How to Calculate Load Factor in Electrical System: Best Guide
Calculating load factor is essential for understanding how efficiently an electrical system uses energy. In electrical engineering, load factor is a measure of how consistently a load is utilized over a period of time. By learning how to calculate load factor in electrical systems, we can make better choices in energy management, cost savings, and system design.
Table of Contents
How to Calculate Load Factor in Electrical System
What is Load Factor?
Load factor is the ratio between the average load and the maximum load during a specified period, often a month or year. It reflects the efficiency of power usage within an electrical system. High load factors indicate steady usage, while low load factors signify more variability, leading to potentially higher costs due to demand charges.
Why Calculate Load Factor?
- Efficiency: High load factors mean better efficiency, reducing demand charges.
- Cost Savings: Understanding the load factor can help minimize peak demand and lower energy bills.
- System Optimization: Helps identify if an electrical system needs redesign or enhancement.
Calculating load factor is particularly important for large facilities, industries, and residential buildings aiming to reduce energy consumption and costs.
Formula for Load Factor Calculation
The general formula for load factor calculation is as follows:
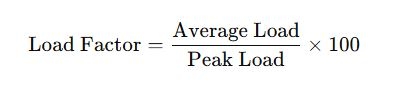
Where:
- Average Load: The average power consumed over a specified period.
- Peak Load: The maximum power used at any point within the same period.
Example of Load Factor Calculation
Suppose a facility’s peak load for a month is 500 kW, and it has an average load of 350 kW. Plugging these values into the formula:
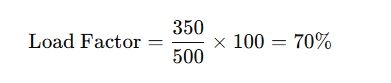
Steps to Calculate Load Factor in Electrical Systems
To perform an electrical load calculation, follow these steps:
Determine the Peak Load: Measure or obtain the maximum load value for the facility within the period you’re analyzing. This can often be found through energy bills or electric meters.
Calculate the Average Load: Sum the total energy consumption for the period, then divide by the time to find the average load.
Apply the Load Factor Formula: Substitute the values into the load factor formula to find the efficiency of power usage.
Note: Use our online electrical load calculator for electrical load calculation here. You can also use voltage drop calculator for voltage drop calculation for cable selection in any single and three phase circuit here. Further explore our online electrical calculators to design your electrical systems in an efficient way.
Related Tools and Tables for Load Factor Calculation
Using tools like an electrical load calculator or a voltage drop calculator can be very helpful in load computations, especially for complex electrical systems. Many online calculators and electrical load calculation worksheets provide simple methods to estimate loads for different appliances and systems. Additionally, electrical load calculation tables list common appliances and their typical loads, which can simplify your calculations.
Improving Load Factor in Electrical Systems
Once you’ve calculated your load factor, you can focus on steps to improve it:
- Shift Load Timing: Move high-consumption activities to off-peak hours.
- Implement Energy-Efficient Devices: Energy-efficient appliances help reduce peak demand.
- Install Load Control Systems: Automated systems can stagger high-demand appliances to reduce peak load.
Practical Examples of Load Factor Calculation
Below are examples of load factor calculations to clarify how the formula applies in different scenarios:
Example 1: Commercial Building
A commercial building has:
- Peak Load: 1,200 kW
- Average Load: 750 kW
Load Factor Calculation:
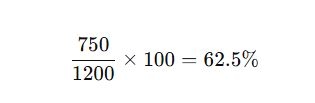
This relatively low load factor suggests opportunities to reduce peak load or spread out energy consumption.
Example 2: Residential Building
A residential building has:
- Peak Load: 15 kW
- Average Load: 10 kW
Load Factor Calculation:
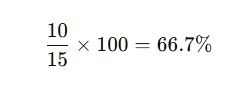
This load factor is moderate, but improvements could reduce energy costs by managing peak demand.
Calculating Electrical Load for Load Factor
Accurate load calculation electrical helps in determining both the peak and average loads, essential for calculating the load factor. Here’s how to perform these calculations:
Step 1: List All Appliances
Use an electric load calculator or a worksheet to identify all appliances in the system and their wattage.
Step 2: Record Operating Hours
Estimate the number of hours each appliance runs daily, then calculate the total load.
Step 3: Calculate Total Load and Peak Load
Use an electrical panel load calculation to sum the individual loads. Peak load often corresponds to times of highest consumption, so analyze usage patterns.
Useful Tips for Load Calculations
- Understand Demand Charges: Demand charges are often based on peak loads, so reducing peak load impacts your energy costs.
- Use an Electrical Load Calculation Table: This table lists common appliances and their power requirements, making it easy to estimate total load.
- Incorporate Voltage Drop Considerations: Especially for large systems, consider using a voltage drop calculator to assess efficiency over long distances.
Load Factor vs. Power Factor
While both terms relate to electrical efficiency, load factor is not the same as power factor. Power factor measures the phase difference between voltage and current, while load factor assesses consumption over time relative to peak demand. Improving load factor can indirectly help reduce costs and improve overall power quality.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Load Factor
- Ignoring Peak Load: Forgetting to account for peak load can distort the load factor.
- Using Monthly Data Incorrectly: Ensure that both average and peak loads are for the same period, such as a day, month, or year.
- Omitting Standby Power: Consider all active and standby appliances, as standby loads can affect the average load.
Benefits of Maintaining a High Load Factor
- Cost Savings: A higher load factor typically reduces peak demand charges.
- Energy Efficiency: Systems with a high load factor are generally more efficient.
- Better Equipment Life: Consistent usage extends the life of electrical equipment by minimizing stress from peak loads.
Final Thoughts on Electrical Load Factor Calculation
Understanding how to calculate load factor in electrical systems is crucial for energy management. By using tools such as an electrical load calculator and incorporating systematic methods for load calculation electrical, you can optimize energy use, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency of your systems.
Regularly assessing your load factor and taking steps to improve it can lead to long-term savings and more efficient energy consumption, benefiting both your financial bottom line and the environment. Whether for a small residential setup or a large industrial facility, load factor calculation is an invaluable step in managing electrical loads effectively.
Follow us on LinkedIn, “Electrical Insights,” to get the latest updates on electrical engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
#ElectricalEngineering, #LoadFactor, #PowerSystem, #EnergyEfficiency, #ElectricalLoadCalculation, #LoadFactorFormula, #ElectricalSystemDesign, #EnergyManagement, #ElectricalCalculations, #PowerQuality, #LoadFactorGuide, #EfficiencyInPower, #EnergyConservation, #IndustrialElectricity, #TechInEngineering