Earthing Cable Size Standard: A Complete Guide
Proper earthing is crucial for ensuring electrical safety and reducing the risk of electric shocks or fire hazards. One of the essential aspects of effective earthing is selecting the correct earthing cable size. In this guide, we’ll explore the earthing cable size standard, explain its significance, and review the factors that influence its selection. By following industry standards, electricians and engineers can achieve safe, reliable earthing systems that protect people, equipment, and property.

What is Earthing Cable Size Standard?
The earthing cable size standard refers to guidelines that specify the appropriate cable size for grounding or earthing purposes. These standards are designed to ensure that the earthing system can handle potential fault currents without overheating or becoming damaged. Proper earthing cable size helps create a secure, conductive path to the ground for electric currents, particularly during fault conditions.
Choosing the right earthing cable size according to standards minimizes risks, enhances safety, and ensures the longevity of the entire electrical system.
Importance of Choosing the Correct Earthing Cable Size
Choosing the correct earthing cable size is essential for several reasons:
- Safety: A properly sized earthing cable reduces the risk of electrical shock.
- Equipment Protection: Proper earthing can protect electrical equipment from damage caused by surges or fault currents.
- System Reliability: With the correct earthing cable size, electrical systems function more reliably.
- Compliance: Following earthing cable size standards is necessary to comply with local and international electrical codes.
In summary, using the correct earthing cable size enhances the safety and performance of electrical systems.
Factors Affecting Earthing Cable Size Selection
To determine the earthing cable size, consider these key factors:
1. Fault Current Level
The expected fault current level, or short-circuit current, is a significant factor in selecting the right cable size. Larger fault currents require larger cables to ensure they can safely conduct the current to the ground without overheating.
2. Type of Installation
Earthing cable sizes may vary based on whether the installation is residential, commercial, or industrial. Industrial settings typically require larger cable sizes due to higher fault current risks and larger equipment needs.
3. Cable Length
The longer the cable, the higher its resistance. Therefore, longer earthing cables may need a larger diameter to maintain low resistance and effective grounding.
4. Soil Resistivity
Soil resistivity can affect grounding effectiveness. High-resistivity soil, like dry sandy soil, may require larger cables or additional grounding measures to ensure adequate conductivity.
Note: Use our online electrical load calculator for electrical load calculation here. You can also use voltage drop calculator for voltage drop calculation for cable selection in any single and three phase circuit here. Further explore our online electrical calculators to design your electrical systems in an efficient way.
Common Earthing Cable Size Standards
Several standards provide guidelines for selecting the appropriate earthing cable size based on these factors. Below are some of the widely recognized standards:
1. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
The IEC 60364 standard specifies guidelines for the earthing and grounding of electrical systems. It provides tables and equations to help determine the suitable cable size based on system parameters like fault current and conductor material. We can easily determine the earthing cable size as per IEC using this guide.
2. National Electrical Code (NEC)
The NEC 250.66 code is widely followed in the United States for earthing cable sizing. It specifies the minimum size requirements for grounding electrodes, which vary based on conductor material and fault current.
3. British Standard BS 7430
The BS 7430 standard provides detailed guidelines for earthing electrical installations in the UK. It includes tables and recommendations for choosing earthing cable sizes in different applications.
4. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
The IEEE 80 standard offers guidelines on earthing cable sizing for electrical substations. IEEE focuses on safety, fault handling, and ensuring proper system grounding.
How to Calculate Earthing Cable Size
Calculating the earthing cable size involves several steps. Although standards and codes offer tables for reference, understanding the basics of calculation can help in custom situations. Here’s a basic approach to determining earthing cable size:
- Determine Fault Current: Identify the maximum expected fault current for the system.
- Select Conductor Material: Earthing cables are typically made of copper, aluminum, or steel, each having different conductivity properties.
- Use Calculation Formula: A commonly used formula is:

where:
- A = cross-sectional area of the conductor
- I = fault current in amperes
- t = fault duration in seconds
- k = constant based on material (e.g., 143 for copper, 94 for aluminum)
Check Standards: Confirm your calculated size against standard tables in IEC, NEC, or IEEE guidelines.
Example Calculation
For a copper cable with a fault current of 10,000A and a fault duration of 1 second:
- Using k = 143 for copper, we find
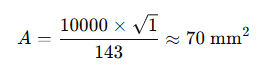
This result suggests a 70 mm² cable size to handle the fault current safely.
Recommended Earthing Cable Sizes Based on Standards
Below are some commonly recommended earthing cable sizes as per industry standards:
| Application | Recommended Earthing Cable Size |
|---|---|
| Residential | 6 mm² to 16 mm² (copper) |
| Small Commercial | 16 mm² to 25 mm² (copper) |
| Large Commercial | 25 mm² to 50 mm² (copper) |
| Industrial | 50 mm² and above |
| Substations | 95 mm² and above |
Note: Always confirm these values with local regulations, as requirements can vary by country and region.
Best Practices for Earthing Cable Installation
For effective earthing, the installation should meet certain best practices:
- Use High-Quality Materials: Choose durable, corrosion-resistant cables, especially for outdoor applications.
- Ensure Proper Connections: Secure connections help prevent corrosion and maintain conductivity.
- Minimize Sharp Bends: Sharp bends can weaken cables and reduce their ability to conduct fault currents.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect earthing cables for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
Additional Tips for Selecting Earthing Cable Sizes
1. Consider Future Expansion
If there’s potential for system expansion, consider slightly larger cables to accommodate future fault current increases.
2. Prioritize Safety and Compliance
While cost is a factor, prioritize safety and compliance with earthing cable size standards over budget constraints.
3. Use Multicore Cables for Complex Installations
Multicore cables can simplify installation in larger systems by bundling multiple cables into a single sleeve, providing an organized and efficient grounding solution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if the earthing cable size is too small?
If the earthing cable is too small, it may overheat, become damaged, or fail during a fault condition, posing a risk of electrical shock or fire.
How often should earthing cables be inspected?
Earthing cables should be inspected periodically, ideally every 3-5 years, or whenever there are major changes to the electrical system.
Can I use aluminum cables for earthing?
Yes, aluminum cables can be used for earthing, but they need to be larger in size than copper due to aluminum’s lower conductivity.
Conclusion
Selecting the right earthing cable size is essential for ensuring electrical safety, protecting equipment, and meeting regulatory standards. By following guidelines from established standards like IEC, NEC, BS, and IEEE, you can accurately determine the appropriate cable size based on fault current, installation type, cable length, and soil resistivity. Remember, while earthing is a critical part of any electrical system, periodic inspections and adherence to standards will help maintain a safe and efficient grounding setup.
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
EarthingCable, #CableSizing, #ElectricalSafety, #EarthingStandards, #GroundingSystem, #ElectricalEngineering, #CableInstallation, #EarthingGuide, #PowerSystems, #CableSizeCalculation, #GroundingSafety, #ElectricalDesign, #ElectricalWiring, #EarthingTips, #ElectricalCodes


