Different sizes of earthing conductors: Typical Applications
Different Sizes of Earthing Conductors
The sizes of earthing conductors is critical in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Different sizes of earthing conductors are used across various applications, each tailored to specific requirements based on factors such as fault current levels, installation conditions, and regulatory standards. Here’s an overview of typical applications for different sizes of earthing conductors.
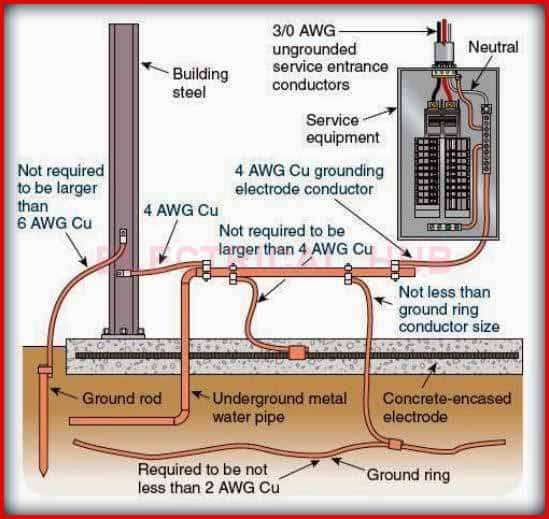
Table of Contents
Typical Applications for Different Sizes of Earthing Conductors
1. Small Residential Installations
- Conductor Size: #10 AWG (approximately 6 mm²) to #8 AWG (approximately 10 mm²)
- Applications:
- Used for grounding small branch circuits in residential settings.
- Suitable for protecting household appliances and lighting circuits.
- Ensures safety against electric shocks and equipment damage.
2. Commercial Buildings
- Conductor Size: 6 mm² to 16 mm² (copper)
- Applications:
- Grounding systems for commercial electrical installations, including offices and retail spaces.
- Provides protection for larger equipment such as HVAC systems and commercial appliances.
- Ensures compliance with local electrical codes, such as NEC or IEC standards.
3. Industrial Facilities
- Conductor Size: 16 mm² to 35 mm² (copper); larger sizes may be required based on fault current calculations.
- Applications:
- Used in factories and manufacturing plants where heavy machinery operates.
- Protects against high fault currents generated by large motors and industrial equipment.
- Essential for maintaining system stability and safety in environments with high electrical loads.
4. High Voltage Installations
- Conductor Size: Typically ranges from 35 mm² to several hundred mm², depending on system requirements.
- Applications:
- Grounding systems for substations, transmission lines, and high-voltage equipment.
- Designed to handle significant fault currents without overheating or causing damage.
- Materials like copper, aluminum, or steel are used based on conductivity and environmental factors [1][2].
5. Telecommunications and Data Centers
- Conductor Size: Generally between 10 mm² to 25 mm² (copper).
- Applications:
- Grounding systems for sensitive electronic equipment in data centers.
- Ensures protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and lightning strikes.
- Provides a reliable path for fault currents to minimize equipment damage.
6. Lightning Protection Systems
- Conductor Size: Varies widely but often requires larger conductors (up to 50 mm² or more) due to the high-energy nature of lightning strikes.
- Applications:
- Grounding conductors used in lightning protection systems for buildings and structures.
- Designed to safely dissipate the energy from lightning strikes into the ground [1][2].
Note: Use our online electrical load calculator for electrical load calculation here. You can also use voltage drop calculator for voltage drop calculation and for cable selection in any single and three phase circuit here. Further explore our online electrical calculators to design your electrical systems in an efficient way.
Summary Table of Different Sizes of Earthing Conductors
| Application Type | Typical Conductor Size | Material Used |
|---|---|---|
| Small Residential Installations | #10 AWG to #8 AWG | Copper |
| Commercial Buildings | 6 mm² to 16 mm² | Copper |
| Industrial Facilities | 16 mm² to 35 mm² | Copper/Aluminum |
| High Voltage Installations | 35 mm² to hundreds of mm² | Copper/Aluminum/Steel |
| Telecommunications/Data Centers | 10 mm² to 25 mm² | Copper |
| Lightning Protection Systems | Up to 50 mm² or more | Copper/Aluminum |
Conclusion
The appropriate size of earthing conductors is determined by the specific application requirements, including the expected fault current levels, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards. Proper sizing is essential for ensuring safety, preventing equipment damage, and maintaining system integrity across various electrical installations. Understanding these applications helps engineers and electricians select the right conductor sizes for their projects.
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
Worth Read Posts
EarthingConductor, #ElectricalSafety, #GroundingSystem, #ElectricalEngineering, #EarthingStandards, #ConductorSize, #GroundingRequirements, #EarthResistance, #EarthingSystem, #ElectricalInstallation, #PowerDistribution, #ElectricalWiring, #ElectricalProtection, #CableSizing, #GroundingConductor




![Best EV Chargers for Hotels & Guest Accommodations [Commercial Grade] 6 Best EV Chargers for Hotels & Guest Accommodations [Commercial Grade]](https://azadtechhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Best-EV-Chargers-for-Hotels-Guest-Accommodations-Commercial-Grade-768x512.jpg)
