Components of HVDC Transmission System: Best Guide
The components of HVDC transmission system form the backbone of modern long-distance and bulk power transfer projects. High Voltage Direct Current technology is widely used where conventional AC transmission becomes inefficient or impractical. From interconnecting asynchronous grids to transmitting power over long submarine cables, HVDC systems rely on several well-engineered components working together as a single unit. Understanding these components is essential for electrical engineers, power planners, and students dealing with modern power systems.
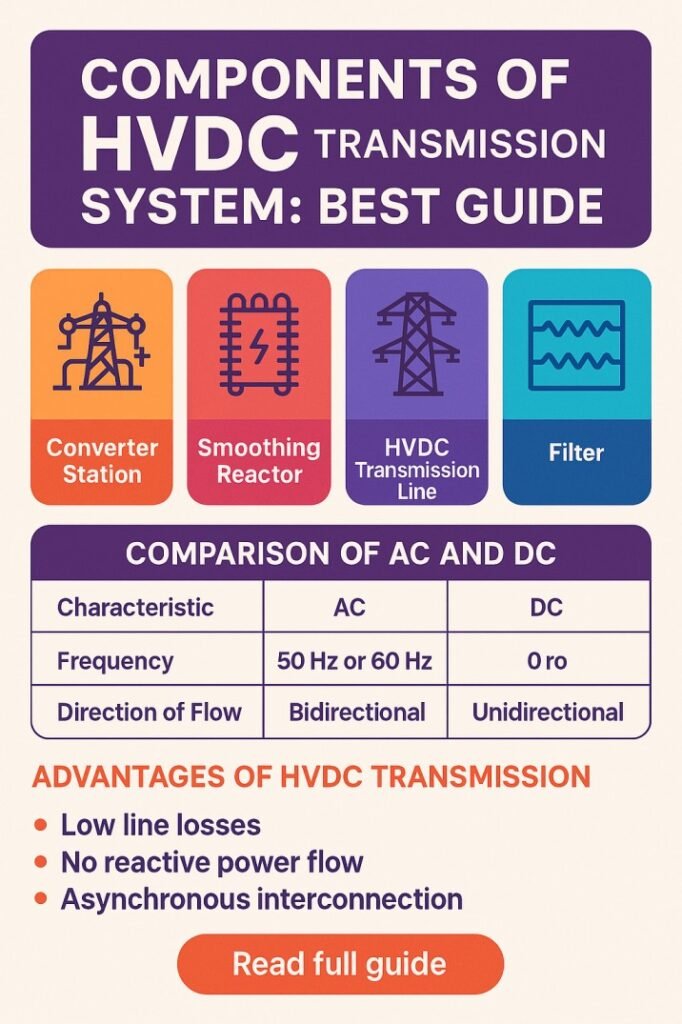
Table of Contents
This article explains the components of HVDC transmission system in a practical and easy-to-understand manner, focusing on their functions, importance, and interaction within the system.
Overview of HVDC Transmission
HVDC transmission uses direct current instead of alternating current to transfer electrical energy over long distances. The system converts AC power to DC at the sending end and then converts it back to AC at the receiving end. This approach reduces transmission losses, improves system stability, and allows precise control of power flow. The components of HVDC transmission system are designed to support these advantages while maintaining reliability and safety.
Know more about HVDC Transmission Explained: Key Components, Working & Real-World Applications
Converter Stations
Converter stations are the most critical components of HVDC transmission system. They perform the conversion between AC and DC power. Each HVDC link has at least two converter stations: one acting as a rectifier and the other as an inverter.
Main functions of converter stations include:
- Conversion of AC to DC and DC to AC
- Control of power flow and direction
- Voltage regulation and system protection
Modern HVDC systems use either line-commutated converters based on thyristors or voltage source converters using IGBTs. Both technologies are key elements within the components of HVDC transmission system, depending on application requirements.
Converter Valves
Converter valves are the heart of the converter station. They control the conduction of current and determine the quality of power conversion. In classic HVDC systems, thyristor valves are used, while newer systems rely on insulated gate bipolar transistors.
Key characteristics of converter valves:
- High voltage and current handling capability
- Precise switching control
- Efficient heat dissipation
Among the components of HVDC transmission system, converter valves directly influence system efficiency and harmonic performance.
Know more about 7 Important HVDC Operating Modes
Converter Transformers
Converter transformers adapt the AC system voltage to the level required by the converter valves. They also provide electrical isolation between the AC network and the DC system.
Important roles of converter transformers include:
- Voltage matching
- Isolation for safety
- Reduction of harmonic interaction with the AC grid
These transformers are custom-designed and represent one of the largest and most expensive components of HVDC transmission system.
Smoothing Reactors
Smoothing reactors are connected in series with the DC line. Their main purpose is to reduce current ripple and limit fault currents in the DC circuit.
Functions of smoothing reactors:
- Reduction of DC current harmonics
- Limitation of fault current rise
- Improvement of system stability
Know more about HVDC Converter Efficiency: 3 Important Formulas
Without smoothing reactors, the performance of other components of HVDC transmission system would be compromised, especially during disturbances.
DC Transmission Lines and Cables
DC transmission lines or cables carry power between converter stations. Overhead lines are common for land-based links, while submarine or underground cables are used for underwater or urban applications.
Key features of DC transmission paths:
- Lower losses compared to AC for long distances
- No reactive power issues
- Simpler line insulation requirements
These elements are among the most visible components of HVDC transmission system and play a major role in project feasibility.
Harmonic Filters
Harmonic filters are installed on both AC and DC sides of the converter station. They eliminate unwanted harmonics generated during the conversion process.
Main purposes of harmonic filters:
- Reduction of voltage and current distortion
- Compliance with grid codes
- Protection of nearby equipment
Harmonic filters also provide reactive power support, making them multifunctional components of HVDC transmission system.
Know more about HVDC Converter: Best Guide to HVDC Transmission System
Reactive Power Compensation Equipment
HVDC converter stations consume reactive power, especially in line-commutated systems. To maintain voltage stability, reactive power compensation equipment is installed.
Common compensation devices include:
- Shunt capacitor banks
- Synchronous condensers
- Static VAR compensators
These devices support the overall performance of the components of HVDC transmission system by maintaining acceptable voltage levels.
Control and Protection Systems
Control and protection systems coordinate the operation of all HVDC components. They ensure stable power transfer and protect equipment during abnormal conditions.
Key responsibilities include:
- Power flow control
- Fault detection and isolation
- Coordination between rectifier and inverter stations
Advanced digital control systems have become essential components of HVDC transmission system due to the complexity of modern power networks.
Know more about Types of Transmission Lines Explained: Overhead vs Underground with Important Applications
Grounding Electrodes
Grounding electrodes provide a return path for current in monopolar or ground-return HVDC systems. They are located away from converter stations to minimize environmental and corrosion effects.
Functions of grounding electrodes:
- Safe dissipation of ground current
- Reduction of step and touch potentials
- Protection of nearby infrastructure
Although often overlooked, grounding electrodes remain important components of HVDC transmission system.
Summary Table of Major Components
| Component | Primary Function | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Converter Station | AC-DC and DC-AC conversion | Sending and receiving ends |
| Converter Valves | Current control and switching | Inside converter station |
| Converter Transformers | Voltage adaptation and isolation | AC side of converter |
| Smoothing Reactors | Ripple reduction and fault limitation | DC side |
| DC Lines/Cables | Power transmission | Between stations |
| Harmonic Filters | Harmonic suppression | AC and DC sides |
| Control Systems | Monitoring and protection | Centralized and local |
| Grounding Electrodes | Ground current return | Remote from stations |
Know more about Types of Transmission Line Conductors Explained: Best Guide for Power Engineers
Importance of Integrated Design
The effectiveness of the components of HVDC transmission system depends on their proper coordination. A failure or poor design of one component can affect the entire link. Engineers must consider electrical performance, thermal limits, insulation coordination, and environmental factors during system design.
Conclusion
The components of HVDC transmission system work together to deliver efficient, stable, and controllable power transmission over long distances. From converter stations and valves to control systems and grounding electrodes, each element plays a distinct role. As global power demand grows and renewable energy integration increases, HVDC technology will continue to expand. A clear understanding of these components is essential for anyone involved in modern power system planning, operation, or education.
Know more about types of faults in transmission lines
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#HVDCTransmission, #HVDCComponents, #PowerTransmission, #ElectricalEngineering, #HighVoltageDC, #EnergySystems, #GridTechnology, #RenewableEnergy, #SmartGrid, #ElectricalPower


