Transformer Bond Sizing: Expert Guide for Safe and Efficient Electrical Systems
Transformer bond sizing is a critical aspect of electrical system design that ensures safety, reliability, and efficient operation of power distribution networks. Improper sizing can lead to hazardous conditions such as electrical faults, equipment damage, or even fire. For engineers, electricians, and technicians, understanding transformer bond sizing is essential to maintain compliance with electrical codes and achieve optimal performance. This guide explores the principles, standards, and practical considerations for accurately sizing transformer bonds.
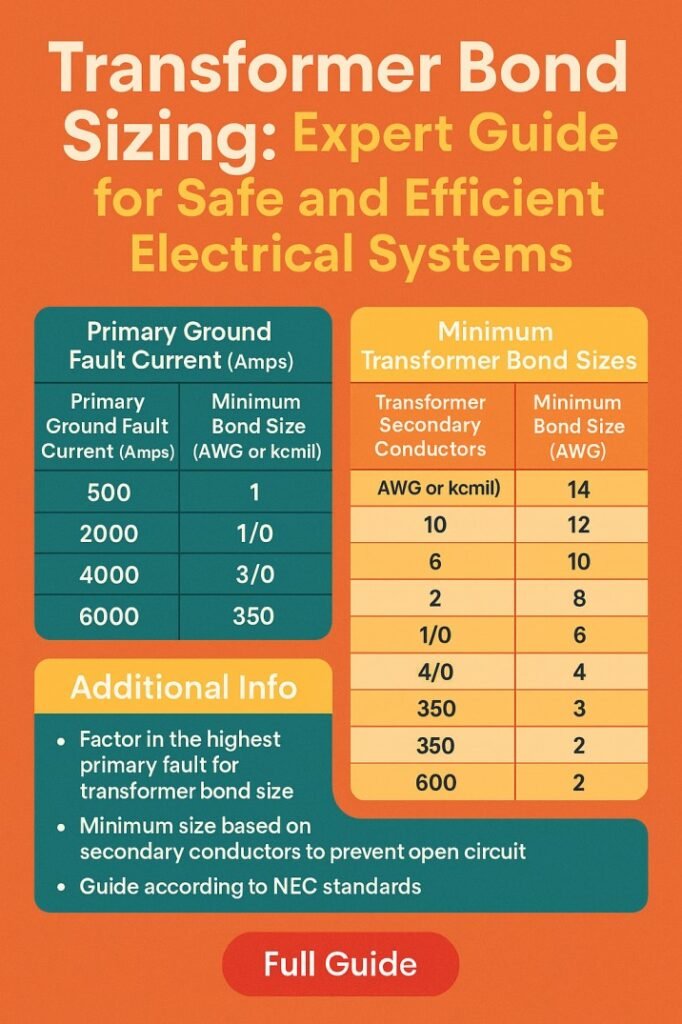
Table of Contents
What is a Transformer Bond?
A transformer bond, also known as a grounding or earthing bond, is the connection between the transformer’s metallic enclosure and the main grounding system of a facility.
The primary purpose of this bond is to provide a low-resistance path for fault currents to safely dissipate into the earth. This helps protect both personnel and equipment in case of short circuits or lightning strikes. Proper transformer bond sizing ensures the bond can carry fault currents without overheating or causing excessive voltage rise.
Start using our online tool today — it’s free Transformer Short Circuit Calculator – Accurate Fault Current & Transformer Protection Tool
Importance of Accurate Transformer Bond Sizing
Correct transformer bond sizing is vital for several reasons. First, it reduces the risk of electrical shock by maintaining a low impedance path to ground. Second, it minimizes the potential for equipment damage during fault conditions. Third, it ensures compliance with national and international electrical standards, such as the NEC (National Electrical Code), IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission). Finally, a correctly sized bond contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the electrical system.
Factors Affecting Transformer Bond Sizing
Several factors influence the sizing of a transformer bond. Understanding these factors helps engineers select the appropriate conductor size and type. Key considerations include:
- Transformer Rating: Larger transformers require heavier bonds to handle higher fault currents.
- Fault Current Levels: The maximum expected short-circuit current at the transformer location determines the minimum bond size.
- Bond Length: Longer bond conductors may need increased size to reduce impedance and voltage drop.
- Material Type: Copper and aluminum are commonly used; copper is preferred for its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance.
- Installation Environment: Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures may necessitate protective measures or increased bond sizing.
Test our online tool for free Transformer Full Load Current Calculator – Accurate Load & Current Calculation Tool for Transformers
Standards and Codes for Transformer Bond Sizing
Compliance with electrical standards ensures safety and uniformity in transformer installations. Some widely referenced standards include:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| NEC (National Electrical Code) | Provides guidelines for grounding and bonding conductors in the U.S. |
| IEEE Std 142 | Recommends grounding and bonding practices for industrial and commercial systems. |
| IEC 60364 | International standard for electrical installations, including bonding requirements. |
| BS 7671 | UK Wiring Regulations covering bonding and earthing of electrical systems. |
These standards specify minimum conductor sizes, fault current capacities, and installation requirements, serving as a reference for engineers during design and construction.
Use our online tool without paying anything Transformer Impedance Calculation Tool – Accurate Transformer Impedance Calculator for Engineers
Calculating Transformer Bond Size
Calculating transformer bond size involves determining the appropriate conductor size to safely carry the maximum fault current. The general approach includes:
- Determine Maximum Fault Current: Obtain the transformer’s rated short-circuit current from manufacturer data or system studies.
- Select Conductor Material: Copper is preferred; aluminum can be used with appropriate derating.
- Determine Bond Conductor Size: Refer to NEC or IEEE tables that correlate fault current and bond conductor size.
- Check Temperature Rise: Ensure the conductor can withstand thermal effects during fault without insulation damage.
- Consider Bonding Path Length: Longer paths may require upsizing to reduce voltage drop and impedance.
Use our tool online at no cost Transformer Losses Calculation Tool – Accurate & Easy Energy Loss Analysis
A simplified example using NEC guidelines:
| Transformer Rating (kVA) | Max Fault Current (kA) | Minimum Copper Bond Size (AWG) |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | 10 | 6 AWG |
| 150 | 15 | 4 AWG |
| 300 | 25 | 2 AWG |
| 500 | 35 | 1/0 AWG |
| 1000 | 50 | 2/0 AWG |
These values are approximate. Engineers should always verify with local codes and actual system calculations.
Find all about Transformer Disconnect Sizing
Practical Tips for Transformer Bonding
Proper installation and maintenance are as important as sizing. Follow these tips to ensure safety and efficiency:
- Use Continuous Conductors: Avoid splices where possible, as joints increase resistance and reduce effectiveness.
- Mechanical Protection: Protect bond conductors from physical damage using conduit or cable trays.
- Periodic Inspection: Check for corrosion, loose connections, or thermal damage during routine maintenance.
- Parallel Bonds: In large installations, parallel bonding conductors can reduce impedance and improve fault current dissipation.
- Document Bond Paths: Maintain clear diagrams showing all bonding points for maintenance and safety audits.
Common Mistakes in Transformer Bond Sizing
Many installations fail due to avoidable mistakes. Awareness of these pitfalls helps engineers design safer systems:
Know more about Transformers Earthspark Size Chart
- Undersized Bonds: Leads to overheating and insufficient fault current carrying capacity.
- Improper Material Selection: Using aluminum without accounting for corrosion or mechanical stress.
- Excessive Lengths: Long conductor runs without upsizing increase impedance and reduce safety.
- Neglecting Standards: Ignoring NEC, IEEE, or IEC recommendations can result in unsafe installations and legal non-compliance.
Advanced Considerations
For complex or high-power systems, additional factors may affect transformer bond sizing:
- Multiple Transformers: Parallel transformers may require coordinated bonding to prevent circulating currents.
- Grounding Electrode Systems: The overall grounding network impacts bond sizing to maintain low system impedance.
- Transient Events: Lightning or switching surges may necessitate oversized bonds or surge protection devices.
- Harmonics: Non-linear loads can produce harmonic currents, affecting bond conductor heating.
Know all about Transformer Sizing for EV Charger
Benefits of Correct Transformer Bond Sizing
Investing time in proper transformer bond sizing delivers long-term benefits:
- Enhances personnel safety by reducing touch potential.
- Protects equipment from fault-related damage.
- Improves system reliability and continuity of power.
- Reduces maintenance costs by preventing thermal or mechanical failures.
- Ensures regulatory compliance, avoiding fines or legal liability.
Summary
Transformer bond sizing is a fundamental aspect of electrical design that ensures safe, reliable, and efficient operation of power systems. By considering transformer rating, fault current, conductor material, and compliance with codes such as NEC, IEEE, and IEC, engineers can select the correct bond size.
Find more Transformer calculators here
Proper installation practices, regular inspection, and awareness of potential pitfalls further enhance system safety and performance. Accurate transformer bond sizing is not just a technical requirement; it is a proactive measure to protect lives, equipment, and investments in electrical infrastructure. Find more Electrical Engineering Tools for easy electrical calculations and estimations.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#TransformerBondSizing, #ElectricalEngineering, #PowerSystems, #TransformerSafety, #ElectricalDesign, #IndustrialPower, #BondingCalculations, #ElectricalStandards, #PowerDistribution, #EngineeringGuides


