Voltage Drop Calculator: Tool for Circuit Efficiency
When designing electrical circuits, calculating voltage drop is crucial. The “Voltage Drop Calculator” is an indispensable tool for anyone involved in electrical projects, from engineers to DIY enthusiasts, ensuring minimal power loss, especially over long cable runs. This article will guide you on using a voltage drop calculator, focusing on essential factors such as conductor material, length, cross-sectional area, and current to achieve optimal results.

Resistance of Copper and Aluminum Conductors
| Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) | Resistance of Copper (Ω/km) | Resistance of Aluminum (Ω/km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 12.1 | 19.5 |
| 2.5 | 7.98 | 12.1 |
| 4 | 4.61 | 7.41 |
| 6 | 3.08 | 4.90 |
| 10 | 1.83 | 3.08 |
| 16 | 1.15 | 1.83 |
| 25 | 0.724 | 1.15 |
| 35 | 0.524 | 0.841 |
| 50 | 0.386 | 0.610 |
| 70 | 0.273 | 0.431 |
| 95 | 0.193 | 0.305 |
| 120 | 0.153 | 0.241 |
| 150 | 0.124 | 0.193 |
| 185 | 0.0993 | 0.155 |
| 240 | 0.0753 | 0.119 |
| 300 | 0.0613 | 0.0984 |
| 400 | 0.0455 | 0.0743 |
| 500 | 0.0371 | 0.0600 |
Copper Conductors: The resistivity of copper is approximately 1.68 × 10^-8 Ω·m at 20°C, which results in the values mentioned in the table.
Aluminum Conductors: The resistivity of aluminum is about 2.82 × 10^-8 Ω·m at 20°C, leading to higher resistance compared to copper.
Table of Contents
What is a Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage as electrical current flows through a conductor. This loss is caused by the conductor’s resistance and is often more pronounced over longer distances. Ensuring minimal voltage drop is critical for electrical efficiency, as high voltage drops can lead to poor equipment performance, overheating, or even equipment failure.
Single-Phase Voltage Drop Formula
For a single-phase circuit, the voltage drop can be calculated using the formula:
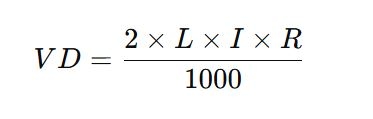
Where:
- VD = Voltage Drop (in volts)
- L = One-way length of the conductor (in Meters)
- I= Current (in amperes)
- R= Resistance of the conductor (in ohms per Km)
Three-Phase Voltage Drop Formula
For a three-phase circuit, the voltage drop can be calculated using the formula:
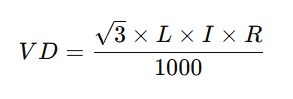
- VD = Voltage Drop (in volts)
- L = One-way length of the conductor (in Meters)
- I= Current (in amperes)
- R= Resistance of the conductor (in ohms per Km)
Additional Considerations
Conductor Material: The resistance RRR varies based on the material (e.g., copper, aluminum) and cross-sectional area of the conductor. You can find resistance values in standard tables.
Temperature Effects: Resistance can change with temperature, so it’s important to consider the operating temperature when using resistance values.
Voltage Drop Percentage: It’s often recommended to keep voltage drop below 3% for branch circuits and below 5% for feeders to ensure efficient operation.
Why Use a Voltage Drop Calculator?
A voltage drop calculator simplifies complex calculations, providing quick and accurate results. This tool is especially useful for:
- Electrical Circuit Design: Ensuring optimal performance by calculating voltage drop in advance.
- Energy Efficiency: Minimizing unnecessary power loss by choosing the right conductor size and material.
- Safety: Reducing the risk of overheating and equipment damage due to excessive voltage drop.
By inputting values such as conductor material, length, cross-sectional area, and current, the calculator quickly determines the voltage drop, helping you make informed decisions about your circuit’s design.
Key Factors in Voltage Drop Calculation
The following factors are essential inputs in a voltage drop calculator and significantly influence the outcome.
1. Conductor Material
The material of the conductor, typically copper or aluminum, directly affects the voltage drop. Copper is more conductive than aluminum, so it has a lower resistance and generally experiences less voltage drop for the same length and thickness.
2. Conductor Length
The length of the conductor is directly proportional to the voltage drop. Longer cables cause more resistance and, therefore, a greater voltage drop. Accurately measuring cable length helps in planning efficient circuits with minimal power loss.
3. Cross-Sectional Area
The cross-sectional area (or thickness) of a conductor impacts its resistance. A larger cross-sectional area allows more current to pass through with lower resistance, resulting in a smaller voltage drop. Choosing an appropriate conductor size is essential, especially in high-current applications.
4. Current
The amount of current flowing through a conductor also impacts voltage drop. Higher current causes a higher voltage drop due to increased resistance. This is why high-current circuits require conductors with larger cross-sectional areas to maintain efficiency.
Using the Voltage Drop Calculator
A voltage drop calculator requires users to input the four key values discussed. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
- Select Conductor Material: Begin by selecting the conductor material—typically copper or aluminum.
- Enter Conductor Length: Input the total length of the conductor in your circuit. Accurate measurements lead to better calculation results.
- Input Cross-Sectional Area: Specify the cross-sectional area of the conductor, usually measured in square millimeters (mm²) or American Wire Gauge (AWG).
- Enter Current Value: Lastly, input the current in amperes (A) flowing through the conductor.
With these inputs, the calculator processes the information and provides the voltage drop value in volts (V). This value gives insights into whether your circuit setup is efficient or requires adjustments.
Advantages of Using a Voltage Drop Calculator
Using a voltage drop calculator brings multiple benefits to circuit design:
- Quick and Accurate Calculations: Avoid lengthy manual calculations and receive accurate results in seconds.
- Enhanced Circuit Design: By understanding voltage drop, you can choose materials and sizes to improve circuit performance.
- Safety and Reliability: Proper voltage drop calculations help in creating circuits that are safe, minimizing overheating risks and potential failures.
- Cost Savings: With minimal voltage drop, circuits operate more efficiently, reducing energy costs over time.
Practical Applications for Voltage Drop Calculations
Understanding and calculating voltage drop is particularly useful in various real-world applications:
- Long Cable Runs in Buildings: For large buildings or industrial facilities with extended cable runs, voltage drop calculation is crucial. It helps maintain the necessary voltage levels across all equipment, even at distant points.
- Renewable Energy Installations: Voltage drop calculation is especially important in solar power installations, where long cables are often used to connect solar panels with inverters.
- Automotive and Marine Wiring: For vehicle and marine electrical systems, voltage drop is a common issue due to extended wiring. Ensuring optimal voltage drop keeps electronic systems within safe operating limits.
Tips to Minimize Voltage Drop in Circuits
To further reduce voltage drop in your circuits, consider the following:
Use Lower-Resistance Conductors: Whenever possible, use copper conductors, as they have a lower resistance than aluminum.
Increase Conductor Size: For longer runs or high-current applications, choose a larger cross-sectional area to reduce resistance.
Limit Cable Length: Shorter cables have lower resistance, so plan circuit layouts to keep conductor lengths as short as possible.
Adjust Circuit Design: Use multiple smaller cables instead of one large cable when high current is needed across a distance to improve efficiency.
Voltage Drop Calculation Example
Let’s go through an example of calculating voltage drop for better understanding.
- Conductor Material: Copper
- Conductor Length: 100 meters
- Cross-Sectional Area: 10 mm²
- Current: 20 A
Using a voltage drop calculator, you enter these values and quickly receive a result. The output will indicate the voltage drop, helping determine if adjustments in conductor size or layout are necessary to achieve optimal performance.
How to Interpret Voltage Drop Results
After using the voltage drop calculator, interpret the result with these guidelines:
- Low Voltage Drop: If the voltage drop is less than 3%, your circuit is efficiently designed.
- Moderate Voltage Drop: A voltage drop between 3-5% may still be acceptable but may benefit from adjustments.
- High Voltage Drop: Any drop over 5% generally requires redesigning the circuit or choosing lower-resistance conductors.
Related Tools and Calculators
Consider these additional calculators for an efficient electrical setup:
- Ohms Law Calculator: Helps determine the relationships between voltage, current, and resistance in your circuit.
- Power Calculator: Useful for determining the power consumption of your devices, especially when designing energy-efficient systems.
- Resistance Calculator: Assists in calculating the resistance of different materials based on length and cross-sectional area.
Conclusion
The Voltage Drop Calculator is an essential tool for designing efficient electrical circuits, allowing users to input key parameters like conductor material, length, cross-sectional area, and current to obtain accurate voltage drop values. This calculation helps design circuits with minimal power loss, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost savings. Whether working on building wiring, renewable energy installations, or automotive systems, this calculator supports optimal circuit performance and energy efficiency.
What is a Voltage Drop Calculator?
A Voltage Drop Calculator is a tool that helps users calculate the reduction in voltage in an electrical circuit due to resistance in the conductor. By inputting values like conductor length, material, cross-sectional area, and current, the calculator provides the voltage drop, ensuring that the circuit operates within safe voltage limits.
Why is calculating voltage drop important?
Calculating voltage drop is essential to ensure that devices and equipment receive sufficient voltage to operate efficiently and safely. Excessive voltage drop can lead to overheating, reduced efficiency, and even equipment damage.
How do I use a Voltage Drop Calculator?
To use the calculator, you need to enter values for conductor material (like copper or aluminum), conductor length, cross-sectional area, and current. The calculator then computes the voltage drop based on Ohm’s Law, giving a reliable estimation of voltage loss in the circuit.
What information is needed to calculate voltage drop?
You typically need the conductor’s material, length, cross-sectional area, and the current flowing through it. Some calculators may also require input of the operating voltage or specific installation conditions (temperature, altitude) if precise values are needed.
How does conductor material affect voltage drop?
The conductor material directly impacts resistance. Copper, for instance, has lower resistance than aluminum, meaning copper conductors will have less voltage drop for the same conditions, making it a more efficient choice for many applications.
What is the acceptable voltage drop limit?
The National Electrical Code (NEC) suggests a maximum voltage drop of 3% for branch circuits and feeders under normal operation, though other standards or applications may have slightly different recommendations. Staying within this limit helps maintain system efficiency and equipment longevity.
Does voltage drop depend on AC or DC current?
Yes, voltage drop can differ for AC and DC currents due to AC’s additional factors like impedance (inductive and capacitive effects). DC circuits typically have a simpler resistance-based calculation, while AC circuits may require adjustments for power factor and impedance.
How does conductor length impact voltage drop?
Voltage drop increases proportionally with conductor length. Longer conductors have higher resistance, leading to greater voltage losses, so reducing length can help minimize voltage drop.
Can I use the Voltage Drop Calculator for both single-phase and three-phase circuits?
Yes, many voltage drop calculators support both single-phase and three-phase circuits. Ensure you choose the correct option based on your circuit type, as the calculation differs slightly for each.
How can I reduce voltage drop in my circuit?
To reduce voltage drop, you can:Use conductors with a larger cross-sectional area.
Select a material with lower resistance (like copper instead of aluminum).
Minimize conductor length.
Lower the current load on the circuit.
Follow us on LinkedIn, “Electrical Insights,” to get the latest updates on electrical engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
#VoltageDropCalculator, #ElectricalEngineering, #OhmsLaw, #ElectricalSafety, #PowerLoss, #CircuitDesign, #ElectricalCalculations, #VoltageDrop, #ConductorSizing, #Wiring, #ElectricalWork, #HomeElectrical, #EngineeringTools, #DIYProjects, #ElectricalTips


