C1815L Transistor: A Comprehensive Overview
The C1815L transistor is a variant of the widely used NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) known as the C1815. The “L” in the part number typically indicates a low-current version of the transistor, suitable for applications with lower current requirements. As an NPN transistor, the C1815L operates with a positive voltage at the collector concerning the emitter.
Read More
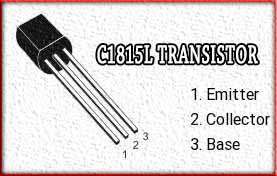
Let’s delve into the features, characteristics, technical specifications, and applications of the C1815L transistor.
Features of C1815L Transistor
NPN Transistor: The C1815L is an NPN-type transistor, allowing it to amplify and control current flow effectively.
Package Type: The C1815L transistor typically comes in a TO-92 package, a widely used through-hole package in various electronic applications.
Low Current Version: The “L” designation in the part number indicates that the C1815L is a low-current version of the C1815 transistor. It is optimized for applications with lower current requirements.
Amplification: The C1815L NPN transistor has a moderate DC current gain, known as the hFE or DC current gain. This feature enables it to amplify weak input signals with a relatively small base current.
Switching Speed: With moderate transition frequency (fT) and low switching times, the C1815L is well-suited for switching applications, allowing it to turn on and off rapidly.
Characteristics of C1815L Transistor
Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): The C1815L transistor typically has a maximum collector-emitter voltage rating of 50V, which specifies the maximum voltage it can withstand when the collector and emitter are reverse-biased.
Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): The maximum collector-base voltage for the C1815L is around 60V, indicating the highest voltage it can withstand between the collector and base when the emitter is open-circuited.
Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): The maximum emitter-base voltage is approximately 5V, signifying the highest voltage the transistor can endure between the emitter and base when the collector is open.
Collector Current (IC): The C1815L transistor can handle a maximum continuous collector current of around 150mA. This rating defines its current-carrying capacity, which is suitable for low-current applications.
Power Dissipation (Ptot): The C1815L can dissipate a maximum power of 400mW, which is the maximum amount of power it can handle without exceeding its temperature limits.
Technical Specifications of C1815L Transistor
- Type: NPN
- Package Type: TO-92
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO): 50V
- Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO): 60V
- Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): 5V
- Maximum Collector Current (IC): 150mA
- Power Dissipation (Ptot): 400mW
- DC Current Gain (hFE): Typically ranges from 70 to 700
Applications of C1815L Transistor
The C1815L transistor finds applications in various electronic circuits that require low-current amplification and switching, including but not limited to:
Audio Amplifiers: The C1815L NPN transistor is commonly used in low-power audio amplifiers and pre-amplifiers.
Signal Amplification: It is suitable for amplifying weak signals in various electronic devices and sensor interfaces.
Switching Circuits: Its moderate switching speed makes it useful for low-current switching applications in digital logic circuits.
LED Drivers: The C1815L can control low-current LED drivers, regulating the brightness of LEDs.
Voltage Regulators: It can be used in low-power voltage regulator circuits to stabilize output voltages in power supplies.
In conclusion, the C1815L transistor is a specialized variant of the C1815, optimized for low-current applications. Its moderate current gain and low power dissipation make it suitable for amplification and switching tasks in low-power electronic circuits.
Designers and hobbyists can confidently use the C1815L transistor in their projects, knowing it offers reliable performance and efficiency in various low-current electronic applications.
Related Posts:
- Floating Gate Transistor: Best Features & Applications
- Transistor S8050 Equivalent: Important Replacements
- S8050 Transistor: Best Functions, Specifications, and Applications
- Transistors BC547: Important Guide to Pinout
- C1815 Datasheet: Important Features to Know About
- 2N3904 Pinout, Datasheet and Equivalent Transistor
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.
