Copper Wire Size Chart awg/swg: All You need to Know in mm or Inches
Copper wiring is the backbone of electrical and electronic systems. From home wiring to industrial panels, the correct wire size ensures safety, efficiency, and long service life. A Copper Wire Size Chart helps electricians, engineers, and buyers quickly compare wire gauges in AWG and SWG with their actual diameters in millimeters or inches.
Understanding this chart saves time, prevents overheating issues, and avoids costly rework. In this detailed guide, you will learn how copper wire sizes are measured, how to read gauge charts, and how to select the right wire for your application with confidence.
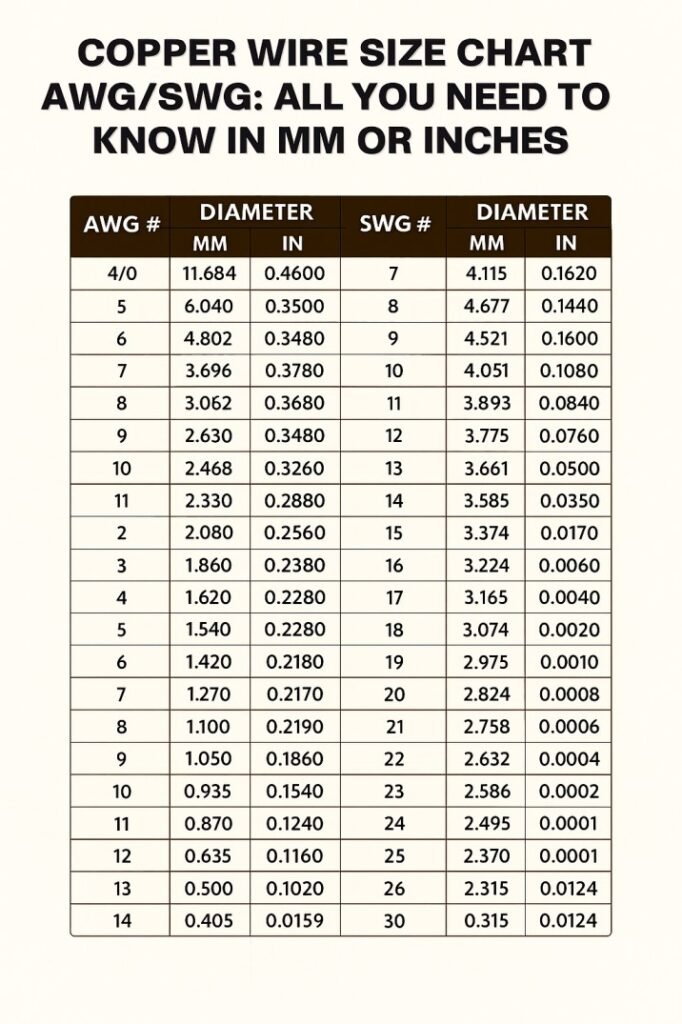
Table of Contents
What is a Copper Wire Size Chart
A Copper Wire Size Chart is a reference table that lists wire gauge numbers alongside their physical dimensions. These dimensions are usually given in millimeters and inches. The chart may also include cross-sectional area and current-carrying capacity. Since copper is widely used due to its high conductivity, accurate sizing becomes critical for voltage drop control and thermal safety.
Use our online tool 3 phase cable size calculator
This chart acts as a common language between manufacturers, installers, and suppliers across different regions.
Understanding Wire Gauge Systems
Different countries follow different wire gauge standards. The most common systems are AWG and SWG. Each system uses a numerical scale, but the logic behind the numbers is not the same. This is why a combined Copper Wire Size Chart is so useful in practical work.
American Wire Gauge AWG
AWG is widely used in the United States and many other regions. In this system, a smaller gauge number means a thicker wire. For example, 10 AWG is thicker than 20 AWG. The scale is logarithmic, which means the size difference between gauges is not linear. AWG is common in building wiring, automotive systems, and electronics.
Try our free online tool today ev charger cable size calculator
Standard Wire Gauge SWG
SWG originated in the United Kingdom and is still referenced in many Commonwealth countries. Like AWG, a lower SWG number indicates a thicker wire. However, the actual diameters differ from AWG values. This makes direct comparison difficult without a Copper Wire Size Chart that shows both systems side by side.
Why Wire Size Matters in Real Applications
Choosing the wrong wire size can lead to serious problems. Undersized wires overheat, waste energy, and increase fire risk. Oversized wires increase cost and make installation harder. A reliable Copper Wire Size Chart helps balance safety, performance, and budget. It also ensures compliance with electrical codes and standards used by inspectors and utilities. Access our powerful online calculator now star delta motor cable size calculator
Copper Wire Size Chart in mm and Inches
The table below shows commonly used copper wire sizes with AWG and SWG references. Diameters are shown in both millimeters and inches for easy comparison.
| AWG | SWG | Diameter (mm) | Diameter (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 26 | 0.51 | 0.020 |
| 22 | 24 | 0.64 | 0.025 |
| 20 | 22 | 0.81 | 0.032 |
| 18 | 20 | 1.02 | 0.040 |
| 16 | 18 | 1.29 | 0.051 |
| 14 | 16 | 1.63 | 0.064 |
| 12 | 14 | 2.05 | 0.081 |
| 10 | 12 | 2.59 | 0.102 |
| 8 | 10 | 3.26 | 0.128 |
| 6 | 8 | 4.11 | 0.162 |
This Copper Wire Size Chart is useful for quick decisions during design, purchasing, and installation. Always verify with manufacturer data when working on critical loads.
Get instant results with our online tool earth cable size calculator
Cross Sectional Area and Current Capacity
Wire diameter alone does not tell the full story. The cross-sectional area determines how much current a copper wire can safely carry. Larger area means lower resistance and less heat generation. Many versions of a Copper Wire Size Chart also include area in square millimeters and approximate ampacity values.
| AWG | Area (mm²) | Typical Current Capacity (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 0.33 | 7 |
| 18 | 0.82 | 14 |
| 16 | 1.31 | 18 |
| 14 | 2.08 | 25 |
| 12 | 3.31 | 30 |
| 10 | 5.26 | 40 |
| 8 | 8.37 | 55 |
| 6 | 13.3 | 75 |
These values are general guidelines. Insulation type, ambient temperature, and installation method all affect actual capacity. Start using our easy-to-use online tool earthing cable size calculator
Solid vs Stranded Copper Wire Sizes
Solid and stranded wires can have the same gauge number but behave differently. Solid wire is a single piece of copper and is common in fixed installations. Stranded wire uses multiple thin strands and is more flexible. A Copper Wire Size Chart usually refers to the overall conductor size, not individual strands. When flexibility is required, stranded copper is preferred even though the gauge remains the same.
How to Choose the Right Copper Wire Size
Start by identifying the load current and voltage level. Then consider the length of the run, as longer distances increase voltage drop. Refer to a Copper Wire Size Chart to match the required current with an appropriate gauge. Always include a safety margin. For commercial or industrial projects, local electrical codes should guide final selection.
Calculate instantly with our smart online tool cable size calculator australia
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One common mistake is assuming AWG and SWG numbers are interchangeable. They are not. Another error is ignoring temperature effects, especially in enclosed conduits. Using a proper Copper Wire Size Chart reduces these risks and improves overall system reliability.
Buying Tips for Higher Value and Longevity
When purchasing copper wire, check for purity, insulation rating, and certification marks. High-quality copper has better conductivity and lasts longer. Buyers often compare sizes using a Copper Wire Size Chart before placing bulk orders, which helps avoid returns and delays. Choosing the right size from the start improves project timelines and profitability.
Explore our professional online tool for quick calculations kw to cable size calculator
Final Thoughts
A clear understanding of wire gauges is essential for anyone working with electrical systems. A well-structured Copper Wire Size Chart bridges the gap between AWG, SWG, and real-world dimensions in millimeters and inches. By using this knowledge, you can design safer circuits, control costs, and improve performance across residential, commercial, and industrial applications. This practical reference will continue to be valuable as long as copper remains the standard for reliable electrical conduction. Access our powerful online calculator now Electrical Diversity Calculator for accurate Load Estimation and efficient electrical Design.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#CopperWireSizeChart, #AWGtoSWG, #WireGaugeChart, #CopperWireSizes, #ElectricalWiringGuide, #AWGChart, #SWGChart, #WireSizeMM, #ElectricalEngineering, #PowerCableSizing


