Acoustic Emission Analysis: Best Guide
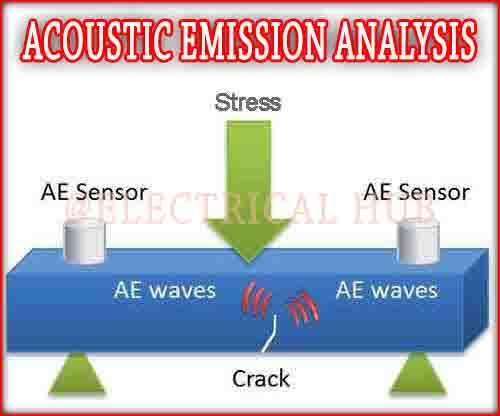
Acoustic emission analysis, a powerful testing method, involves affixing tiny sensors onto a tested component. These sensors convert stress waves into electrical signals, relayed to an acquisition PC for processing.
When the component undergoes external stimuli like high pressures or temperatures, stress waves are captured. As damage progresses, more energy is released. Monitoring the rates, activity, and intensity of these emissions aids in structural integrity assessment and component health monitoring.
Acoustic Emission Analysis: Methods and Techniques
Similar to tiny earthquakes within materials, acoustic emission analysis globally monitors defects in components, enabling seamless monitoring of large structures and machines during operation, avoiding destructive testing.
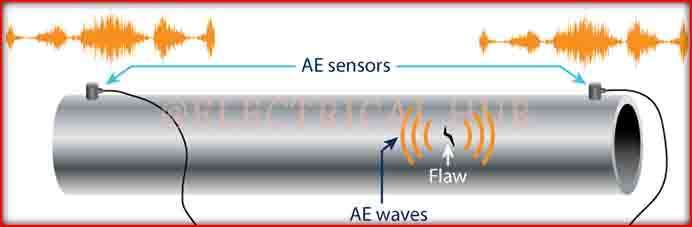
This technique, using multiple sensors, pinpoints emission sources, aiding damage localization. Transient and continuous methods are employed for AE testing, with the former capturing bursts exceeding a threshold, ideal for detecting defects like cracks. The latter method captures all AE within a timeframe, suited for applications with background noise or low AE amplitude, such as gearbox testing.
Advantages
Acoustic emission analysis boasts numerous advantages, including detecting various damage mechanisms early on, operating in hazardous environments, and offering remote analysis capabilities.
Early Detection of Various Damage Mechanisms: Identifies damage mechanisms like fiber breakages, impacts, friction, cracks, delamination, and corrosion in their early stages.
Monitoring During Operation and Testing: Enables testing while structures or machines are operational, providing insights into real-time conditions and performance during qualification or proof testing.
Global Monitoring and Damage Localization: Facilitates global monitoring of structures or machines, aiding in locating and distinguishing sources of damage based on their acoustic signatures.
Non-Invasive and Suitable for Hazardous Environments: Non-intrusive technique suitable for environments with high temperatures, pressures, corrosive substances, or nuclear conditions.
Remote Analysis and Accessibility: Allows remote analysis of data collected and can detect damages in areas challenging to access through conventional testing methods.
However, it also has limitations, such as the need for further inspection after detecting issues and limitations in detecting stationary defects.
Limitations of Acoustic Emission Analysis
Supplementary Inspection Required: While it identifies issues, further inspection is often necessary for a comprehensive diagnosis and to understand the extent of identified problems.
Inability to Detect Stationary Defects: It may not effectively identify defects that are stationary or do not undergo movement or growth, limiting its scope in certain scenarios.
Comparative Slower Pace: In some cases, acoustic emission analysis might be slower in comparison to other non-destructive testing techniques, affecting the speed of assessment.
Applications of Acoustic Emission Analysis
The versatility of acoustic emission analysis extends across diverse applications, from structures like bridges and aircraft to machines like gearboxes and electrical machinery. Its usage spans additive manufacturing, leak detection in pipelines, and monitoring frictional processes.
Acoustic emission analysis is a technique used to monitor the structural integrity and detect potential faults or defects in materials or structures. It works by detecting and analyzing the ultrasonic waves or acoustic emissions produced by a material when it undergoes stress, deformation, or damage.
Structures: Used for assessing concrete structures like bridges and buildings, metallic structures such as pressure vessels, pipelines, storage tanks, aircraft components, and steel cables.
Machines: Applied in monitoring rotating machinery, detecting early wear in bearings and gearboxes, as well as in electrical machinery to detect partial discharge in transformers and bushings.
Processes: Utilized in additive manufacturing for assessing build quality during the process, detecting leaks in pipelines and pressure systems, and monitoring particle impacts and frictional processes.
In practical terms, this method involves placing sensors or transducers on the surface of a material or structure under investigation. When the material is subjected to mechanical stress or experiences changes, such as cracking, micro-fracturing, or other forms of deformation, it emits ultrasonic waves. These emissions are captured by the sensors, converted into electrical signals, and analyzed to identify any abnormal patterns or frequencies.
This technique is widely used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, civil engineering, and manufacturing, for assessing the structural integrity of components such as pipelines, bridges, turbines, and pressure vessels. Acoustic emission analysis aids in early detection of potential failures or defects, allowing for timely maintenance or repairs, ultimately enhancing safety and reliability in various applications.
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
