Applications of HVDC Transmission: Where High-Voltage DC Outperforms AC in Modern Power Grids
The applications of HVDC transmission have expanded rapidly as modern power systems demand higher efficiency, longer transmission distances, and better control over power flow. High Voltage Direct Current transmission is no longer limited to a few niche projects. It has become a practical and preferred solution for utilities facing challenges such as long-distance bulk power transfer, grid interconnection, and large-scale renewable energy integration.
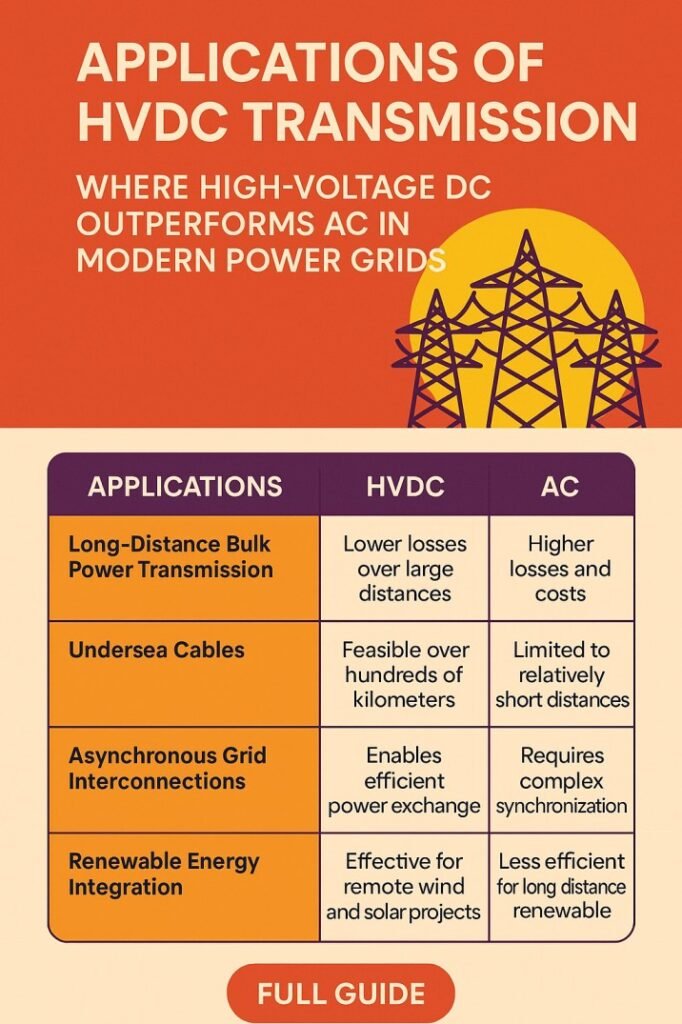
Table of Contents
This article explains the major applications of HVDC transmission focusing on real world power system requirements.
Long Distance Bulk Power Transmission
One of the most important applications of HVDC transmission is long-distance bulk power transfer. When power needs to be transmitted over distances greater than 600 to 800 km by overhead lines, HVDC becomes technically and economically superior to HVAC. DC lines have lower line losses, no reactive power flow, and better voltage regulation over long distances.
Utilities often use HVDC links to transmit power from remote generating stations to major load centers. Hydropower plants located in mountainous or sparsely populated regions are classic examples. The controlled power flow of HVDC ensures stable and efficient delivery even under changing load conditions.
Key advantages in long-distance transmission include:
- Lower transmission losses compared to AC
- Reduced conductor and tower requirements
- No need for intermediate reactive power compensation
- Improved system stability
These benefits explain why long-distance corridors remain one of the strongest applications of HVDC transmission worldwide.
Know more about types of faults in transmission lines
Submarine and Underground Cable Transmission
Submarine cable transmission is another critical area where the applications of HVDC transmission clearly outperform HVAC. For AC cables, charging current limits the maximum practical length. HVDC cables do not suffer from this limitation, making them ideal for undersea and underground routes.
HVDC is widely used for:
- Interconnection of islands with mainland grids
- Offshore wind farm connections
- Power transmission across seas, straits, and rivers
- Underground transmission in densely populated urban areas
For example, cross-sea interconnectors between countries rely on HVDC technology to transfer large amounts of power with high reliability. In congested cities, underground HVDC cables help avoid right-of-way issues while maintaining high transmission capacity.
Asynchronous Grid Interconnection
One of the most strategic applications of HVDC transmission is the interconnection of asynchronous or weak power grids. Many regional and national grids operate at different frequencies or lack synchronized operation. HVAC interconnection is not feasible in such cases.
HVDC links act as electrical firewalls between grids. They allow controlled power exchange without transferring disturbances, frequency deviations, or faults from one system to another. This feature improves overall grid security and operational flexibility.
Common uses include:
- Interconnection of national grids with different operating standards
- Linking weak grids to strong networks
- Controlled power exchange between utilities
This capability makes HVDC a preferred solution for cross-border power trading and regional grid integration.
Know more about bus differential protection
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy integration is one of the fastest growing applications of HVDC transmission. Large renewable projects are often located far from load centers. Offshore wind farms, desert-based solar plants, and remote hydropower stations all benefit from HVDC links.
HVDC systems offer precise control of active power, which is essential when integrating variable renewable energy. They help stabilize voltage, support weak grids, and reduce congestion in existing AC networks.
Typical renewable-related applications include:
- Offshore wind farm grid connections
- Long-distance solar power transmission
- Hydropower export from remote regions
By enabling efficient renewable energy transfer, the applications of HVDC transmission directly support global decarbonization goals.
Urban Power Supply and Right-of-Way Constraints
Urban power systems face severe space and right-of-way limitations. Expanding AC transmission corridors in cities is often impractical due to land constraints and public opposition. HVDC provides a compact and high-capacity alternative.
With higher power density and fewer conductors, HVDC transmission can deliver more power using narrower corridors. Underground HVDC cables further reduce visual impact and environmental concerns.
Know more about hvdc transmission
Urban utilities use HVDC for:
- Strengthening city power supply networks
- Upgrading existing transmission corridors
- Reducing congestion in urban grids
These factors make city power reinforcement an emerging application of HVDC transmission.
Power System Stability and Control
Modern power systems require advanced control to maintain stability under dynamic conditions. HVDC offers fast and precise control of power flow, which is not possible with conventional AC lines.
By modulating power electronically, HVDC links can:
- Dampen power oscillations
- Improve transient and dynamic stability
- Support voltage control in weak networks
- Limit short-circuit levels
These features are particularly valuable in large interconnected grids where disturbances can propagate quickly. Stability enhancement remains a technically important application of HVDC transmission.
Know more about Types of Transmission Line Conductors Explained: Best Guide for Power Engineers
Comparison of Major HVDC Applications
The table below summarizes key applications and their primary benefits.
| Application Area | Typical Use Case | Main Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Long-distance overhead lines | Remote generation to load centers | Lower losses and cost |
| Submarine cables | Island and offshore connections | No charging current limit |
| Asynchronous interconnection | Cross-border grid links | Improved grid security |
| Renewable energy integration | Offshore wind and solar plants | Controlled power flow |
| Urban power supply | Underground transmission | Space efficiency |
| Stability control | Large interconnected grids | Enhanced system stability |
Industrial and Dedicated Power Supply
Some industrial loads require highly reliable and controlled power supply. HVDC transmission is used to supply power to large industrial complexes such as aluminum smelters, mining operations, and petrochemical plants.
Dedicated HVDC links ensure:
- Stable voltage and power quality
- Reduced impact of grid disturbances
- Optimized energy delivery for continuous processes
In such cases, the applications of HVDC transmission directly contribute to higher productivity and reduced downtime.
Know more about Types of Transmission Lines Explained: Overhead vs Underground with Important Applications
Future Trends in HVDC Applications
As power electronics continue to advance, the scope of HVDC is expanding further. Voltage Source Converter technology has made multi-terminal HVDC networks technically feasible. These developments will enable meshed DC grids and flexible power routing.
Future applications are expected in:
- Supergrids connecting continents
- Large-scale offshore renewable hubs
- Hybrid AC-DC transmission networks
- Smart grid and energy storage integration
The growing complexity of power systems ensures that the applications of HVDC transmission will continue to increase in both scale and importance.
Know more about HVDC Transmission Explained: Key Components, Working & Real-World Applications
Conclusion
The applications of HVDC transmission cover a wide range of technical and economic needs in modern power systems. From long-distance bulk power transfer to renewable energy integration and grid interconnection, HVDC provides solutions that traditional AC systems cannot offer efficiently. Its ability to transmit large amounts of power with lower losses, better control, and higher reliability makes it a key technology for present and future electricity networks. As global demand for clean, reliable, and flexible power grows, HVDC transmission will remain a central pillar of power system development.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#HVDCTransmission, #HVDCApplications, #PowerTransmission, #ElectricPowerSystems, #HighVoltageDC, #GridInterconnection, #RenewableEnergyGrid, #LongDistancePower, #ElectricalEngineering, #SmartGrid






