What is an Overcurrent Relay and How Does It Work? Best Guide
Overcurrent relays are critical devices in electrical power systems. They protect electrical circuits from excessive current that can damage equipment or cause fires. But what is an overcurrent relay, and how does it function in real-world applications? In this article, we will explain its operation, types, applications, and technical details.
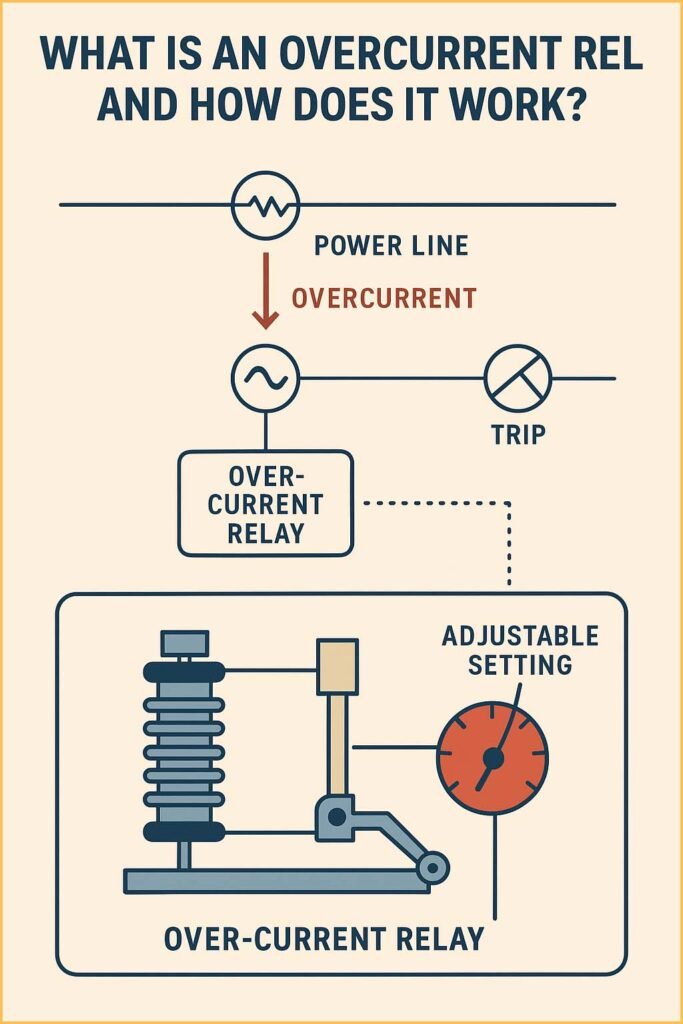
Table of Contents
What is an Overcurrent Relay?
An overcurrent relay is a protective device that operates when the current in a circuit exceeds a preset limit. It detects abnormal currents caused by short circuits, overloads, or equipment faults and isolates the faulty part to prevent damage. These relays are widely used in transmission and distribution systems to ensure the safety and reliability of electrical networks.
Know more about Working Principle of an Earth Fault Relay: How It Protects Electrical Systems
The primary function of an overcurrent relay is to sense the magnitude of the current and compare it to a predetermined threshold. When the current exceeds this limit, the relay trips the circuit breaker, cutting off the electrical flow and protecting the system. Read in detail about types of transformer protection relays
Working Principle of an Overcurrent Relay
The working principle of an overcurrent relay is simple. It relies on the fact that excessive current in a circuit indicates a fault. The relay continuously monitors the current through a current transformer (CT) and operates when the current surpasses the set value.
Mathematically, the tripping condition can be expressed as:
I > I_set
Where:
- I = Measured current in the circuit
- I_set = Relay’s preset current value
The relay can be designed to operate instantly or with a time delay, depending on the protection scheme.
Types of Overcurrent Relays
Overcurrent relays are categorized based on their operating characteristics and applications.
1. Instantaneous Overcurrent Relay
This type of relay operates without any intentional time delay. The moment the current exceeds the preset value, the relay trips the circuit breaker. It is mainly used for short-circuit protection.
Advantages:
- Fast response
- Simple design
Limitations:
- May cause unnecessary tripping during temporary surges
Uncover insights on high impedance protection
2. Definite Time Overcurrent Relay
In this type, the relay operates after a fixed time delay once the current exceeds the preset limit. This delay allows selectivity in protection, ensuring only the faulted section is disconnected.
Formula for operation time:
t = T_fixed
Where T_fixed is the set time delay.
3. Inverse Time Overcurrent Relay
Inverse time relays are more sophisticated. The higher the current, the faster the relay operates. This characteristic matches the severity of the fault with the response time, providing optimal system protection.
Formula for inverse time:
t = k / (I/I_set – 1)
Where:
- t = Operating time
- I = Measured current
- I_set = Relay setting
- k = Constant based on relay type
This type is widely used in power distribution networks because it ensures coordination between multiple protective devices.
Find out more about transformer differential protection
Construction and Components
An overcurrent relay consists of several essential components:
- Current Transformer (CT): Steps down high current to a measurable value.
- Relay Coil: Energized by the current passing through it.
- Operating Mechanism: Trips the circuit breaker when the relay coil energizes.
- Time-Setting Device: Adjusts the time delay in definite and inverse time relays.
Modern overcurrent relays are often digital or microprocessor-based, offering better accuracy, programmable settings, and remote monitoring.
Table: Comparison of Overcurrent Relay Types
| Type | Time Delay | Application | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Instantaneous | None | Short-circuit protection | Very fast | May trip unnecessarily |
| Definite Time | Fixed | Overload & coordination | Simple & reliable | Not adaptive to fault severity |
| Inverse Time | Variable | Distribution networks | Matches fault severity | More complex |
How Overcurrent Relays Operate in a Circuit
Overcurrent relays are usually connected in series with the circuit they protect. They detect abnormal currents via the CT, convert it into a measurable signal, and activate the relay mechanism. Once the relay trips, it sends a trip signal to the circuit breaker.
For example, in a power distribution system:
- Normal operation: Current flows through the CT to the relay without any tripping.
- Fault occurs: Excessive current flows due to short-circuit or overload.
- Relay senses current above I_set.
- Depending on the relay type, it operates instantly or after a calculated delay.
- Trip command sent to circuit breaker, isolating the faulty section.
This sequence ensures minimum disruption and protects both equipment and personnel.
Explore details on IEC Standard for Differential Protection
Key Settings and Calculations
To ensure proper operation, overcurrent relays require careful setting of two parameters:
- Current Setting (I_set): The value of current above which the relay should operate. It is often set slightly above the normal maximum load current.
- Time Setting (T): Determines the delay before the relay operates. For inverse-time relays, this is calculated based on the desired protection coordination.
Example Calculation:
Suppose a feeder line has a normal load current of 200 A, and the maximum fault current is 1000 A. An inverse-time relay is set with:
- I_set = 250 A
- k = 0.14
If a fault occurs with a current of 500 A, the operating time will be:
t = 0.14 / (500/250 – 1) = 0.14 / 1 = 0.14 s
This rapid response ensures the fault is cleared quickly.
Know more about alternator protection scheme
Applications of Overcurrent Relays
Overcurrent relays are used in various applications:
- Power Generation: Protect generators and transformers from overload.
- Power Transmission: Ensure safe operation of high-voltage transmission lines.
- Industrial Systems: Protect motors, cables, and industrial equipment.
- Distribution Networks: Maintain coordination between feeders and substations.
Advantages of Overcurrent Relays
Overcurrent relays provide several benefits:
- Fast and reliable protection against faults
- Simple design and easy to maintain
- Flexible settings for current and time
- Compatibility with modern digital protection systems
- Coordination with multiple relays in complex networks
Get complete information about protection of alternator
Challenges and Considerations
While overcurrent relays are essential, certain challenges must be considered:
- Selectivity Issues: Improper settings can lead to tripping non-faulted circuits.
- CT Saturation: At high fault currents, CTs may saturate, affecting relay accuracy.
- Coordination with Other Relays: Careful coordination is required to avoid system-wide outages.
Modern digital relays and smart protection systems have addressed many of these challenges, allowing for precise protection schemes and real-time monitoring. Dive deeper into differential protection of alternator
Final Thoughts
An overcurrent relay is a fundamental device in electrical protection systems. It detects excessive currents, operates either instantly or after a delay, and isolates faulty sections to prevent damage. Understanding its types, working principle, components, and applications is essential for engineers and technicians working in power systems.
Learn more about types of generator protection relays
By setting the relay correctly and choosing the right type for the application, overcurrent relays provide reliable protection, minimize downtime, and ensure safety across electrical networks. Whether in industrial plants, substations, or distribution networks, these relays remain a cornerstone of electrical protection.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#OvercurrentRelay, #ElectricalProtection, #PowerSystemProtection, #RelayProtection, #ElectricalEngineering, #OvercurrentProtection, #CircuitSafety, #IndustrialElectrical, #RelayWorking, #ElectricalCircuit







Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites