Corner Frequency: Understanding Its Role in Signal Processing
What is Corner Frequency?
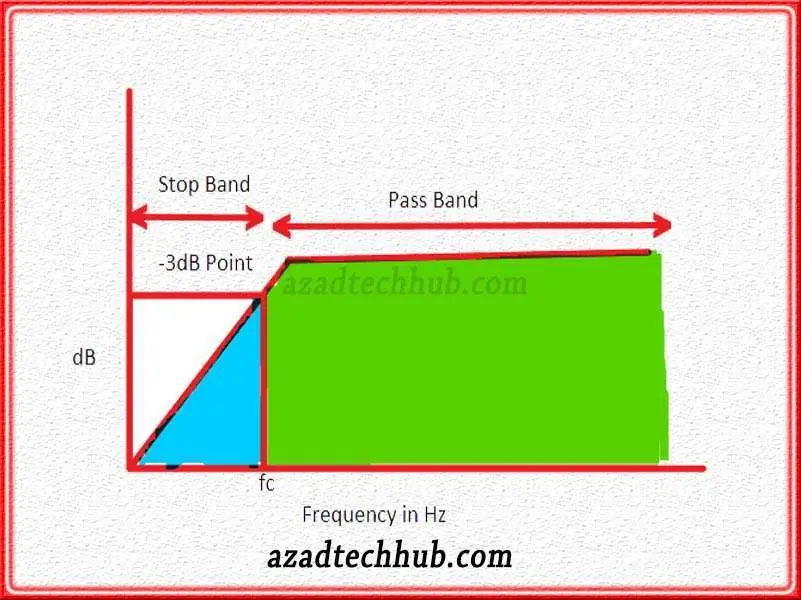
The corner frequency, also known as the cutoff frequency, is the frequency at which the power of a signal is reduced to half its original value. It marks the boundary between the passband (frequencies that are allowed to pass through a filter) and the stopband (frequencies that are attenuated or blocked by the filter).
This frequency is crucial because it determines how effectively a filter can separate or pass different frequency components of a signal.
The corner frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) and is defined for different types of filters:
- Low-pass filter: Frequencies below the corner frequency are allowed to pass, and those above it are attenuated.
- High-pass filter: Frequencies above the corner frequency are passed, and those below it are blocked.
- Band-pass filter: A specific range of frequencies is passed, and others are attenuated, with two corner frequencies defining the bandwidth.
- Band-stop filter: A specific range of frequencies is blocked, with corner frequencies marking the start and end of the stopband.
In technical terms, the corner frequency is the point at which the filter’s frequency response decreases by 3 dB, equivalent to a reduction in power to half its original value.
Importance of Corner Frequency in Signal Processing
The concept of corner frequency plays an integral role in a variety of applications, including:
Filter Design: When designing electronic filters, knowing the corner frequency helps in selecting appropriate components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors to achieve the desired filtering behavior.
Frequency Response Analysis: Corner frequency helps in understanding how a system responds to different frequencies and how efficiently it filters out undesired noise or interference.
Signal Integrity: Maintaining the integrity of signals is critical in communications, audio processing, and instrumentation. Corner frequency ensures that only the desired signal frequencies pass through while attenuating unwanted components.
System Optimization: Corner frequency aids in optimizing system performance, particularly in communication systems where bandwidth and noise rejection are essential.
How to Calculate Corner Frequency
The corner frequency is commonly calculated based on the components of an analog filter circuit, such as resistors and capacitors (RC circuits) or inductors and capacitors (LC circuits). Below are the formulas used for different types of filters:
Low-Pass Filter
For a simple low-pass filter, the corner frequency fc is given by:
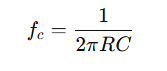
Where:
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
- C is the capacitance in farads (F)
- π\pi is approximately 3.1416
This formula indicates that the corner frequency depends on the values of the resistor and capacitor.
High-Pass Filter
For a high-pass filter, the corner frequency is calculated similarly:
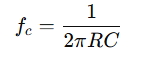
The formula is identical to the low-pass filter, but in the high-pass filter, frequencies above the corner frequency are allowed to pass.
Band-Pass Filter
For a band-pass filter, two corner frequencies fc1 and fc2 define the bandwidth. The center frequency f0 of the band-pass filter is given by:
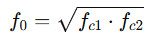
The bandwidth B is:
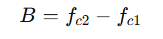
Where:
- fc1 and fc2 are the lower and upper corner frequencies, respectively.
Band-Stop Filter
In a band-stop filter, the corner frequencies also define the bandwidth of the frequency band that is attenuated. The formula for the corner frequency in this case is the same as for the band-pass filter.
Corner Frequency in Practical Applications
Audio Filters
In audio processing, the corner frequency is used to design filters that can modify the frequency content of sound signals. For example, in a high-pass filter used in an audio system, the corner frequency might be set at 80 Hz to remove low-frequency rumble from recordings, ensuring that only higher frequencies are transmitted.
Communication Systems
Communication systems rely heavily on filters to separate different frequency channels. The corner frequency plays a crucial role in ensuring that the transmitted signal lies within the allocated bandwidth, while filtering out any out-of-band noise or interference.
Image Processing
In image processing, corner frequencies are used in various techniques like Fourier transform-based filtering. The corner frequency helps in identifying the edges and boundaries of objects within an image. By setting appropriate corner frequencies, filters can highlight specific features while suppressing unwanted noise.
Control Systems
In control systems, especially in feedback loops, corner frequency is used to design systems that can handle a range of frequencies. The corner frequency ensures that the system operates efficiently within the desired frequency range while avoiding instability caused by higher or lower frequency components.
The Relationship Between Corner Frequency and Filter Response
The relationship between the corner frequency and the filter response is critical for determining how well the filter performs in real-world scenarios. For instance, the roll-off of the filter response is determined by how quickly the filter attenuates frequencies outside the passband. Filters with a lower corner frequency will allow a broader range of frequencies to pass, while those with a higher corner frequency will restrict more of the signal.
Filter Order and Corner Frequency
The order of the filter also influences the behavior of the corner frequency. A higher-order filter has a steeper roll-off around the corner frequency, meaning that it can more sharply differentiate between passing and attenuating frequencies. This is important in applications where precise control over the frequency response is necessary.
Time Domain and Frequency Domain Relationship
In the time domain, filters with a lower corner frequency will allow slower changes in the signal to pass through, while higher corner frequencies are used to filter out faster transients. In the frequency domain, the corner frequency determines the boundaries of the frequency bands that are passed or rejected.
Corner Frequency in Digital Filters
While the above discussion largely focused on analog filters, corner frequency is equally important in digital filters. In digital signal processing (DSP), the concept of corner frequency is adapted to the discrete nature of digital signals. Digital filters, like their analog counterparts, can be designed with specific corner frequencies to shape the frequency response of a signal.
The formula for calculating corner frequency in digital filters depends on the sampling rate and the design of the filter. For instance, in a digital low-pass filter, the normalized corner frequency fc is related to the sampling rate fs by:
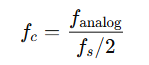
Where fanalog is the corner frequency in the analog domain.
Conclusion
In summary, corner frequency is a fundamental concept in signal processing, particularly in the design of filters. It defines the frequency at which the filter begins to attenuate the signal, marking the boundary between the passband and stopband. Whether in analog or digital systems, understanding the corner frequency is essential for designing filters that optimize signal integrity and performance.
From audio applications to communication systems, the corner frequency enables engineers to control the frequency content of signals, improving the overall system efficiency. By calculating and adjusting corner frequencies, engineers can fine-tune systems to perform better under a variety of conditions, making it an indispensable tool in modern signal processing and system design.
Learn More About.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering.
CornerFrequency, #FilterDesign, #SignalProcessing, #FrequencyResponse, #LowPassFilter, #HighPassFilter, #Bandwidth, #CutoffFrequency, #FrequencyAnalysis, #DigitalFilters, #AnalogFilters, #CircuitDesign, #SignalFiltering, #FilterTheory, #FrequencySweep
