What Does SCADA Stand For? Discover Its Important Role in Industrial Automation in 2026
If you have ever worked in industrial environments or explored modern manufacturing processes, you might have come across the term SCADA. But what does SCADA stand for, and why is it crucial in industrial automation? Understanding SCADA is essential for engineers, technicians, and anyone involved in managing industrial systems. SCADA, which stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, is a control system architecture that monitors, collects, and analyzes real-time data from industrial processes.
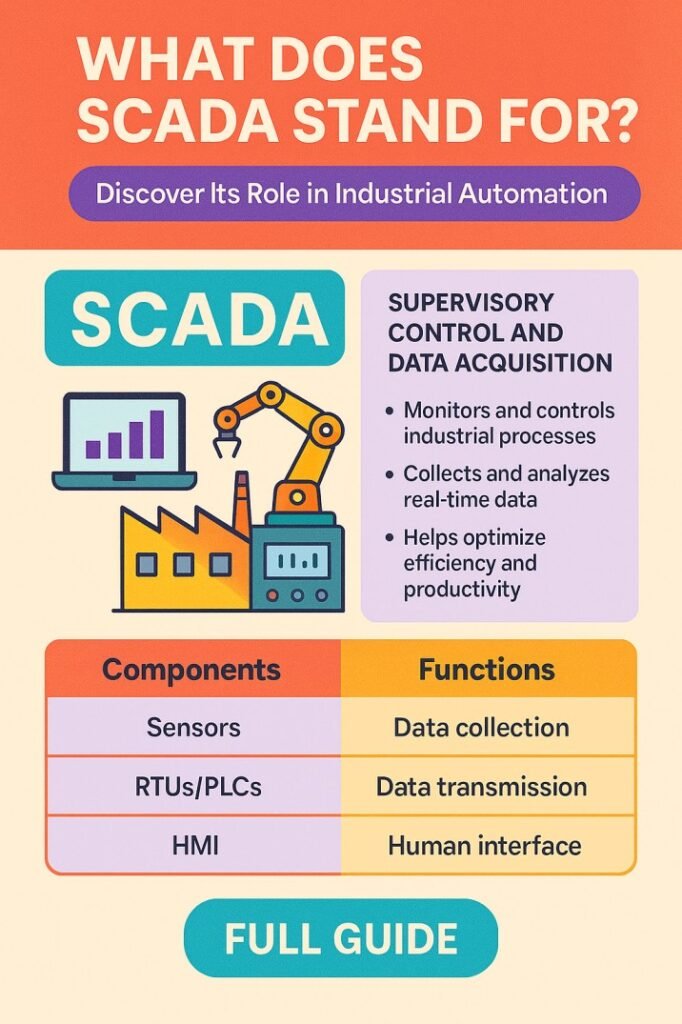
Table of Contents
It plays a vital role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and productivity across various industries, including manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and transportation. SCADA systems are not just software or hardware alone. They are a combination of multiple components working together to provide real-time control and monitoring of industrial operations.
At its core, SCADA helps operators make informed decisions by providing visual dashboards, alarms, and reports that reflect the status of the entire system. Modern SCADA systems can integrate with advanced technologies like IoT, cloud computing, and predictive analytics, making them indispensable in today’s automated industrial landscape.
Understanding what does SCADA stand for is just the first step. To fully appreciate its role, it is important to explore the structure, components, and functionalities that make it effective in industrial automation.
Know more about SCADA HMI Software Cost in 2026 – Pricing, Licenses & Best Value Options
Key Components of SCADA
A typical SCADA system consists of several interconnected components, each serving a specific function. These components work in harmony to monitor and control industrial processes.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): This is the user interface where operators interact with the system. HMIs provide visual representations of the industrial process, including dashboards, graphs, and alerts.
- Supervisory System: This software layer collects data from field devices, processes it, and sends commands to control devices as needed.
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs): These units are installed at the field level and gather real-time data from sensors and actuators. RTUs communicate this information to the central system.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): PLCs are used for process automation, executing control logic and directly controlling machines.
- Communication Infrastructure: SCADA relies on reliable networks such as Ethernet, fiber optics, or wireless connections to transfer data between the field devices and supervisory system.
- Data Historian: This component stores historical process data for analysis, reporting, and compliance purposes.
Know more about HMI vs SCADA: Which System Should You Choose?
The table below summarizes these components for clarity:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Human-Machine Interface | Allows operators to monitor and control processes visually |
| Supervisory System | Processes data and manages system control commands |
| Remote Terminal Units | Collects real-time data from field sensors and devices |
| Programmable Logic Controllers | Automates machinery and executes control logic |
| Communication Infrastructure | Ensures seamless data transmission between devices and central system |
| Data Historian | Stores historical data for analysis, optimization, and reporting |
SCADA System Structure
The structure of a SCADA system is designed for reliability and scalability. At the base level, sensors and actuators collect data from industrial equipment. These devices send signals to RTUs or PLCs, which act as intermediaries between the field and supervisory system. The supervisory system then processes the information and displays it on HMIs for operators. In addition to real-time monitoring, the system can trigger alarms, log data, and even execute automated control actions.
Know more about Top SCADA Software Platforms for Energy Sector
Modern SCADA structures often include multiple layers:
- Field Layer: Sensors, actuators, RTUs, and PLCs directly interacting with industrial machinery.
- Control Layer: Centralized servers and software that process data, execute control commands, and communicate with HMIs.
- Management Layer: Data historians, reporting tools, and decision-making software that help optimize operations.
This layered architecture ensures that SCADA systems are robust, efficient, and capable of handling large-scale industrial operations with minimal downtime.
Importance of SCADA in Industrial Automation
SCADA is essential for modern industrial automation due to several reasons:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Operators can track system performance, detect anomalies, and respond quickly to emergencies.
- Process Optimization: By analyzing data trends, SCADA helps identify inefficiencies and improve productivity.
- Enhanced Safety: SCADA systems can automatically shut down equipment or alert personnel to prevent accidents.
- Cost Reduction: Optimized operations and predictive maintenance reduce unnecessary expenses.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Historical data stored in the system helps managers make informed operational decisions.
Know more about Industrial IoT Sensors in Automation: Cost and Integration
Industries like power generation, oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing rely heavily on SCADA for smooth and safe operations. For example, a water treatment plant uses SCADA to monitor pump pressures, chemical levels, and flow rates, ensuring that water quality standards are met consistently.
Common SCADA Applications
SCADA systems are versatile and can be applied across various sectors:
- Manufacturing plants for production line monitoring
- Electrical grids for energy distribution control
- Water and wastewater management
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Transportation systems for traffic and railway management
The table below highlights the applications with their specific SCADA benefits:
| Industry | SCADA Benefits |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Production monitoring, quality control, and predictive maintenance |
| Energy & Power | Load management, fault detection, and grid optimization |
| Water & Wastewater | Flow monitoring, chemical dosing, and leak detection |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline monitoring, pressure control, and safety alarms |
| Transportation | Traffic monitoring, signaling control, and operational efficiency |
Know more about OPC UA vs MQTT: Protocol Comparison for Industrial Control
Future of SCADA in Industrial Automation
The role of SCADA is evolving with the advent of Industry 4.0. Integration with IoT devices, cloud computing, and AI-driven analytics is transforming SCADA systems from simple monitoring tools to intelligent, predictive platforms. These advanced SCADA systems offer real-time insights, remote monitoring capabilities, and enhanced cybersecurity features, making them indispensable in modern industrial automation.
In conclusion, understanding what does SCADA stand for is fundamental to appreciating its importance in industrial automation. SCADA systems, with their well-structured components and real-time monitoring capabilities, ensure efficient, safe, and optimized industrial operations. Whether you are an engineer, technician, or industry manager, mastering SCADA concepts is critical for success in today’s automated world.
Know more about Modbus Communication Protocol: Master-Slave Explained
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#SCADA, #SCADAStandFor, #IndustrialAutomation, #ProcessControl, #SCADASystems, #AutomationTechnology, #SmartIndustry, #SCADAExplained, #EngineeringTools, #FactoryAutomation


