Lightning Protection Australian Standard: Essential Guide to AS1768 Compliance & Safety
Lightning is a natural phenomenon that poses significant risks to both life and property. In Australia, the increasing frequency of severe thunderstorms has highlighted the critical importance of robust lightning protection systems. To mitigate these risks effectively, adherence to the lightning protection Australian standard—AS1768—is essential. This standard provides comprehensive guidance on designing, installing, and maintaining lightning protection systems, ensuring safety and regulatory compliance for residential, commercial, and industrial structures.
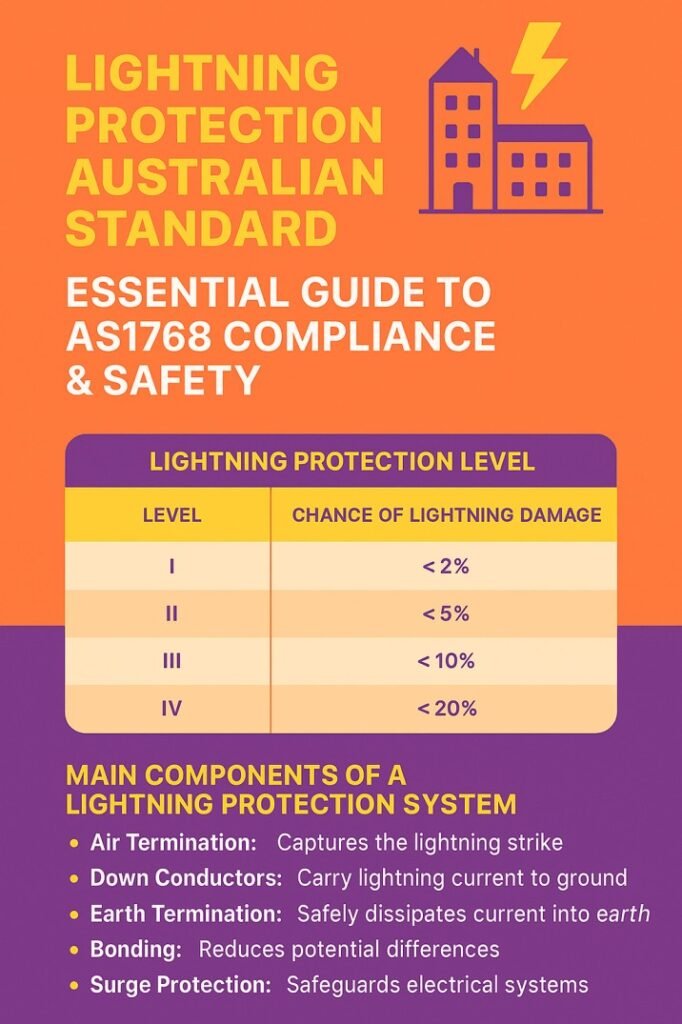
Table of Contents
Understanding the lightning protection Australian standard is crucial for engineers, electricians, architects, and property owners. It not only minimizes the potential for lightning-related damage but also ensures that insurance and safety regulations are met. This guide provides a detailed overview of AS1768 compliance, key components of lightning protection systems, and practical strategies to maintain safety and efficiency.
Know more about Top 10 Lightning Protection Design Softwares: Best Guide
What is AS1768?
AS1768, titled “Lightning Protection,” is the Australian standard that sets the framework for designing and implementing lightning protection systems. Its primary purpose is to safeguard structures, electrical installations, and occupants from lightning strikes. The standard covers risk assessment, system design, component selection, installation procedures, and ongoing maintenance.
The standard is designed to address three key types of lightning-related threats:
- Direct strikes to buildings and structures.
- Electrical surges caused by lightning activity.
- Indirect effects, such as fire hazards or equipment damage.
By adhering to AS1768, organizations and property owners can implement an integrated approach that combines air terminals, conductors, earth electrodes, and surge protection devices to minimize lightning risks.
Know more about What Is Early Streamer Emission A Practical Guide for Engineers, Standards, and Lightning Protection Design
Key Components of Lightning Protection Systems
Implementing the lightning protection Australian standard involves several critical components that work together to provide a complete safety solution. Understanding these components helps ensure compliance with AS1768 requirements.
1. Air Terminals
Air terminals, commonly known as lightning rods, are installed at strategic points on a structure to attract lightning strikes and direct them safely to the ground. According to AS1768, the positioning and height of air terminals should be based on risk assessment and structural geometry.
2. Conductors
Conductors provide a controlled path for lightning currents from the air terminals to the ground. Copper or aluminum conductors are typically used due to their excellent electrical conductivity. Proper sizing and routing are essential to comply with the lightning protection Australian standard. Know more about Types of Lightning Arrester Explained: Important Guide for Power Systems & Substations
3. Earth Electrodes
Earth electrodes are critical for safely dissipating lightning energy into the ground. AS1768 specifies the design and installation of earth electrodes to ensure low resistance paths, reducing the risk of side-flashes or potential differences that could endanger equipment or occupants.
4. Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Lightning surges can damage sensitive electronic equipment. SPDs are installed in electrical panels and critical circuits to divert transient voltage and maintain system integrity. AS1768 emphasizes the correct specification and placement of SPDs in line with system requirements.
Risk Assessment According to AS1768
AS1768 mandates a systematic risk assessment to determine the necessity and extent of lightning protection measures. Risk assessment considers factors such as:
- Building height and location
- Occupancy type and value of assets
- Historical lightning incidence in the region
- Likelihood of indirect damage
The risk assessment process allows for the classification of structures into risk categories, guiding the design and level of protection needed. This ensures that lightning protection Australian standard requirements are applied proportionally, optimizing both safety and cost-efficiency.
Know more about What Is Air Terminal in Lightning Protection? Function, Types & Installation Explained
Installation Guidelines for AS1768 Compliance
Compliance with the lightning protection Australian standard extends beyond system design to precise installation practices. Key installation guidelines include:
- Maintaining continuous, low-resistance bonding between system components.
- Avoiding sharp bends in conductors, which can increase the risk of side-flashes.
- Ensuring that air terminals and conductors are mechanically secure and corrosion-resistant.
- Verifying proper grounding using resistance testing and earth potential measurements.
- Installing surge protection devices near entry points of electrical and communication services.
Following these guidelines not only meets AS1768 compliance but also enhances the long-term reliability and safety of lightning protection systems.
Maintenance and Inspection
Ongoing maintenance is crucial to the effectiveness of lightning protection systems. AS1768 recommends periodic inspection and testing to detect corrosion, loose connections, or other potential failures. The frequency of inspections depends on environmental conditions and system complexity, but annual checks are generally recommended for most installations.
Know more about Earth Cable Size for Lightning Protection
Lightning Protection Inspection Checklist
| Component | Inspection Requirement | Recommended Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Air Terminals | Check for corrosion, damage, and secure connections | Annually |
| Conductors | Ensure continuity, no sharp bends, and mechanical integrity | Annually |
| Earth Electrodes | Measure earth resistance, inspect for corrosion or damage | Every 1-2 years |
| Surge Protection Devices | Test operation and replace if damaged | Annually |
| Bonding & Connections | Verify secure connections and continuity | Annually |
Regular maintenance ensures that the system continues to meet the lightning protection Australian standard, providing confidence in both safety and regulatory compliance.
Common Misconceptions About Lightning Protection
Despite its importance, there are several misconceptions about lightning protection systems in Australia:
- Lightning rods attract lightning unnecessarily – In reality, properly designed air terminals provide a controlled path, not an increased risk.
- Insurance alone is sufficient – Insurance cannot prevent structural damage or equipment loss; compliant lightning protection is essential.
- All buildings require the same protection – AS1768 requires risk assessment to determine the appropriate level of protection based on specific building characteristics.
Know more about Leakage Current in Lightning Arrester: Best Guide
Understanding these points helps property owners and professionals implement effective measures that truly enhance safety and comply with the standard.
Benefits of Adhering to AS1768
Compliance with the lightning protection Australian standard offers numerous benefits:
- Minimizes the risk of fire and structural damage.
- Protects critical electrical and electronic systems.
- Reduces downtime for businesses dependent on uninterrupted power.
- Ensures insurance validity and regulatory compliance.
- Enhances occupant safety and peace of mind.
These advantages make adherence to AS1768 not just a legal or technical requirement but a practical investment in long-term safety.
Lightning Protection and Building Codes
Australian building codes often reference AS1768 to ensure that new structures meet safety standards. Integration with building codes means that architects and engineers must plan for lightning protection early in the design phase. Coordination between structural, electrical, and safety engineers is crucial to meet lightning protection Australian standard requirements efficiently.
Know more about IEC Standard for Lightning Protection: A Complete Technical Guide
Surge Protection Integration
Modern buildings often rely heavily on electronic systems, making surge protection an integral part of AS1768-compliant lightning safety. SPDs mitigate the effects of transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes. Correct integration of SPDs involves:
- Selecting devices based on voltage rating and discharge capacity.
- Installing SPDs at service entry points and critical equipment.
- Ensuring proper grounding and bonding with the main lightning protection system.
This integration enhances overall system resilience while maintaining compliance with the standard.
Conclusion
The lightning protection Australian standard—AS1768—provides a comprehensive framework for safeguarding life, property, and electronic systems against lightning risks. By understanding its requirements, implementing correctly designed systems, performing thorough risk assessments, and conducting regular maintenance, property owners and professionals can ensure compliance and maximize safety.
Know more about IEC Standard for Lightning Arrester – IEC 60099 Guide for Surge and Overvoltage Protection
In an environment where lightning incidents are both common and increasingly severe, adherence to AS1768 is not optional. It represents a critical component of responsible building design, electrical safety, and risk management. From air terminals to surge protection devices, each element of a lightning protection system plays a vital role in reducing hazards, protecting assets, and meeting regulatory standards.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#LightningProtection, #AustralianStandard, #AS1768, #SurgeProtection, #ElectricalSafety, #LightningSafety, #BuildingCodeCompliance, #LightningRiskAssessment, #ASStandards, #ElectricalEngineering