Cable Size Chart Copper and Aluminium: Exact Amp Ratings & Best Selection Guide
Selecting the correct electrical cable is one of the most critical decisions in any wiring project. A wrong cable size can cause overheating, voltage drop, energy loss, and even fire hazards. This is why electricians, engineers, and installers rely on a reliable cable size chart copper and aluminium to make accurate and safe choices. This guide explains amp ratings, practical selection rules, and real-world factors that affect cable performance, all in clear and professional language.
Whether you are working on residential wiring, industrial panels, solar systems, or motor connections, understanding a cable size chart copper and aluminium will help you choose the right conductor every time without guesswork.
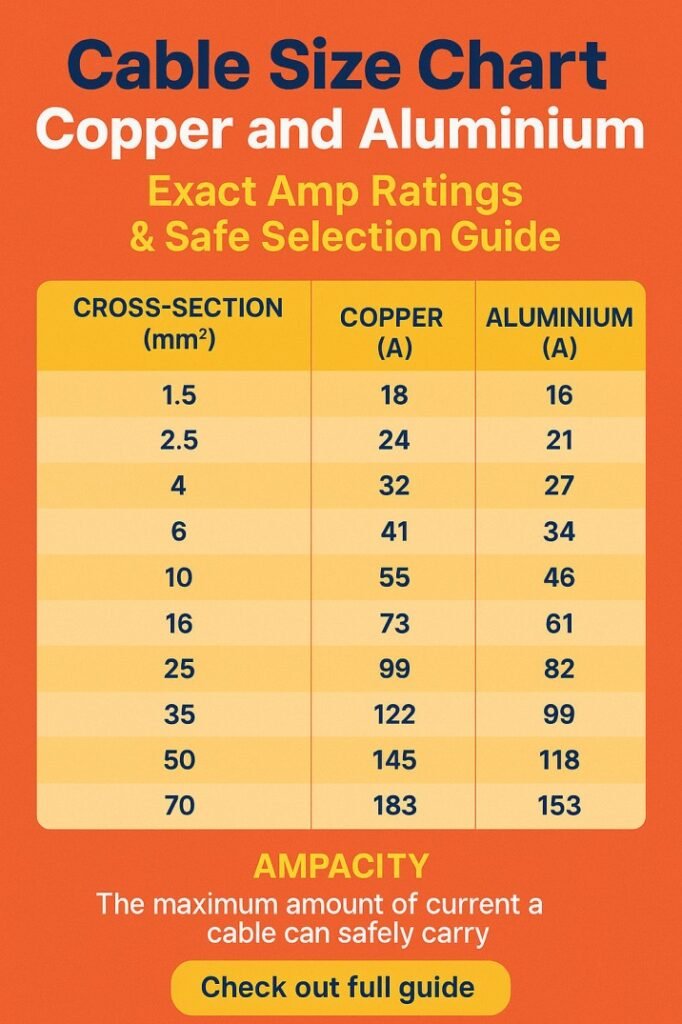
Table of Contents
Why Cable Size Matters in Electrical Systems
Cable size directly controls how much current a conductor can safely carry. If the conductor is undersized, resistance increases, leading to excessive heat. Over time, insulation damage and system failure become likely. A properly selected cable maintains safe temperature limits, reduces power loss, and ensures long service life.
Try this tool out to save time and effort for easy conversions Amps to Wire Size Calculator – Choose the Right Cable for 10A, 20A, 40A Loads
A cable size chart copper and aluminium provides standardized ampacity values so designers can match load current with conductor size. These ratings are based on material properties, insulation type, ambient temperature, and installation method.
Copper vs Aluminium Cables Explained
Copper and aluminium are the two most common conductor materials used worldwide. Each has unique electrical and mechanical properties that influence sizing decisions.
Copper cables have lower electrical resistance and higher conductivity. This means they can carry more current in a smaller cross-section. Aluminium cables are lighter and more cost-effective but require a larger size to carry the same current safely.
Use our online tool 3 phase cable size calculator
When using a cable size chart copper and aluminium, you will always notice aluminium sizes are one or two steps larger for the same amp rating.
Key material differences include:
- Copper offers higher conductivity and better mechanical strength
- Aluminium is lighter and cheaper for long cable runs
- Copper handles terminations better with less oxidation
- Aluminium requires proper lugs and anti-oxidation treatment
Understanding Amp Ratings and Cable Size Charts
Amp rating, also called ampacity, is the maximum continuous current a cable can carry without exceeding its temperature limit. Cable size charts are developed using international standards such as IEC, NEC, and BS.
A cable size chart copper and aluminium typically lists conductor cross-section, current rating, and recommended applications. These charts assume standard conditions, so derating may be required for higher temperatures or bundled cables.
Cable Size Chart Copper and Aluminium – Current Carrying Capacity
Below is a practical cable size chart copper and aluminium based on common PVC insulated cables under normal installation conditions.
Calculate instantly with our smart online tool cable size calculator australia
Table 1: Single Core Copper and Aluminium Cable Amp Ratings
| Cable Size (mm²) | Copper Amp Rating (A) | Aluminium Amp Rating (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 18 | 14 |
| 2.5 | 24 | 18 |
| 4 | 32 | 25 |
| 6 | 41 | 32 |
| 10 | 57 | 45 |
| 16 | 76 | 60 |
| 25 | 101 | 80 |
| 35 | 125 | 100 |
| 50 | 150 | 120 |
| 70 | 195 | 155 |
| 95 | 235 | 190 |
| 120 | 270 | 215 |
This cable size chart copper and aluminium is widely used for power distribution, control panels, and feeder cables. Always confirm local standards before final selection.
How to Select the Correct Cable Size Safely
Using a cable size chart copper and aluminium is only one part of proper cable selection. Real installations involve additional factors that must be considered.
Explore our professional online tool for quick calculations kw to cable size calculator
Important selection steps include:
- Calculate full load current accurately
- Choose copper or aluminium based on cost and space
- Check amp rating from the cable size chart copper and aluminium
- Apply derating factors if required
- Verify voltage drop limits
- Ensure protective device coordination
Ignoring any of these steps can result in poor system performance even if the chart value seems correct.
Voltage Drop Considerations for Long Cable Runs
Voltage drop is a critical factor in cable sizing, especially for long distances. Excessive voltage drop reduces equipment efficiency and can cause motors to overheat.
Copper performs better in voltage drop performance due to lower resistance. Aluminium requires a larger cross-section to keep voltage drop within limits. This is why engineers often upsize aluminium conductors beyond the basic cable size chart copper and aluminium recommendation.
Typical acceptable voltage drop limits are:
- 3 percent for lighting circuits
- 5 percent for power circuits
- 2 percent for sensitive electronic loads
Access our powerful online calculator now Electrical Diversity Calculator for accurate Load Estimation and efficient electrical Design.
Cable Size Chart Copper and Aluminium for Three-Phase Systems
Three-phase systems are common in industrial and commercial installations. Current distribution and heat dissipation differ compared to single-phase circuits.
Table 2: Three-Phase Cable Size Chart Copper and Aluminium
| Cable Size (mm²) | Copper 3-Phase Current (A) | Aluminium 3-Phase Current (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 28 | 22 |
| 6 | 36 | 28 |
| 10 | 50 | 40 |
| 16 | 68 | 54 |
| 25 | 90 | 72 |
| 35 | 110 | 88 |
| 50 | 135 | 108 |
| 70 | 175 | 140 |
| 95 | 210 | 170 |
This cable size chart copper and aluminium is commonly applied to motors, transformers, and industrial feeders.
Use our online tool for free Wire Size Calculator for Motors – Accurate Motor Cable Sizing Tool for Electric Loads
Temperature and Installation Derating Factors
Standard cable charts assume an ambient temperature of around 30°C. Higher temperatures reduce current carrying capacity. Similarly, cables installed in trays, conduits, or underground may need derating.
Common derating conditions include:
- Ambient temperature above 40°C
- Multiple cables grouped together
- Installation in thermal insulation
- Underground installation without ventilation
Always adjust the base values from the cable size chart copper and aluminium to maintain safe operation under real conditions.
Copper and Aluminium Cable Applications
Choosing between copper and aluminium depends on application type, budget, and available space.
Copper cables are preferred for:
- Residential wiring
- Control circuits
- High-temperature environments
- Compact panels with limited space
Aluminium cables are commonly used for:
- Long distance feeders
- Utility power distribution
- Industrial substations
- Cost-sensitive large installations
In each case, the cable size chart copper and aluminium ensures the conductor can safely carry the expected load.
Check out this tool that makes the process much easier and faster MM to AWG Wire Size Calculator According to IEC and NEC
Common Mistakes in Cable Size Selection
Even experienced installers sometimes make avoidable errors when relying on cable charts.
Typical mistakes include:
- Selecting cable size only by load current
- Ignoring voltage drop calculations
- Not applying temperature derating
- Using copper ratings for aluminium cables
- Assuming all insulation types have same ratings
A correct reading of the cable size chart copper and aluminium prevents these issues and improves system reliability.
Safety Standards and Compliance
Cable sizing must comply with local electrical codes and international standards. These regulations are designed to protect people, equipment, and property.
Following a standardized cable size chart copper and aluminium helps ensure compliance with:
- Electrical safety regulations
- Fire prevention guidelines
- Equipment manufacturer requirements
- Insurance and inspection criteria
Never compromise on cable sizing to reduce cost, as long-term risks far outweigh short-term savings.
You might find this tool useful for tackling similar tasks Sub Panel Wire Size Calculator – Accurate Wire Gauge & Load Sizing Tool
Final Thoughts on Cable Size Selection
A well-designed electrical system always starts with correct cable sizing. Using a trusted cable size chart copper and aluminium allows professionals to select conductors that operate safely, efficiently, and reliably under real-world conditions.
Copper offers higher performance in compact installations, while aluminium provides economical solutions for large power distribution. By understanding amp ratings, voltage drop, and derating factors, you can confidently select the right cable for any project.
When used correctly, a cable size chart copper and aluminium is not just a reference table but a practical safety tool that supports long-term system performance and electrical integrity.
We recommend this tool for anyone struggling with the sizing of subpanels. Try here Wire Size Calculator for Subpanels and Feeders – NEC Guidelines Included
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#CableSizeChart, #CopperAndAluminiumCable, #ElectricalCableSizing, #WireGaugeChart, #PowerCableSelection, #CopperCableSize, #AluminiumCableSize, #ElectricalDesignGuide, #CableCurrentRating, #ElectricalEngineering


