Electrical Switchgear Components: Complete Guide to Types, Functions, and Industrial Applications
Electrical switchgear components form the backbone of every safe and reliable power distribution system. From a small commercial facility to a large industrial plant, properly selected and maintained electrical switchgear components ensure protection, control, and isolation of electrical equipment. Without them, electrical faults would cause severe damage, extended downtime, and serious safety hazards.

Table of Contents
In this complete guide, we will explore electrical switchgear components in detail, including their types, working principles, practical functions, and industrial applications. Whether you are an electrical engineer, technician, student, or plant manager, this guide will help you understand how these critical elements operate inside modern power systems.
What Are Electrical Switchgear Components?
Electrical switchgear components are devices used to control, protect, and isolate electrical circuits and equipment. They are installed in power systems to manage voltage levels ranging from low voltage (LV) to medium voltage (MV) and high voltage (HV).
In simple terms, electrical switchgear components detect abnormal conditions such as short circuits, overloads, and earth faults. Once detected, they disconnect the faulty section to protect transformers, motors, generators, cables, and other connected loads.
Switchgear assemblies are typically installed in substations, manufacturing plants, renewable energy facilities, commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects. Their main objective is operational safety and system reliability.
Use our online tool for free Sub Panel Wire Size Calculator – Accurate Wire Gauge & Load Sizing Tool
Core Functions of Electrical Switchgear Components
Electrical switchgear components perform three primary functions in power systems. Each function supports stability and safe operation.
1. Protection
Protection is the most critical function. When faults occur, protective devices isolate the affected section immediately. This prevents fire, equipment damage, and system collapse.
Examples include:
- Short circuit protection
- Overcurrent protection
- Earth fault protection
- Differential protection
2. Control
Control devices allow operators to start, stop, and regulate electrical circuits safely. Motor control centers (MCC), control relays, and contactors fall under this category.
3. Isolation
Isolation ensures safe maintenance. Isolators and disconnect switches provide visible breaks in the circuit so technicians can work safely.
Together, these roles make electrical switchgear components essential for system coordination and reliability.
Use our online tool for free Wire Size Calculator for Subpanels and Feeders – NEC Guidelines Included
Main Types of Electrical Switchgear Components
Electrical switchgear components can be categorized based on their function and voltage level. The following table summarizes key components and their primary purpose.
Table 1: Major Electrical Switchgear Components and Their Functions
| Component | Primary Function | Voltage Level | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circuit Breaker | Interrupt fault current | LV, MV, HV | Substations, Plants |
| Isolator | Provide safe isolation | MV, HV | Maintenance safety |
| Fuse | Overcurrent protection | LV, MV | Distribution boards |
| Relay | Fault detection and trip | LV, MV, HV | Protection panels |
| Contactor | Switching control | LV | Motor control |
| Busbar | Power distribution | LV, MV | Switchboards |
| Instrument Transformer | Measurement and protection | MV, HV | Metering systems |
Let us examine these electrical switchgear components in more detail.
Know more about Industrial Control Panel Design Software – Best Tools, Features & Pro Tips for Engineers
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are among the most critical electrical switchgear components. They interrupt fault currents automatically when abnormal conditions are detected.
Types of circuit breakers include:
- Air Circuit Breaker (ACB)
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
- Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB)
- SF6 Circuit Breaker
In low voltage panels, MCCBs and ACBs are common. In medium voltage switchgear, VCBs dominate due to their reliability and low maintenance requirements.
A breaker must interrupt fault current within milliseconds. The breaking capacity is selected based on system fault level calculations.
Use our online tool for free Electrical Panel Upgrade Cost Calculator: Best Tool
Protective Relays
Protective relays are intelligent electrical switchgear components responsible for detecting system faults. They monitor current, voltage, frequency, and impedance.
Modern digital relays offer advanced features such as:
- Overcurrent and earth fault protection
- Differential protection
- Distance protection
- Arc flash detection
- Event recording
Relays work in coordination with circuit breakers. When a fault is detected, the relay sends a trip signal to the breaker.
Isolators and Disconnect Switches
Isolators are mechanical electrical switchgear components used for safe isolation. Unlike breakers, they do not interrupt load current. They operate only when the circuit is already de-energized.
In substations, isolators provide visible isolation. This ensures safety during maintenance activities.
Know more about mcc panel design software
Fuses
Fuses are simple yet effective electrical switchgear components for overcurrent protection. They consist of a metal element that melts when excessive current flows.
Common fuse types include:
- HRC (High Rupturing Capacity) fuse
- Cartridge fuse
- Drop-out fuse
Fuses are widely used in distribution boards, capacitor banks, and transformer protection systems.
Busbars and Conductors
Busbars distribute electrical power inside switchgear panels. They are usually made of copper or aluminum. Proper sizing is essential to handle rated current and temperature rise.
The following table shows typical busbar material comparison.
Table 2: Copper vs Aluminum Busbars
| Property | Copper | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity | Higher | Moderate |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Installation Size | Compact | Larger cross-section |
Selection depends on budget, space, and thermal performance.
Explore everything about electrical control panel design training
Instrument Transformers
Instrument transformers are specialized electrical switchgear components used for measurement and protection.
They include:
- Current Transformer (CT)
- Potential Transformer (PT)
CTs reduce high current to measurable values for relays and meters. PTs step down voltage to safe levels. Accuracy class and burden rating must be selected carefully for precise readings.
Industrial Applications of Electrical Switchgear Components
Electrical switchgear components are used across various industries. Their configuration depends on system voltage, load type, and safety requirements.
1. Manufacturing Plants
In heavy industries such as cement, steel, and chemical plants, switchgear controls large motors and process equipment. Motor control centers use breakers, contactors, and protection relays.
2. Power Generation
Thermal, hydro, and renewable energy plants rely on electrical switchgear components for generator protection and grid synchronization.
Find out the mcc panel design guide pdf in detail here.
3. Oil and Gas Facilities
Hazardous environments demand reliable and explosion-proof switchgear. Proper fault isolation ensures plant safety.
4. Commercial Buildings
Low voltage switchgear distributes power to lighting, HVAC systems, and elevators.
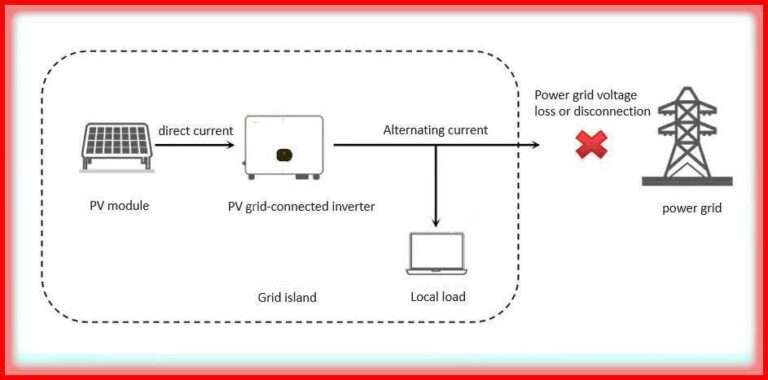
5. Renewable Energy Projects
Solar and wind farms use switchgear for inverter output protection and grid interconnection.
Voltage-Based Classification
Electrical switchgear components are also classified by voltage rating.
Table 3: Switchgear Voltage Classification
| Voltage Level | Range | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Low Voltage (LV) | Up to 1 kV | Buildings, Small industries |
| Medium Voltage (MV) | 1 kV to 36 kV | Industrial plants |
| High Voltage (HV) | Above 36 kV | Transmission systems |
Each level requires different insulation systems and interrupting technologies.
Know more about GIS vs AIS Switchgear: Best Key Differences Every Electrical Engineer Must Know
Selection Criteria for Electrical Switchgear Components
Proper selection of electrical switchgear components depends on technical and environmental factors.
Key considerations include:
- Rated voltage and current
- Short circuit level
- Breaking capacity
- Protection coordination
- Ambient temperature
- IP rating and enclosure type
- Compliance with IEC or ANSI standards
Engineers perform load flow and short circuit studies before finalizing specifications.
Find more about Low Voltage Switchgear vs Medium Voltage Switchgear: Important Differences Every Engineer Must Know
Maintenance of Electrical Switchgear Components
Routine maintenance improves lifespan and reliability. Neglecting maintenance can lead to arc flash incidents or equipment failure.
Best practices include:
- Thermal scanning for hot spots
- Insulation resistance testing
- Contact resistance measurement
- Relay testing and calibration
- Mechanical inspection of breakers
Predictive maintenance using condition monitoring systems is becoming standard in modern facilities.
Safety Considerations
Electrical switchgear components must comply with safety standards. Arc flash hazards are a major concern in switchgear rooms.
Important safety measures:
- Proper earthing and bonding
- Arc-resistant switchgear design
- Use of PPE
- Interlocking systems
- Clear labeling and documentation
Following lockout and tagout procedures ensures worker safety during maintenance.
Find all about Top 15 Medium Voltage Switchgear Manufacturers in UAE: Ultimate Guide for Engineers & Buyers
Future Trends in Switchgear Technology
Technology continues to improve electrical switchgear components. Key advancements include:
- Digital protection relays
- Smart grid integration
- IoT-based condition monitoring
- Gas-insulated switchgear (GIS)
- Environment-friendly insulation alternatives
These innovations improve system reliability and reduce maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Electrical switchgear components play a vital role in modern electrical infrastructure. They protect equipment, ensure operational continuity, and safeguard human life. From circuit breakers and relays to busbars and instrument transformers, each component serves a specific purpose within the power distribution system.
Understanding electrical switchgear components helps engineers design safer and more efficient electrical networks. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance ensure long-term reliability across industrial, commercial, and utility applications.
Know more about Top 15 Electrical Switchgear Companies in UAE | Leading Power Distribution & MV/LV Manufacturers
As industries expand and energy demand increases, the importance of electrical switchgear components will continue to grow. Investing in quality switchgear solutions is not just a technical decision. It is a commitment to safety, efficiency, and operational excellence.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#ElectricalSwitchgearComponents, #SwitchgearDesign, #PowerDistributionSystems, #MediumVoltageSwitchgear, #LowVoltageSwitchgear, #CircuitBreakers, #ProtectionRelays, #ElectricalEngineering, #SubstationEquipment, #IndustrialPowerSystems