IEC Standard for Short Circuit Calculation: How Engineers Accurately Calculate Fault Levels
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation plays a critical role in modern power system design and analysis. Every electrical engineer working with generation, transmission, or industrial distribution systems must understand how fault levels are calculated and why international standards matter. Incorrect short circuit values can lead to undersized equipment, unsafe installations, and costly failures. This is why engineers worldwide rely on IEC methodologies to ensure consistency, safety, and accuracy when determining short circuit currents.
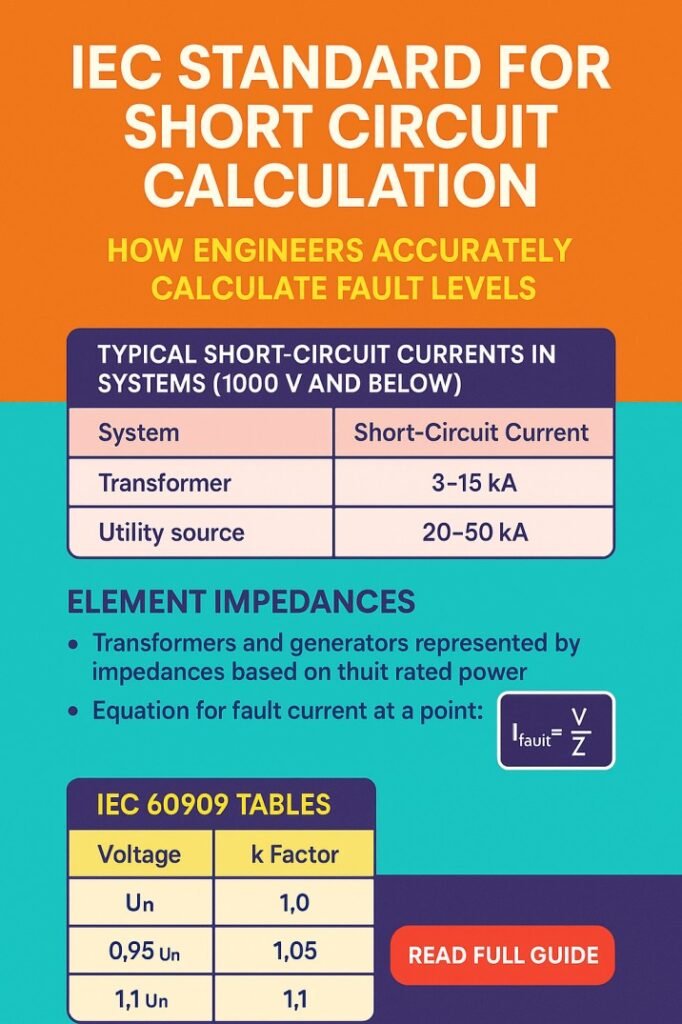
Table of Contents
Short circuit studies are not just theoretical exercises. They directly affect switchgear ratings, cable sizing, protection coordination, and overall system reliability. The IEC approach provides a structured and practical framework that aligns closely with real-world operating conditions, making it a preferred choice across many regions.
Why Short Circuit Calculations Matter in Power Systems
Short circuit currents occur when an abnormal connection creates a low-impedance path between conductors or to ground. These currents are often many times higher than normal load current and can cause severe thermal and mechanical stress.
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation ensures that engineers calculate fault levels in a consistent manner so that equipment such as circuit breakers, busbars, transformers, and protective relays can safely withstand and interrupt these currents. Without accurate fault calculations, even well-designed systems can become unsafe.
Use our online tool Transformer Short Circuit Calculator – Accurate Fault Current & Transformer Protection Tool
From an operational perspective, short circuit studies support system expansion planning, fault analysis, and compliance with international electrical standards.
Overview of IEC 60909 Standard
The primary IEC standard for short circuit calculation is IEC 60909. This standard defines procedures for calculating short circuit currents in three-phase AC systems with nominal voltages up to 550 kV.
Unlike some other methodologies, IEC 60909 focuses on practical engineering assumptions. It introduces voltage factors, correction coefficients, and standardized impedance values that reflect real operating conditions.
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation addresses both maximum and minimum fault currents. Maximum values are used to verify equipment withstand capability, while minimum values are critical for protection sensitivity and relay operation.
Types of Short Circuits Covered by IEC
The IEC methodology considers several common fault types encountered in power systems.
Three-phase short circuits are symmetrical faults and usually result in the highest fault currents. These are critical for determining the breaking capacity of circuit breakers.
Single line-to-ground faults are the most frequent in practical systems. The IEC approach accounts for earthing methods such as solid grounding, resistance grounding, and isolated neutral systems.
Line-to-line and double line-to-ground faults are also addressed, allowing engineers to assess a wide range of fault scenarios using a unified method.
Use our online tool Short Circuit Current Calculator for Motors: Best Tool
Key Parameters Used in IEC Calculations
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation relies on a defined set of parameters to maintain accuracy and consistency.
Rated system voltage is adjusted using voltage factors to account for operational variations. These factors differ for maximum and minimum short circuit conditions.
Source impedance includes generators, transformers, and the upstream network. IEC provides correction factors for rotating machines to represent subtransient reactance during initial fault conditions.
Network impedance, including cables and overhead lines, is calculated using positive, negative, and zero-sequence components where required.
The table below summarizes common parameters used in IEC-based studies.
| Parameter | Description | Engineering Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage factor | Adjustment to nominal voltage | Accounts for system variations |
| Source impedance | Generator and grid contribution | Determines fault magnitude |
| Transformer impedance | Percentage or per-unit value | Limits fault current |
| Network impedance | Lines and cables | Reflects fault location |
Use our online tool Short Circuit Current Calculator: Best Tool
Calculation of Initial Short Circuit Current
One of the defining features of the IEC method is the calculation of the initial symmetrical short circuit current, often denoted as Ik”.
This current represents the RMS value at the instant just after fault inception, before any decay effects. It forms the basis for determining thermal and mechanical stress on equipment.
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation uses standardized formulas that combine system voltage, impedance, and correction factors. This structured approach reduces ambiguity and improves comparability across projects.
Peak Short Circuit Current and Its Importance
In addition to RMS values, IEC emphasizes the calculation of peak short circuit current. This value is critical for mechanical design, as it represents the maximum instantaneous force experienced by conductors and busbars.
Peak current depends on the DC component of the fault current, which is influenced by system X/R ratio. IEC provides empirical coefficients to estimate this effect without complex transient simulations.
Accurate peak current estimation ensures that switchgear and supports can withstand electrodynamic forces during faults.
Know more about Short Circuit Calculation Methods: IEC vs ANSI
Breaking and Making Currents in IEC Methodology
The IEC approach clearly differentiates between breaking current and making current.
Breaking current refers to the current that a circuit breaker must interrupt safely. It is typically lower than the initial short circuit current due to current decay.
Making current, on the other hand, represents the current at the moment a breaker closes onto a fault. This value is higher and directly related to peak short circuit current.
By defining both values, the IEC standard for short circuit calculation helps engineers select equipment that meets both interrupting and closing requirements.
Maximum and Minimum Short Circuit Conditions
IEC calculations are performed for two extreme conditions.
Maximum short circuit current assumes high system voltage, minimum impedance, and full source contribution. This scenario is used for equipment rating and thermal checks.
Minimum short circuit current assumes lower voltage and higher impedance. This case is critical for protection studies, ensuring that relays and fuses operate correctly even under weak fault conditions.
This dual approach improves system safety and reliability across all operating scenarios.
Know more about What is the Maximum Value for Short Circuit Protection for Multi-Motor Branch Circuits
Comparison with Other Standards
While IEC is widely used, other standards such as ANSI and IEEE also exist. The IEC methodology differs in its use of voltage factors and correction coefficients.
Engineers often prefer the IEC standard for short circuit calculation in international projects due to its conservative yet realistic assumptions. It also integrates well with modern power system analysis software.
Understanding these differences is essential when working on multinational projects or reviewing designs prepared under different standards.
Practical Applications in Engineering Projects
IEC-based short circuit calculations are applied at multiple stages of a project.
During design, they help in selecting circuit breakers, switchgear, and busbar systems. During operation, they support system upgrades and fault level assessments.
In industrial plants, accurate fault calculations prevent equipment damage and reduce downtime. In utility networks, they ensure compliance with grid codes and safety regulations.
Know more about Fault Current and Short Circuit Current: A Quick Guide
The table below highlights typical applications.
| Application Area | Purpose of Calculation |
|---|---|
| Switchgear selection | Verify breaking capacity |
| Cable sizing | Thermal withstand checks |
| Protection coordination | Ensure relay sensitivity |
| System expansion | Assess fault level increase |
Role of Software Tools in IEC Calculations
Modern power system software implements the IEC methodology to handle complex networks efficiently. These tools allow engineers to model large systems, simulate different fault types, and generate detailed reports.
Even with software support, a solid understanding of the IEC standard for short circuit calculation is essential. Engineers must verify input data, interpret results correctly, and apply engineering judgment to final decisions.
Common Mistakes and Engineering Best Practices
One common mistake is using incorrect voltage factors or outdated impedance data. Another is ignoring minimum fault conditions, which can lead to protection failures.
Best practice involves validating assumptions, cross-checking results, and documenting calculation methods clearly. Regular review of IEC updates also ensures continued compliance.
Know more about What Provides Short Circuit Protection for the Motor
Conclusion
The IEC standard for short circuit calculation provides engineers with a reliable and internationally accepted framework for determining fault levels in power systems. By combining practical assumptions with standardized formulas, it ensures safety, consistency, and accuracy across a wide range of applications.
Understanding how IEC methodologies handle fault types, current components, and operating conditions enables engineers to design robust systems and select appropriate equipment. As power networks continue to grow in complexity, mastering IEC-based short circuit calculations remains a fundamental skill for every electrical engineer.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#IECShortCircuitCalculation, #IECStandard, #ShortCircuitAnalysis, #ElectricalFaultCalculation, #PowerSystemProtection, #ElectricalEngineeringStandards, #FaultLevelCalculation, #IEC60909, #PowerEngineering, #ElectricalDesign


