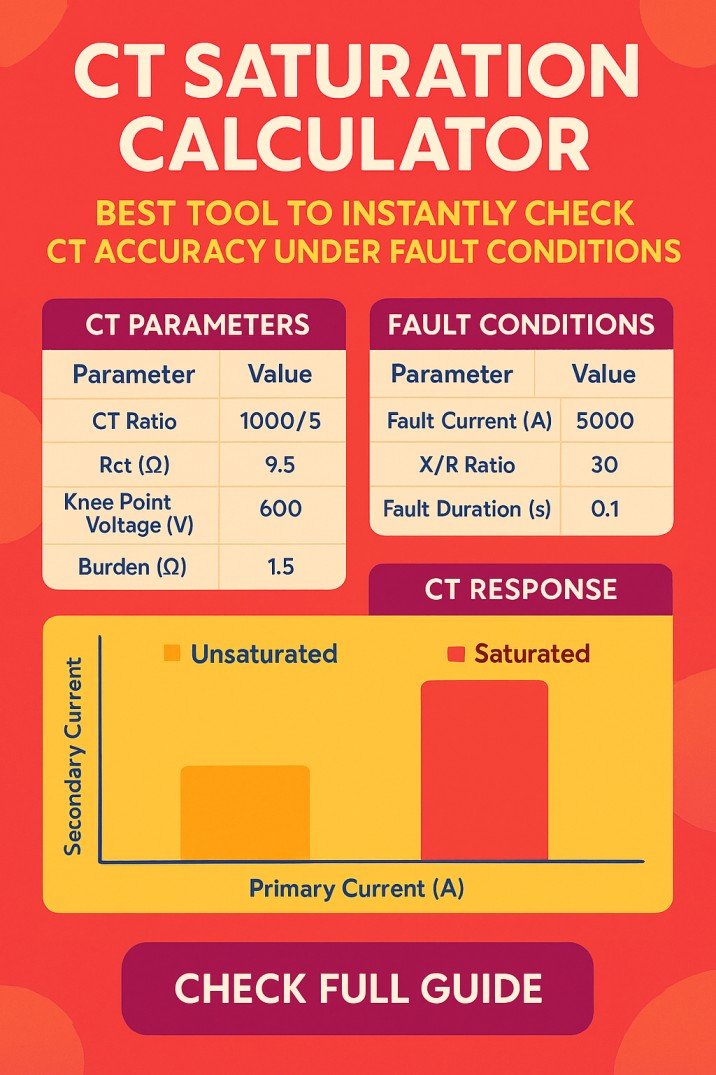
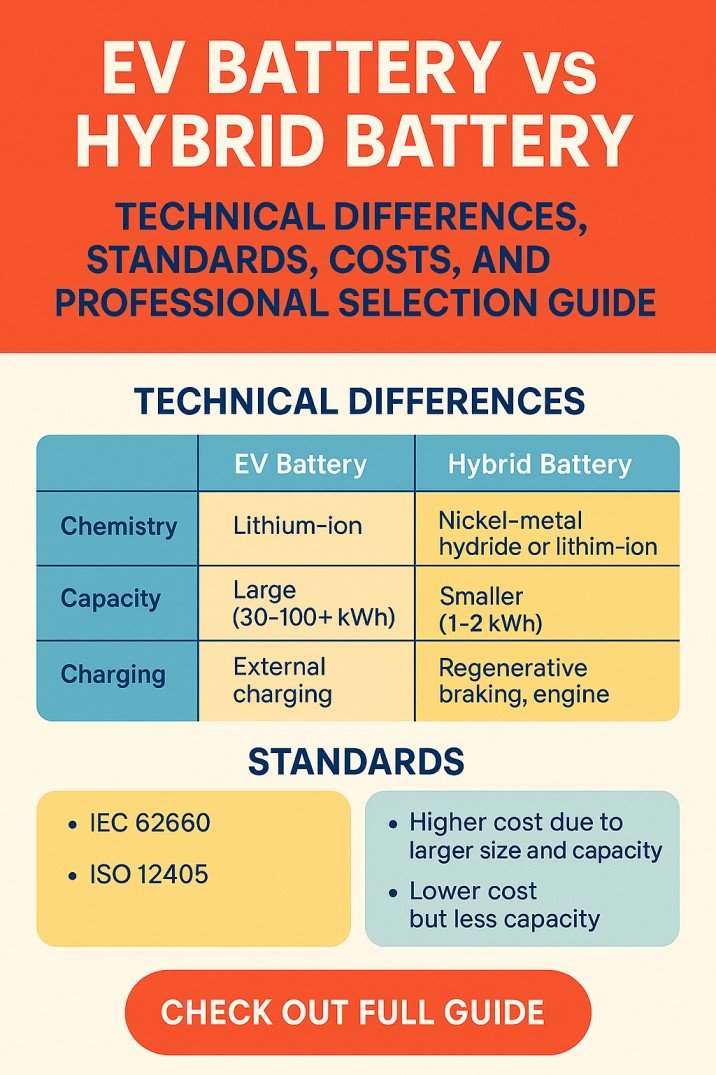
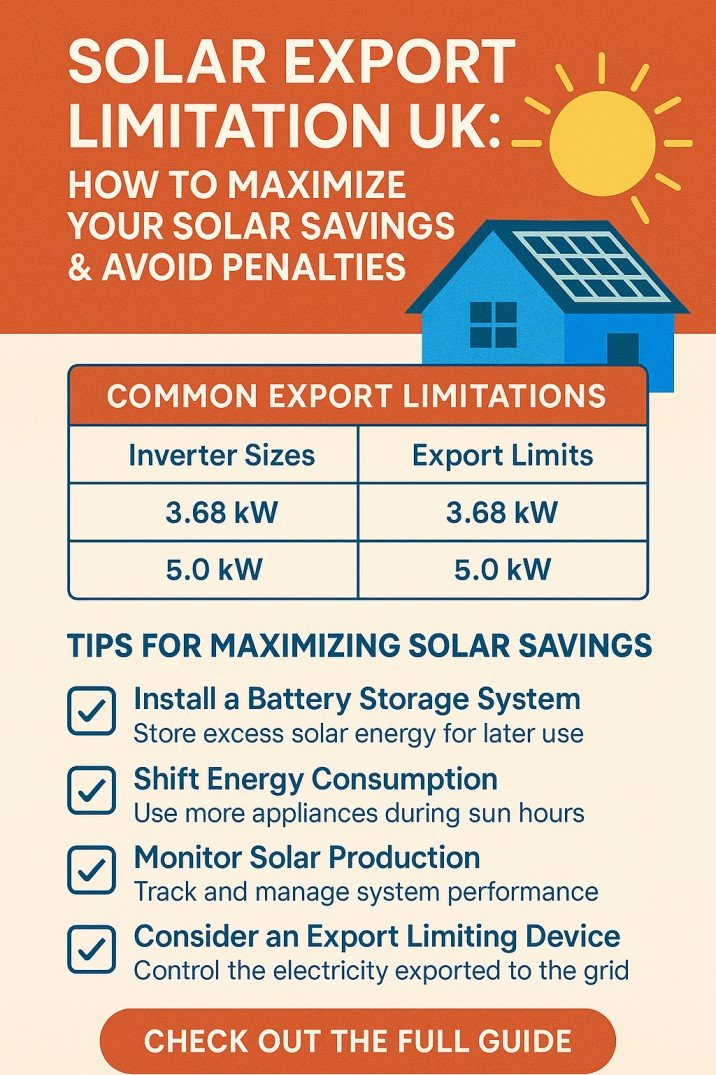
AC to DC Converter: Everything You need to Know
You may know that an AC to DC converter or power supply can convert AC voltage and current into DC voltage and current. But do you know how to build one? Or how to select components? In this article, I am going to give you a very simple way to design an AC to DC converter or power supply by using basic electronic components.
Read More
The basic concept of Power Supply
It is an electrical device or power supply which takes electricity from a grid-based power source and changes its voltage, current, and frequency. This conversion takes place to supply an electrical component in any circuit with the appropriate power according to its power rating.
This AC-to-DC converter delivers DC power to the devices which normally operate or run-on batteries. AC to DC power supply plays an important role due to the lack of other power sources for components running on DC.
Why do we need AC to DC Converter?
Before diving into the working of ac to dc converter, let’s have a look at the categories of electricity that we use in our circuits or daily applications. There are two categories of electricity available to us.
Alternating current “AC”
The first one is the alternating current “AC” in which the current or voltage waveform oscillates between zero and crossing in a complete cycle. Therefore completes 50 cycles in one second comprising one Hz off frequency. This form of electricity has further two types single phase and three-phase electricity. Want to know more about single phase and three phases, click here to read more.
Direct Current “DC”
The second category is the direct current “DC”. In this category, the voltage and current are in phase and form a straight line. There is no oscillation involved and therefore the frequency in the dc circuit is zero. This form of electricity we normally use in our dc electronic circuits and equipment.
Most of the power supplies and electronic equipment operate on direct current. That’s the reason for the importance of AC to DC converters and power supplies. Have a look at the important considerations below.
Vrms vs Vpeak Values of Voltage and current
We denote Ac voltages in root mean square values which we normally call RMS values. There is an important relationship between peak values and RMS values. The highest value of the AC waveform is named the Peak value and the value between positive peak to negative peak is said to be peak to peak value. The relationship between peak values and RMS values is described below.
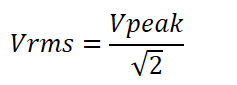
We can also define it as the DC power required to produce the same heating as much produced by the equivalent AC.
So, from the above details, we know that there are two different types of powers and now need to see why we need two types of powers. The answer to this question will be clear with a daily life example.
Daily life Example of AC to DC Converter
Suppose we have a car and we can’t start the car because of a dead battery. So, the battery needs charging and we can’t directly connect the 220volts supply source to its terminals. As per the above detail, we know both sources are different.
Therefore, we require circuitry which will convert the voltage from ac to dc and at a lower level of around 12 volts. The same requirement is for the currently available “AC”. So, right there an ac to dc converter comes in place to feed our requirement.
We are clear about basics and daily life requirements, now let’s have a look at ac to dc converter working and components.
Half-wave “AC” to “DC” Converter Circuit
It is an AC to DC converter consisting of one diode connected to the power supply source. As we know the diode only allows to flow of the current in one-half cycle, there will be ripples at the output. Below is a half-wave rectifier circuit diagram.

From the above “AC” to “DC” converter circuit, the diode only permits the flow of current during the positive half cycle of the input AC supply. The diode stops the flow of electricity when the input voltage is negative or in the negative half cycle.
The positive half cycle of the AC signal travels across resistor terminals, but the current remains unidirectional.
Full wave “AC” to “DC” Converter Circuit
This is an “AC” to “DC” converter or rectifier circuit which converts the alternating current “AC” into direct current “DC”. A full-wave rectifier circuit is also named a “diode bridge circuit” and is also called a bridge rectifier. Only two of the four diodes are able to conduct the current in the positive half cycle of the AC supply signal.
The other two diodes permit the flow of current during the negative half cycle of the input “AC” supply signal. In this way, all the input signal is converted to dc. The placement of the diodes results in a unidirectional flow of current through the resistor. let’s see what it will look like.
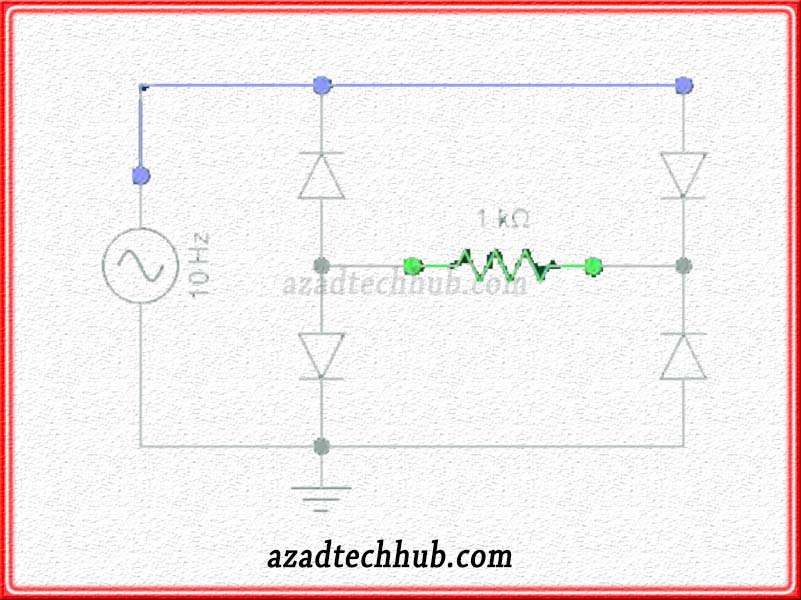
in the above figure, we can see that during the +ve half cycle, two diodes become forward-biased and permit the flow of current through the Load “Resistor”. Then in the negative half cycle, the other two diodes are forward-biased and permit the flow of current in the same direction. In this way, the current through the resistor will remain in the same direction converted to Dc.
Block Diagram of AC to Dc Converter
From the above details, we know how the AC input transforms into a DC signal. The DC at output somehow looks like a rippled one, not a straight line.

We have covered the rectifier part, now we need to have a look at the filter circuit. Filter circuits include two basic types of filters. These filter circuits include low-pass filters and high-pass filter type of circuits. A low pass filter allows low-frequency signals to pass on the output whereas a high pass filter allows high-frequency signals.
The signal we get at the output of full wave ac to dc converter is not a straight line. It has ripples in it. It looks like the below figure.
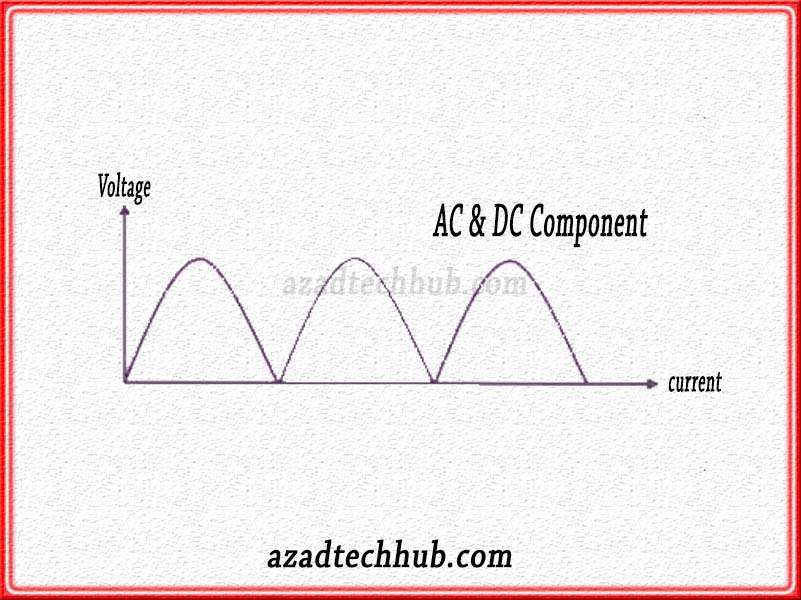
As we can see in the above figure there are ripples in the output signal, filters play an important role in removing these ripples and distortion or noise from the signal. You can also read about low-pass filters and high-pass filters.
Filter circuit types for AC to DC Converter
There are three different types of filter circuits for “AC” to “DC” converters.
- An Input capacitor filter circuit
- Choke “input filter” circuit or LC Filter circuit
- Pi Filter circuit
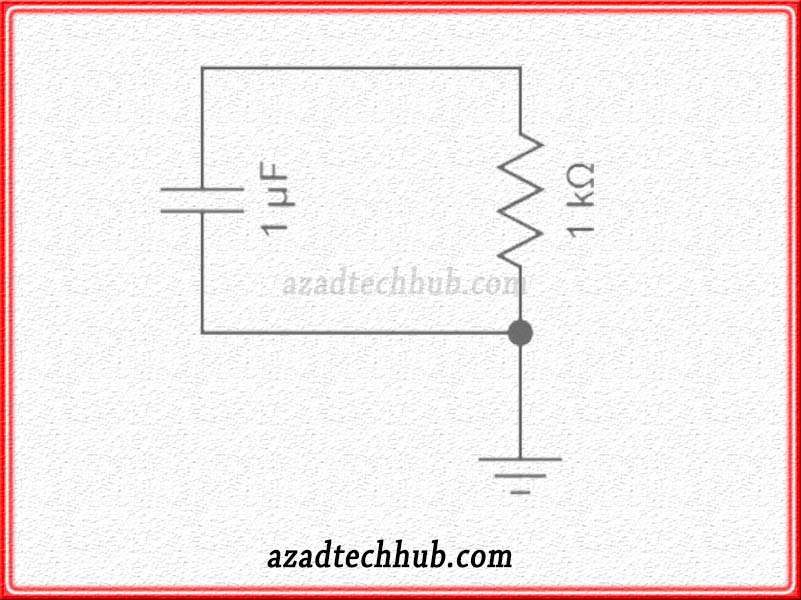
“Capacitor” Filter Circuit
The capacitor “C” linked with the load in parallel makes up the capacitor filter circuit. In this way, the capacitor receives the pulsing rectified output across its terminals. It’s in fact a low pass filter that blocks the AC ripples but allows DC components to reach across load terminals.
In this way, the output is free of ripples and we get a pure Dc signal at the output. Read more regarding the low pass filter .

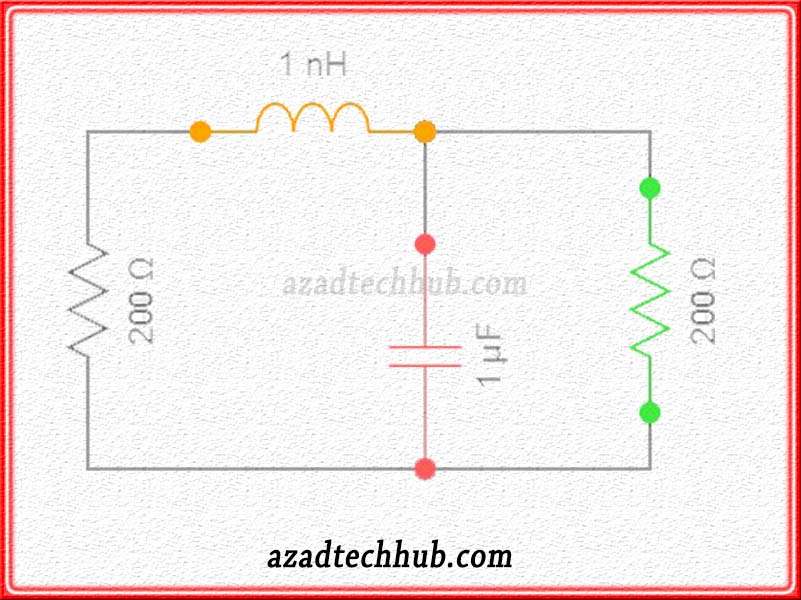
Choke input filter circuit or LC Filter circuit
At the rectifier’s output, when we connect an inductor in series with the output of the “rectifier circuit” and a capacitor is connected in parallel with the “load” or resistor, we call it a choke input filter circuit. Choke “L” or inductor permits the DC component to flow through but blocks the AC component.
In this way, a major part of the AC signal is removed. The capacitor removes the remaining ripples through its low reactance and allows the dc component to reach across load terminals as explained above.
PI Filter Circuit
In this type of filter circuit, the output from ac to dc converter first applies across capacitor C1. Then the signal after filtering passes through the inductor which removes the ripples of the AC signal and allows the DC component to pass.
At the end before moving towards the load end, the signal is applied across capacitor C2 which further filters out the dc component. you can have a look at the below circuit to have a clear understanding.
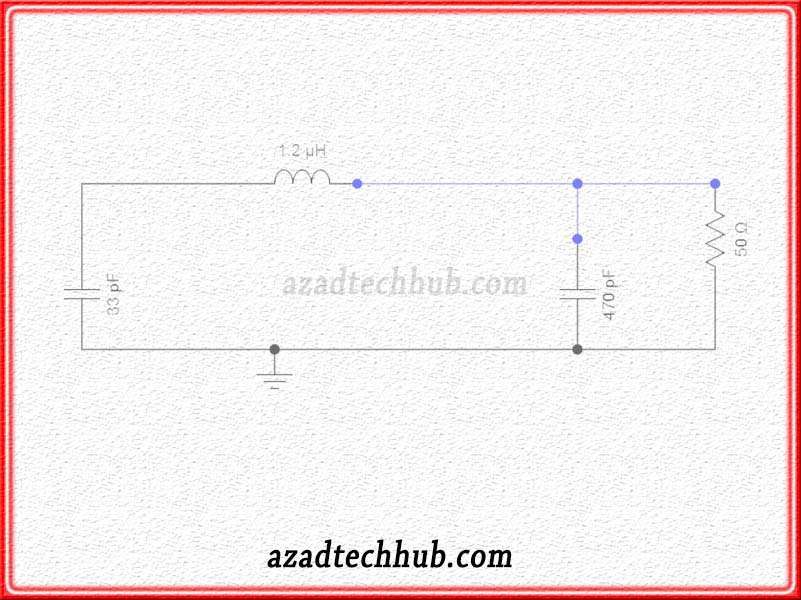
Hopefully, you have understood the basics of ac to dc converter or power supply. If you want to explore dc to dc converters, read our detailed article on dc to dc converter circuits. Further, if you want to know more about filters including low-pass and high-pass filters, you can read about their equations and characteristics. Further, you can also read about oscillator circuits to have a basic understanding of different oscillations.
Related Posts:
- A Quick Guide to Oscillator Circuit Diagram and Working
- AC to DC Converter: Everything You need to Know
- How to Choose the Right Type of HIGH PASS FILTER!
- How To Make Your Product Stand Out With LOW PASS FILTER?
- Schmitt Trigger: Important Types, Working & Applications
Follow us on LinkedIn”Electrical Insights” to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering. You can also Follow us LinkedIn and Facebook to see our latest posts on Electrical Engineering Topics.