Load Computation: Complete Guide for Electrical Systems
Accurate load computation is fundamental for designing safe, efficient electrical systems, especially when planning for capacity and preventing overloads. This article will guide you through the essentials of load computation, also known as electrical load calculation, providing step-by-step instructions, an electrical load calculator approach, and a worksheet you can refer to for different scenarios. Whether you’re an electrical engineer, a contractor, or a DIY enthusiast, this guide will simplify the process of calculating electrical loads to enhance the safety and reliability of your electrical systems.

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Understanding Load Computation
Load computation determines the total power demand of an electrical system, taking into account the connected appliances, devices, and future expansions. The main goal is to ensure that circuits can safely handle the anticipated load without tripping breakers or causing overheating.
Key Factors in Load Computation
- Total Connected Load: This includes all electrical appliances and fixtures connected to a circuit or panel.
- Demand Factor: Used to adjust the load computation based on expected usage levels.
- Diversity Factor: Allows flexibility by estimating that not all connected devices will operate simultaneously.
The process helps you estimate the capacity required for a circuit or an electrical panel, preventing overloading and ensuring efficient power distribution. Use our free load computation calculator here.
Why Load Computation Matters
Proper load computation ensures that:
- Electrical circuits remain safe under maximum load conditions
- Power distribution is optimized, reducing unnecessary energy costs
- Electrical panels are adequately sized to handle the load, with room for future upgrades
How to Calculate Electrical Load for Residential and Commercial Buildings
Step 1: Gather Electrical Load Information
- List all appliances, devices, and fixtures on each circuit
- Identify the wattage or amperage rating for each item
- Use an electrical load calculation table or worksheet to organize this information
Step 2: Calculate the Total Load
- Wattage Calculation: Multiply the amperage by the voltage for each device (W = V x A) know more about power triangle.
- Kilowatt Calculation: If needed, divide the wattage by 1,000 to convert to kilowatts (kW)
Step 3: Apply Demand and Diversity Factors
Adjust the total load using demand and diversity factor in electrical load calculation, especially for commercial settings. Residential loads may apply lower demand factors due to the likelihood of simultaneous use. Know more about electricity load calculator in kw for home here.
Using an Electrical Load Calculator for Efficient Load Computation
An electrical load calculator simplifies load computation by automating complex calculations and offering pre-set factors based on appliance types. These calculators save time and reduce errors, providing an accurate snapshot of your total load and recommended panel capacity.
Note: Use our online electrical load calculator for electrical load calculation here. You can also use voltage drop calculator for voltage drop calculation for cable selection in any single and three phase circuit here. Further explore our online electrical calculators to design your electrical systems in an efficient way.
Steps for Using an Electric Load Calculator
- Input Load Values: Enter the wattage or amperage of each appliance
- Select Circuit Type: Choose whether it’s a single-phase or three-phase circuit
- Review Suggested Load and Panel Sizing: The calculator will display the calculated electrical load and suggested panel capacity
These calculators are ideal for residential and light commercial projects and can be found online or as part of electrical software packages.
Common Methods of Calculating Electrical Load
The choice of method for calculating electrical load depends on the type and complexity of the electrical system.
1. Per-Circuit Load Calculation
This approach calculates the load for each circuit independently, helping ensure that no individual circuit exceeds its rating.
2. Panel Load Calculation
Used for calculating the total load on an electrical panel, especially useful in determining the need for an upgrade or modification. In electrical panel load calculation, the total load for each connected circuit is combined, then adjusted based on demand and diversity.
3. General Lighting Load Calculation
For lighting systems, load computation typically uses the square footage of a space and a standard lighting wattage factor. This method is suitable for planning circuit load requirements in large buildings. Use free load computation calculator for lighting load calculation.
4. NEC Standard Load Calculation
The National Electrical Code (NEC) provides formulas and tables that serve as a guideline for safe and effective load computation. This approach is highly recommended for both residential and commercial settings. know more about NEC 220 here.
Essential Tools for Electrical Load Computation
An electric load calculator and worksheets can simplify the process. Additionally, software programs designed for electrical load calculation help save time, especially in larger projects. Learn more about electrical design software here.
Suggested Tools:
- Electrical Load Calculator: For quick, accurate calculations
- Load Calculation Worksheet: Helps you organize and structure your computation process
- Software Programs: Ideal for complex projects with multiple panels or circuits
Sample Electrical Load Calculation Table
Below is an example of an electrical load calculation table to guide you through a straightforward method of load computation.
| Appliance/Device | Wattage (W) | Voltage (V) | Amperage (A) | Demand Factor (%) | Adjusted Load (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | 500 | 120 | 4.17 | 80% | 400 |
| HVAC | 2000 | 240 | 8.33 | 100% | 2000 |
| Refrigerator | 1500 | 120 | 12.5 | 90% | 1350 |
| Washer | 1200 | 120 | 10.0 | 75% | 900 |
Tips for Accurate Load Computation
- Use updated information for appliances and devices
- Apply correct demand factors based on NEC guidelines
- Use an electric load calculator or software tools for large projects
- Regularly update your load computation as appliances are added or replaced
Electrical Load Calculation for Panels and Circuits
When planning for an electrical panel load calculation, it’s crucial to consider the future expansion potential and balance the load across circuits. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- List the Circuit Loads: For each circuit, sum up the wattages or amperages for each appliance connected
- Apply the Panel’s Capacity: Ensure the panel’s maximum amperage can handle the total load
- Balance the Load: Evenly distribute high-load circuits to avoid overloading specific areas
Electrical Load Calculation Worksheet Example
To create a worksheet for calculating electrical loads, list the appliances and their wattage requirements, demand factors, and adjusted loads. Below is an example:
| Circuit Description | Total Load (W) | Circuit Breaker (A) | Diversity Factor (%) | Total Adjusted Load (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kitchen Circuit | 1800 | 15 | 80% | 1440 |
| Living Room Circuit | 1000 | 10 | 100% | 1000 |
| Bedroom Circuit | 1200 | 15 | 85% | 1020 |
| HVAC Circuit | 3500 | 20 | 100% | 3500 |
Conclusion
Accurate load computation is essential for safe and efficient power distribution. By following these steps, using load calculators, and applying the right demand factors, you can ensure your electrical systems are designed for both current and future needs. Whether it’s for residential or commercial setups, a well-executed electrical load calculation prevents overloads and promotes safe operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is electrical load computation?
Electrical load computation is the process of calculating the total electrical demand a system requires to operate efficiently. This includes assessing the power requirements of all appliances, devices, and machinery within a specific area or building. Accurate load computation helps in designing and sizing electrical components like transformers, conductors, and circuit breakers to prevent overloads and ensure safe operation.
Why is load computation essential in electrical systems?
Load computation ensures that all components in an electrical system can handle the expected demand without risk of overload or failure. Proper load calculation prevents electrical hazards, enhances energy efficiency, and reduces equipment wear. It also aids in planning for future expansions and assessing the need for backup power.
What are the basic types of electrical loads?
Electrical loads are typically categorized into three types:
Resistive Loads: Devices like heaters and incandescent lights where current and voltage are in phase.
Inductive Loads: Motors and transformers which cause a phase difference between current and voltage, requiring more complex calculations due to power factor.
Capacitive Loads: Rare in most applications, but found in systems like capacitor banks for power factor correction.
How is total connected load calculated in a residential setup?
The total connected load in a residence is calculated by summing the rated power (in watts or kilowatts) of each appliance and fixture. Multiply the number of each type of appliance by its power rating and add up all results.
For example: Total Load=Lighting Load+Heating Load+Appliance Load+HVAC Load
What is the difference between connected load and demand load?
The connected load is the sum of the maximum load each device could draw if operated simultaneously. Demand load, however, represents the actual peak load expected based on usage patterns, typically lower than the connected load due to the diversity factor (not all devices run at the same time).
What role does power factor play in load computation?
Power factor, which is the ratio of real power to apparent power, significantly impacts load computations, especially in systems with inductive loads. A lower power factor means more apparent power is needed to supply the same real power, resulting in higher current draw and potential increases in conductor size and losses. Improving the power factor can reduce load requirements.
How do you calculate load in terms of amperes?
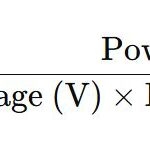
To calculate the load in amperes, use the formula
This conversion is essential for designing circuits, as it helps determine the conductor size and circuit breaker rating needed for safe operation.
What is a demand factor, and how is it applied in load computation?
The demand factor is the ratio of the maximum demand of a system to its total connected load. It helps in determining realistic load requirements as not all devices operate at full capacity simultaneously. For example, in a commercial building, lighting and HVAC loads are reduced based on typical usage patterns.
What tools and software are commonly used for load computation?
Various tools and software can assist with load computation, including:Manual Calculation Tools: Load calculators and electrical code guidelines.
Software: Programs like ETAP, SKM PowerTools, and AutoCAD MEP, which offer detailed simulation, analysis, and design capabilities for complex systems.
How do you size a generator based on load computation?
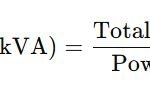
To size a generator, calculate the total load in kilowatts (kW), then apply a margin (typically 20-30%) for start-up surges and future expansions. Convert to kilovolt-amperes (kVA) if needed, using the formula:
This ensures the generator can handle peak demands and maintain steady operation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, “Electrical Insights,” to get the latest updates on electrical engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
LoadComputation, #ElectricalSystems, #ElectricalLoadCalculation, #PowerDemand, #EnergyManagement, #ElectricalEngineering, #LoadBalancing, #CircuitDesign, #ElectricalInstallations, #PowerDistribution, #SystemEfficiency, #LoadManagement, #ElectricalLoadGuide, #PowerCalculation, #ElectricalAnalysis







I am really glad to read this blog posts
which includes tons of useful data, thanks for providing these data.