Wire Gauge Amperage Chart – Find the Safe Current Limit for Every Wire Size
Choosing the correct wire size is one of the most important steps in any electrical installation. A small mistake can lead to overheating, voltage drop, equipment damage, or even fire hazards. That is why a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart is considered a basic but critical reference for electricians, engineers, and DIY users alike. This guide explains how wire gauge relates to current capacity, how to read amperage charts correctly, and how to apply them in real-world electrical systems.
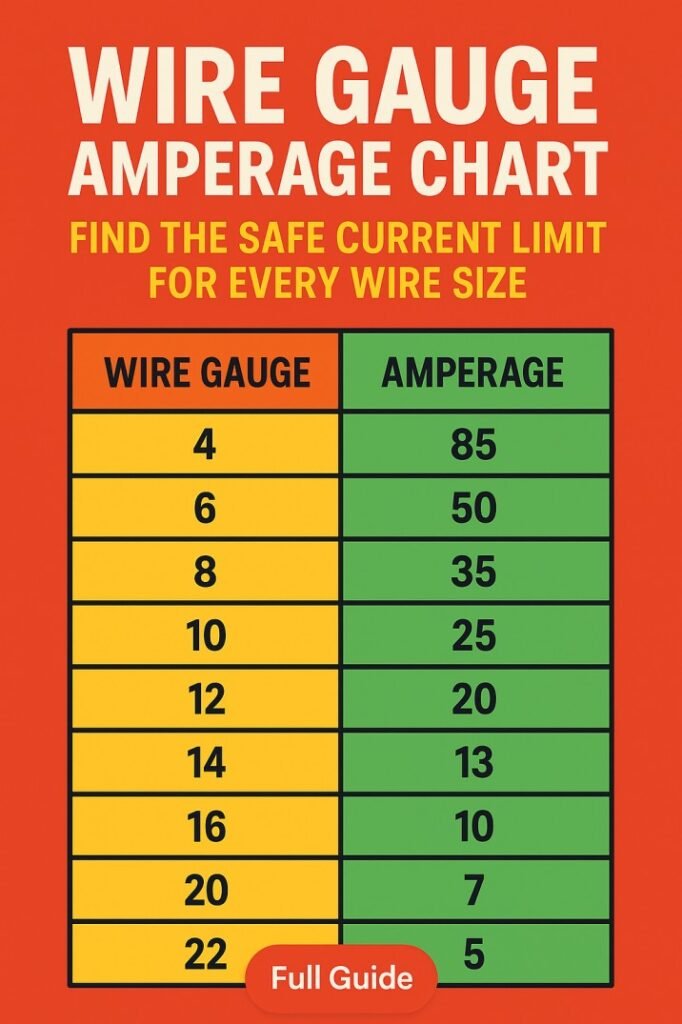
Table of Contents
Understanding these limits not only improves safety but also helps you design efficient circuits that meet code requirements and perform reliably over time.
What Is a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart
A wire gauge amperage chart shows the maximum current a wire can safely carry without exceeding its temperature rating. It is based on the American Wire Gauge system, commonly known as AWG, which standardizes wire sizes in North America and many other regions.
The Wire Gauge Amperage Chart connects three key factors:
- Wire size or gauge number
- Maximum allowable current in amperes
- Conductor material and insulation type
As the gauge number decreases, the wire becomes thicker and can carry more current. For example, a 10 AWG wire carries significantly more current than a 14 AWG wire.
Use our online tool for free Wire Size Calculator for Motors – Accurate Motor Cable Sizing Tool for Electric Loads
Why Wire Size and Amperage Matter
Electrical current flowing through a wire generates heat. If the wire is too thin for the load, the heat cannot dissipate properly. Over time, this can damage insulation and create serious safety risks.
Using a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart helps you:
- Prevent overheating and insulation failure
- Reduce voltage drop across long cable runs
- Comply with electrical codes and standards
- Extend the life of electrical equipment
Correct wire sizing is not only about safety but also about efficiency and long-term reliability.
Access our powerful online calculator now Electrical Diversity Calculator for accurate Load Estimation and efficient electrical Design.
Standard Wire Gauge Amperage Chart for Copper Conductors
The table below shows typical safe current limits for copper wires with common insulation ratings. These values are widely used for residential and light commercial installations.
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Max Amperage (60°C) | Max Amperage (75°C) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 AWG | 7 A | 10 A | Low-voltage circuits, controls |
| 16 AWG | 10 A | 13 A | Extension cords, lighting |
| 14 AWG | 15 A | 20 A | Residential outlets, lighting |
| 12 AWG | 20 A | 25 A | Kitchen circuits, appliances |
| 10 AWG | 30 A | 35 A | Water heaters, AC units |
| 8 AWG | 40 A | 50 A | Subpanels, large motors |
| 6 AWG | 55 A | 65 A | Feeders, heavy equipment |
| 4 AWG | 70 A | 85 A | Service conductors |
This Wire Gauge Amperage Chart assumes copper conductors installed under normal conditions. Always check local electrical codes for exact limits.
Aluminum Wire Amperage Comparison
Aluminum wires are lighter and less expensive than copper, but they have lower current-carrying capacity. This means you usually need a larger gauge to carry the same load.
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Max Amperage Aluminum | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 12 AWG | 15 A | Light branch circuits |
| 10 AWG | 25 A | Small appliances |
| 8 AWG | 35 A | Feeders |
| 6 AWG | 40 A | Service connections |
When using aluminum conductors, always refer to a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart specific to aluminum to avoid undersizing.
Factors That Affect Amperage Rating
Amperage values are not fixed in every situation. Several factors can change how much current a wire can safely handle.
- Insulation temperature rating
- Ambient temperature
- Installation method such as conduit or open air
- Number of current-carrying conductors
For example, wires bundled together in a conduit may need to be derated. A reliable Wire Gauge Amperage Chart often includes correction factors to account for these conditions.
Make your task simple with our online tool electrical cable size calculator
Understanding Voltage Drop and Wire Length
Even if a wire meets the amperage requirement, excessive length can cause voltage drop. This results in reduced performance and wasted energy.
General guidelines include:
- Keep voltage drop below 3 percent for branch circuits
- Increase wire size for long cable runs
- Use charts that combine amperage and distance
Many professionals consult a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart alongside a voltage drop chart to ensure optimal performance.
Common Residential Wiring Examples
Using the correct wire size is especially important in homes, where overloaded circuits are a leading cause of electrical fires.
Typical residential examples include:
- 14 AWG for 15-amp lighting circuits
- 12 AWG for 20-amp kitchen and bathroom circuits
- 10 AWG for 30-amp appliances like dryers
In each case, the Wire Gauge Amperage Chart ensures that the wire matches the breaker rating and expected load.
Explore our professional online tool for quick calculations kw to cable size calculator
Industrial and Commercial Applications
In industrial settings, wire sizing becomes even more critical due to higher currents and continuous loads.
Common considerations include:
- Motor starting current
- Continuous operation at high load
- Higher ambient temperatures
Industrial electricians rely heavily on a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart combined with code tables to select conductors that can handle demanding conditions.
How to Use a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart Correctly
To apply a chart effectively, follow a simple process.
- Identify the load current in amperes
- Determine conductor material and insulation rating
- Check installation conditions
- Select the appropriate wire gauge
This systematic approach ensures that the Wire Gauge Amperage Chart is used accurately and safely.
Use our online tool 3 phase cable size calculator
Safety Tips When Selecting Wire Size
Even with charts available, good judgment is essential.
- Never exceed the rated amperage of a wire
- Match wire size with circuit breaker rating
- Avoid mixing aluminum and copper without proper connectors
- Consult local electrical codes when in doubt
Using a Wire Gauge Amperage Chart is a strong foundation, but safety always comes first.
Final Thoughts
A properly sized wire is the backbone of any safe electrical system. The Wire Gauge Amperage Chart provides a clear and reliable way to match wire size with current demand, reducing risks and improving performance. Whether you are wiring a home circuit, designing an industrial panel, or troubleshooting an existing installation, understanding amperage limits is essential.
By applying the principles explained here and referring to accurate charts, you can ensure safe, efficient, and code-compliant electrical work that stands the test of time.
Access our powerful online calculator now star delta motor cable size calculator
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#WireGaugeAmperageChart, #WireSizeAmpChart, #ElectricalWireGauge, #AmperageCapacity, #AWGChart, #ElectricalSafety, #PowerWiring, #VoltageDrop, #CableSizing, #ElectricianGuide






