Motor Overload Protection Chart: Important Concepts
Choosing the right protection level for a motor can make a big difference in its performance and lifespan. When a motor runs under excessive load, the windings heat up. If this continues, the insulation weakens and the motor becomes vulnerable to failure. This is where a motor overload protection chart becomes essential.
It helps you compare overload settings, current values, trip classes, and frame sizes. It also guides technicians and engineers in selecting the correct overload relay settings for safe operation.
Table of Contents
Motors are exposed to dust, voltage drops, jammed loads, long starting cycles, and even mechanical faults. These real-world conditions make overload protection a necessary safety layer. A clear chart allows quick decisions and reduces the chances of human error during setup or troubleshooting.
What a Motor Overload Protection Chart Shows
A motor overload protection chart gives an organized view of current ratings, thermal characteristics, and protection ranges. It is used during commissioning, maintenance, and even design stages. The goal is simple. Match the motor’s full load current with the correct relay setting to prevent overheating. Engineers also match the chart with nameplate values to ensure accuracy.
Know more about Working Principle of an Earth Fault Relay: How It Protects Electrical Systems
Different manufacturers use different formatting, but key elements remain the same. These include overload classes, current settings, frame suitability, and recommended relay types. Using a chart also helps avoid upsizing or downsizing mistakes.
Why You Need the Right Overload Setting
Incorrect settings can cause nuisance tripping or, even worse, delayed tripping. Nuisance tripping interrupts processes and reduces productivity. Delayed tripping exposes the motor to excessive heat. The motor overload protection chart ensures the correct balance. It keeps the motor protected while maintaining smooth operation.
When motors are part of pumps, conveyors, HVAC units, or compressors, the need for consistent protection becomes even stronger. Load demand changes, and a stable overload relay ensures the equipment remains safe in every cycle.
Table: Typical Overload Classes and Their Applications
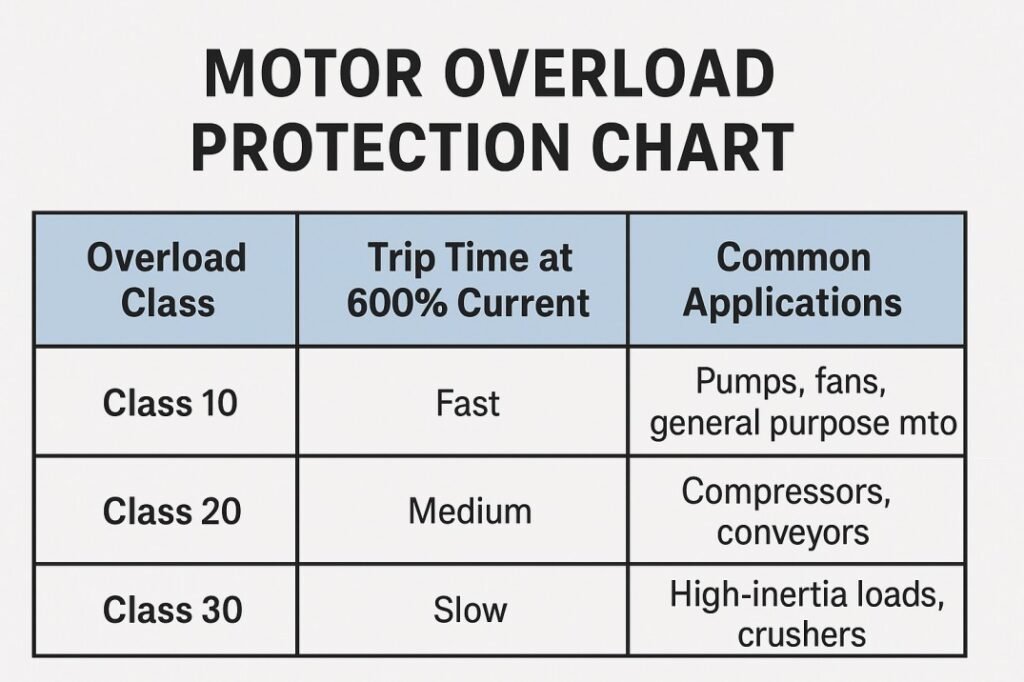
| Overload Class | Trip Time at 600% Current | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Class 10 | Fast | Pumps, fans, general purpose motors |
| Class 20 | Medium | Compressors, conveyors |
| Class 30 | Slow | High-inertia loads, crushers |
This table offers a quick reference when checking a motor overload protection chart and deciding which class works best for your application.
Know more about VLF Testing vs Hipot: Best Guide on Key Differences and Applications
Understanding Motor Current Ratings
Every motor has a rated full load current. Relay settings must be aligned with it. When the current increases beyond this limit, heat builds up. Overload relays sense this and trip before damage occurs. Using a motor overload protection chart helps keep the settings within the safe band. It also ensures compatibility with the motor’s nameplate values.
Motor currents vary with voltage, design, and efficiency. That is why selecting protection purely on horsepower is risky. Current-based selection is more reliable. The chart offers a quick lookup, reducing guesswork.
Table: Sample Full Load Current Reference
| Motor HP | Voltage | Approx. FLC (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 HP | 400V | 1.8 A |
| 5 HP | 400V | 7.6 A |
| 10 HP | 400V | 14.8 A |
| 20 HP | 400V | 28 A |
Such tables support the values you see in a motor overload protection chart and help in cross-checking relay settings.
Know more about Best Rotor Earth Fault Protection for Brushless Generator | Working, Types & Settings Explained
Types of Overload Relays Used With These Charts
Overload relays come in thermal, electronic, and bimetal types. Thermal relays use heat to trigger a trip. Electronic relays offer better accuracy, especially in fluctuating conditions. Bimetal relays remain popular for smaller motors.
Regardless of the type, each relay follows the values shown in a motor overload protection chart to operate correctly. Matching relay type to the chart values improves reliability and minimizes fault risks.
How to Use a Motor Overload Protection Chart in Real Projects
Start by noting the motor’s full load current from the nameplate. Then compare it with the chart to find the correct relay setting. Check the range, class, and frame size. Make sure you are not choosing a setting too close to the upper limit. A small buffer prevents nuisance trips.
The motor overload protection chart also guides you when loads change. If a motor is derated due to temperature or altitude, adjusting the relay setting becomes easier with the chart.
Table: Example Overload Setting Selection
| Motor FLC | Relay Range | Recommended Setting |
|---|---|---|
| 12 A | 10–16 A | Set between 12–13 A |
| 18 A | 16–25 A | Set between 18–19 A |
| 32 A | 25–40 A | Set between 32–33 A |
Such values match the guidance typically found in a motor overload protection chart and help prevent errors during installation.
Use our online tool Electrical Insurance Premium Calculator – Estimate Your Electrical Coverage Cost Online
Preventing Common Overload Mistakes
One mistake is setting the relay too high. This delays protection and exposes the motor to heat damage. Another mistake is ignoring the ambient temperature. Relays behave differently in hot areas. Using a motor overload protection chart helps adjust values based on surrounding conditions.
Engineers also avoid setting the relay lower than the motor’s rated current. This causes unnecessary trips. Looking at the chart before locking the setting prevents these issues. Regular inspections ensure the relay continues to operate within the charted range.
Why Charts Improve Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance teams use these charts for quick diagnosis. When a motor frequently trips, comparing the relay setting with the chart reveals mismatches instantly.
The motor overload protection chart also helps identify whether the problem is mechanical or electrical. If the setting is correct yet the relay trips, the load may be jammed or misaligned.
Charts also serve as training tools. New technicians learn faster by referencing visual data instead of only relying on manuals.
Using Charts for Energy Efficiency and Motor Life
Correct overload settings reduce energy waste. When the motor runs within its safe zone, the power factor and efficiency remain stable. A motor overload protection chart helps achieve this balance.
Proper protection also extends motor life. Windings last longer and require fewer repairs. Over time, this reduces operating costs and improves system reliability.
Know more about Contact Resistance Test Acceptable Value for Breaker
When to Review or Update Your Chart
If you upgrade equipment, change load conditions, or replace motors, review the existing chart. Voltage changes and operational shifts also make updates necessary.
Using the latest motor overload protection chart ensures that all relay settings reflect current requirements. This keeps the system safe and maintains compliance with electrical standards.
Final Thoughts
A motor overload protection chart is more than a reference sheet. It is a tool that helps protect motors, prevent downtime, and support smooth operation. It guides technicians, improves decisions, and reduces errors. When used correctly, it enhances safety, boosts equipment life, and ensures consistent performance.
With accurate chart data and properly selected overload settings, motors run safely and efficiently. This makes the chart an essential part of every electrical maintenance and installation project.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#motoroverloadprotectionchart, #motorprotection, #overloadrelay, #thermalrelay, #motorsafety, #electricalengineering, #industrialmaintenance, #motorstarter, #electricalprotectivedevices, #engineeringsolutions






