Load Factor Calculation in Electricity Bill
Electricity bills often surprise people with fluctuating costs even when their usage seems the same. One key reason behind this variation is something most people overlook — the load factor. Understanding load factor calculation in electricity bill helps you identify inefficiencies and reduce power costs. Let’s explore this concept in detail with clear examples and practical insights.
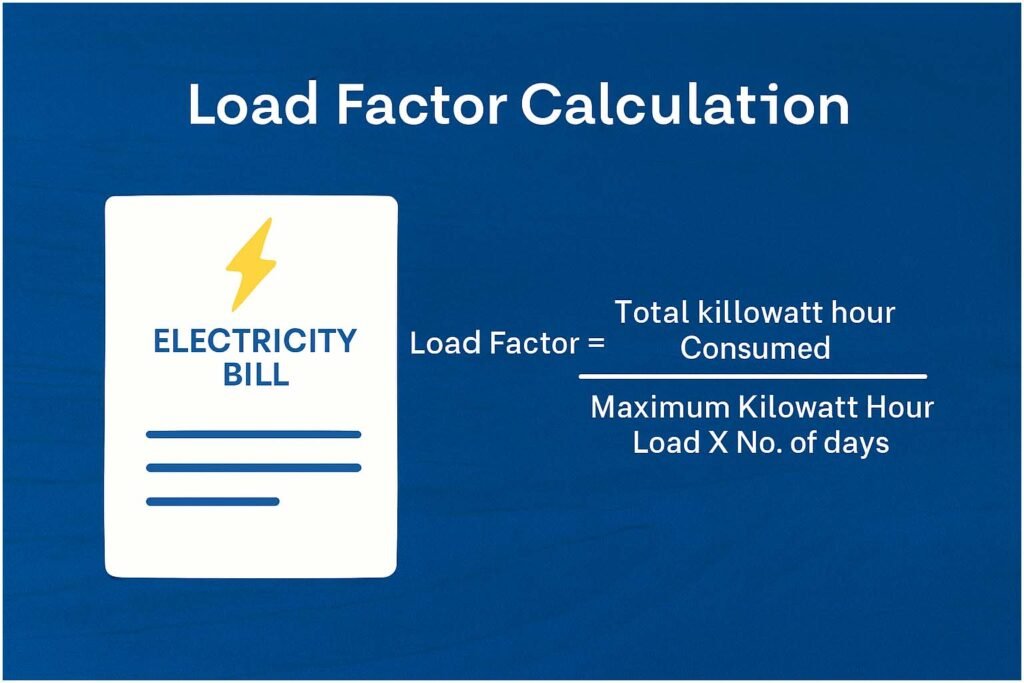
Table of Contents
What is Load Factor in Electricity Bill?
The load factor is a measure of how efficiently you use electricity over a specific period. It shows how consistently electrical power is consumed compared to the maximum power demand. In simple terms, it tells you whether your electricity usage is smooth or uneven.
If your energy usage remains steady throughout the day, your load factor will be high. If your usage fluctuates — heavy during certain hours and low at others — your load factor will be low.
A higher load factor means better utilization of electrical power and a lower cost per unit. A lower load factor means you are using electricity inefficiently and might be paying more in demand charges.
Importance of Load Factor Calculation in Electricity Bill
The load factor calculation in electricity bill is crucial for both residential and industrial users. Utilities often use it to determine demand charges. A poor load factor means that even if your total energy consumption is not high, your maximum demand during peak hours can increase your bill significantly.
Understanding and improving load factor helps in:
- Reducing peak demand charges
- Improving system efficiency
- Lowering overall electricity bills
- Planning energy usage more effectively
In commercial and industrial facilities, utilities reward users who maintain a high load factor because it helps stabilize the power grid.
Know more about Capacity Factor vs Load Factor – Key Differences, Formula, and Examples Explained
Formula for Load Factor Calculation in Electricity Bill
The formula for calculating load factor is:
Load Factor = (Total Energy Consumed in kWh) ÷ (Maximum Demand in kW × Number of Hours in Period)
This formula gives a ratio that can be expressed either as a decimal or percentage. The closer it is to 1 or 100%, the more efficient your power usage is.
Example 1: Basic Load Factor Calculation
Let’s say a factory consumed 36,000 kWh of energy in one month. The maximum demand recorded was 100 kW, and the month has 30 days.
Number of hours = 30 × 24 = 720 hours
Now,
Load Factor = (36,000) ÷ (100 × 720)
Load Factor = 36,000 ÷ 72,000
Load Factor = 0.5 or 50%
This means the factory utilized only half of its available capacity.
Example 2: Higher Load Factor Scenario
If another factory consumed 54,000 kWh with the same maximum demand of 100 kW, the load factor would be:
Load Factor = (54,000) ÷ (100 × 720)
Load Factor = 54,000 ÷ 72,000
Load Factor = 0.75 or 75%
This indicates better energy utilization and more stable demand, which usually results in a lower average cost per unit of electricity.
Use our online tool DC Circuit Breaker Sizing Calculator – Accurate Tool for DC Load Protection
Understanding the Components of Load Factor
To understand load factor calculation in electricity bill, you need to know three important components:
- Total Energy Consumption (kWh) – This is the total amount of energy used over a billing period.
- Maximum Demand (kW) – The highest rate of electricity usage recorded during that period.
- Time Period (hours) – The total number of hours in the billing cycle, usually a month or a year.
Example Table: Load Factor Comparison
| Parameter | Consumer A | Consumer B |
|---|---|---|
| Total Energy (kWh) | 36,000 | 54,000 |
| Maximum Demand (kW) | 100 | 100 |
| Time Period (hours) | 720 | 720 |
| Load Factor | 50% | 75% |
The above table shows that Consumer B uses electricity more evenly, resulting in a higher load factor and lower cost per unit.
How Load Factor Affects Electricity Bill
Utility companies design tariff structures based on both energy consumption and demand. Demand charges are applied based on your maximum demand, while energy charges depend on your total consumption.
When your load factor is low, it means you have a high peak demand but low overall usage. The result is a higher demand charge, which increases the total bill.
Example: Impact of Load Factor on Bill
| Description | Factory X | Factory Y |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumed (kWh) | 36,000 | 54,000 |
| Maximum Demand (kW) | 100 | 100 |
| Load Factor | 50% | 75% |
| Demand Charge (Rs. 400/kW) | Rs. 40,000 | Rs. 40,000 |
| Energy Charge (Rs. 15/kWh) | Rs. 540,000 | Rs. 810,000 |
| Total Bill | Rs. 580,000 | Rs. 850,000 |
| Cost per Unit (Rs./kWh) | 16.1 | 15.7 |
Even though Factory Y used more energy, its cost per unit is lower due to better utilization and a higher load factor.
Use our online tool Street Light Voltage Drop Calculator – Accurate Cable Sizing & Power Loss Estimation Tool
Factors That Influence Load Factor
Several factors affect the load factor calculation in electricity bill, including:
- Operating hours: More consistent operation leads to a higher load factor.
- Equipment usage: Running heavy machinery during peak hours reduces load factor.
- Shift patterns: Spreading work evenly throughout the day improves utilization.
- Demand management: Using demand controllers or scheduling can reduce peaks.
Industrial users can monitor their load profiles using smart meters and adjust operations to balance their loads more efficiently.
How to Improve Load Factor
Improving your load factor means using electricity more uniformly over time. Here are some effective ways:
- Distribute loads evenly: Avoid running all high-power equipment simultaneously.
- Shift operations: Move certain activities to off-peak hours.
- Install energy management systems: Use automatic controllers to manage peak loads.
- Maintain equipment: Efficient machines consume power evenly, improving load factor.
- Use capacitor banks: These reduce reactive power, improving power factor and overall efficiency.
Example of Improvement
If a manufacturing unit currently has a load factor of 40% and takes measures to spread operations over the entire day, it could raise its load factor to 70%. This improvement can lead to 10–15% savings in electricity bills.
Benefits of High Load Factor
A high load factor not only reduces the cost per unit of energy but also improves overall system reliability. Key benefits include:
- Reduced demand charges from utilities
- More stable power consumption patterns
- Better utilization of electrical infrastructure
- Lower strain on transformers and cables
- Potential eligibility for rebates or incentives from the utility company
For industrial plants, maintaining a high load factor is part of energy management strategies aimed at long-term cost savings.
Use our online tool Fault Loop Impedance Calculator Australia – Accurate Electrical Testing Tool
Common Mistakes in Load Factor Calculation
While performing load factor calculation in electricity bill, many people make simple errors that lead to incorrect results:
- Using average demand instead of maximum demand
- Not converting units properly (kWh vs kW)
- Ignoring the total number of hours in the billing period
- Failing to use consistent time frames for energy and demand readings
Accurate calculation ensures you get the right insights to optimize your power usage.
Real-Life Example of Load Factor in Industrial Setting
Consider an industrial plant that has a connected load of 200 kW. Over a month, it consumes 90,000 kWh. The highest demand recorded is 180 kW.
Number of hours = 30 × 24 = 720 hours
Load Factor = (90,000) ÷ (180 × 720)
Load Factor = 90,000 ÷ 129,600
Load Factor = 0.694 or 69.4%
If the company manages to distribute its operations evenly and reduce its peak demand to 150 kW without reducing production, then:
Load Factor = (90,000) ÷ (150 × 720)
Load Factor = 90,000 ÷ 108,000
Load Factor = 0.833 or 83.3%
This simple operational adjustment improves efficiency and reduces demand charges significantly.
Use our online tool Transformer Sizing Chart Calculator – Calculate the Right Transformer Size for Your Load
Conclusion
Understanding load factor calculation in electricity bill is essential for controlling electricity costs and improving energy efficiency. It reflects how effectively you are using your electrical capacity and helps you identify ways to reduce wasteful peaks.
By monitoring consumption, managing demand, and spreading loads evenly, both industrial and commercial users can maintain a high load factor. A higher load factor leads to stable power usage, reduced demand charges, and long-term savings on electricity bills.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#LoadFactor, #ElectricityBill, #EnergyEfficiency, #PowerConsumption, #LoadFactorCalculation, #ElectricalEngineering, #EnergyManagement, #SmartEnergy, #IndustrialElectricity, #PowerFactor, #ElectricitySavings, #EnergyAudit, #ElectricLoad, #UtilityBills, #ElectricityUsage






