Phase to Phase Clearance as per IEC 61439: Best Guide
Phase to phase clearance as per IEC 61439 is one of the core safety requirements in low-voltage switchgear and control gear assemblies. This standard ensures that electrical equipment operates safely under normal and abnormal conditions.
Clearance values affect insulation, fault protection, dielectric withstand capability, and overall system reliability. Many designers, panel builders, and engineers refer to these requirements to avoid electrical breakdowns caused by arcing or insufficient air gaps. A clear understanding of the standard helps improve equipment safety and long-term performance.
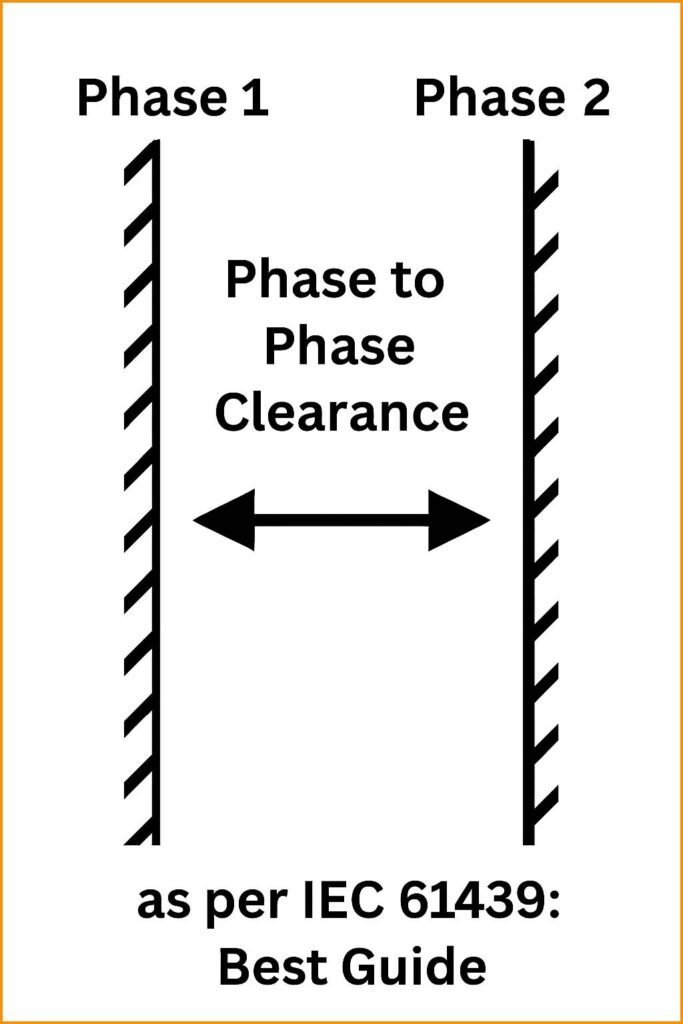
Table of Contents
IEC 61439 defines the minimum air clearance between two live parts that belong to different phases. This distance prevents short circuits and flashovers when voltage stress increases. It also reduces operational risks caused by pollution, humidity, dust, or mechanical movement inside electrical panels.
The standard sets specific values based on system voltage, the type of equipment, and insulation coordination. It also explains the influence of overvoltage category and pollution degree on clearance selection.
What Phase to Phase Clearance Means in Practical Design
Air clearance is the shortest distance in air between two conductive parts. In a three-phase system, the gap between different phase conductors must be large enough to handle the system’s peak voltage. If the distance is too small, air may ionize and form an electric arc. This can damage equipment or cause safety hazards. IEC 61439 ensures that these distances are standardized globally, which is important for consistent product quality and safety. Learn more about contact resistance test iec standard
Panel designers follow these values to layout busbars, terminals, and breakers. Manufacturers also test their assemblies under dielectric withstand tests to verify compliance. If actual clearance is lower than required, the assembly will not pass routine and type tests.
Phase to Phase Clearance as per IEC 61439
The table below provides typical minimum clearances for common system voltages. These values depend on pollution degree 3 and overvoltage category III, which are common in industrial installations. Actual projects may require confirmation from the full standard.
Minimum Air Clearance Values (Typical Reference)
| Rated Voltage (Ue) | Minimum Phase to Phase Clearance (mm) |
|---|---|
| 230/240 V | 3.0 mm |
| 400/415 V | 5.5 mm |
| 500 V | 8.0 mm |
| 690 V | 10.0 mm |
| 1000 V | 14.0 mm |
These values help maintain insulation integrity. They also support proper dielectric withstand levels during high-voltage testing. Designers should always confirm clearance requirements for the exact equipment category and environment. Discover everything about contact resistance test acceptable value
Factors That Influence Phase to Phase Clearance
Pollution Degree
IEC 61439 recognizes pollution levels inside the enclosure. Pollution degree 1 means a clean environment. Pollution degree 3 means conductive dust or moisture may be present. The higher the pollution degree, the larger the clearance required.
Overvoltage Category
Electrical installations face temporary overvoltages caused by switching or lightning. Overvoltage category III is typical for distribution-level equipment. Higher categories need increased phase to phase clearance to avoid flashover.
Altitude
Altitude reduces air density. As elevation increases beyond 2000 meters, dielectric strength decreases. The standard requires applying correction factors. This increases the phase to phase clearance for reliable insulation.
Material and Design Constraints
Busbar spacing, mechanical tolerances, and thermal expansion also influence clearance. Designers consider these during layout so that clearances remain within limits under all operating conditions. Find out more about contact resistance test acceptable value for busbar
Importance of Compliance with IEC 61439
Safety and Risk Reduction
Compliant clearance eliminates the risk of phase-to-phase faults due to reduced air gaps. It prevents arcing faults, which can lead to fire, equipment damage, and downtime.
Certification and Testing
Passing dielectric tests is mandatory for assembly certification. Insufficient clearance will cause failure during high-voltage withstand tests. Compliance ensures trouble-free testing and acceptance.
Equipment Longevity
Adequate clearance improves insulation life. Over time, dust and humidity may degrade air insulation. Higher clearances provide an extra safety margin and prolong the service life of electrical panels.
Practical Guidelines for Designers and Installers
Use Correct Busbar Spacing
Busbars should follow the recommended spacing from the standard. The table above is a practical starting point. However, always check the manufacturer’s tested values for assemblies. Explore details on contact resistance measurement
Maintain Clearance During Installation
Installers must ensure that wiring, lugs, or accessories do not reduce the minimum gap. Even a misplaced cable tie or terminal can violate clearance, causing the panel to fail inspection.
Verify with Dielectric Tests
Routine testing ensures that the assembly withstands the test voltage without breakdown. This test verifies spacing and insulation coordination.
Consider Future Maintenance
Clearances must remain intact during maintenance. Ensure there is no risk of accidental bending of conductors or displacement of parts that may reduce the air gap over time.
Get complete information about contact resistance test
Example Comparison: Clearance Variation with Conditions
| Condition | Required Clearance Adjustment |
|---|---|
| High pollution environment | Increase clearance |
| Altitude above 2000 m | Apply correction factor |
| Higher overvoltage category | Increase clearance |
| Compact panel design | Use additional insulation |
This comparison helps engineers understand when standard values are not enough. Supplementary insulation, barriers, or moulded components help achieve compliance in compact or high-demand designs.
Learn more about circuit breaker contact resistance test
Conclusion
Phase to phase clearance as per IEC 61439 is essential for electrical safety and reliability in low-voltage assemblies. It defines the minimum air distance needed to prevent flashover between phases. Designers, manufacturers, and installers follow these values to maintain insulation integrity, pass dielectric tests, and ensure safe operation under harsh industrial conditions.
When factors like pollution, overvoltage, and altitude are considered, the final design becomes more robust. Applying the correct clearances leads to better system performance, fewer failures, and safer electrical installations. Dive deeper into contact resistance measurement test
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#IEC61439, #ElectricalSafetyStandards, #PhaseToPhaseClearance, #PanelBoardDesign, #LowVoltageSwitchgear, #ElectricalCompliance, #SwitchboardStandards, #ClearanceRequirements, #ElectricalEngineeringGuide, #SafetyRegulations