhibits specific electrical characteristics, such as its maximum voltage ratings (VCEO, VCBO, VEBO), maximum collector current (IC), power dissipation (Ptot), transition frequency (fT), and low VCE(sat) for efficient switching.
Applications: The BC547B finds applications in a wide range of circuits, including audio amplifiers, signal amplifiers, voltage regulators, switching circuits, sensor interfaces, and more.
In conclusion, the BC547B transistor is a versatile NPN BJT with enhanced performance characteristics compared to its predecessors. Its compact TO-92 package, combined with its electrical specifications and high-frequency capabilities, makes it suitable for various small-signal amplification and switching applications.
Designers and hobbyists often rely on the BC547B transistor for their electronic projects due to its reliable performance and wide availability in the market.
Related Posts:
- Floating Gate Transistor: Best Features & Applications
- TIP120 Transistor Pinout, Datasheet and Equivalent
- TIP122 Transistor Pinout, Datasheet & Applications
- Transistors BC547: Important Guide to Pinout
- C1815 Datasheet: Important Features to Know About
Subscribe to our Newsletter “Electrical Insights Daily” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
