What Is Early Streamer Emission A Practical Guide for Engineers, Standards, and Lightning Protection Design
Lightning protection is a critical part of modern electrical and structural design, especially for tall buildings, industrial plants, and sensitive facilities. One technology that often creates discussion among engineers is Early Streamer Emission. Many professionals search for a clear answer to what is early streamer emission because it directly affects risk assessment, system layout, and compliance decisions. Understanding what is early streamer emission helps engineers design safer structures and evaluate whether this technology fits a specific project.
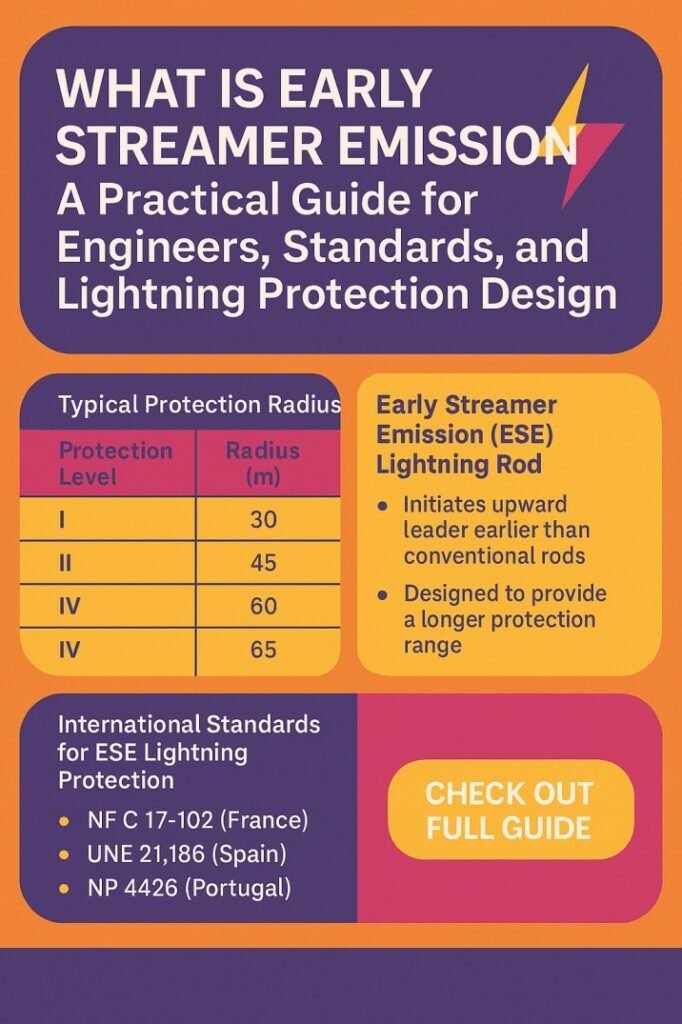
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Lightning Protection
Before going deeper into what is early streamer emission, it is important to review how lightning protection works in general. A lightning protection system provides a controlled path for lightning current to travel safely to the ground. Its main goal is to protect structures, equipment, and people from direct strikes and secondary effects like surges and fire.
A complete lightning protection system usually includes:
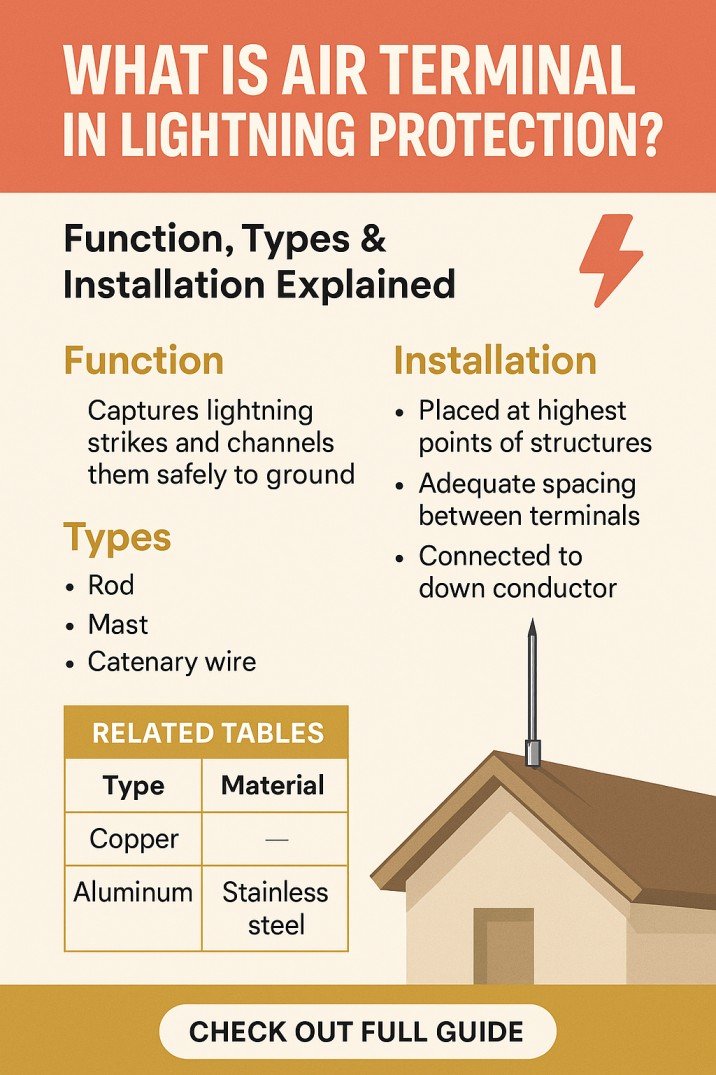
- Air terminals or strike receptors
- Down conductors
- Grounding or earthing system
- Bonding between metallic parts
- Surge protection devices for internal systems
Know more about Types of Lightning Arrester Explained: Important Guide for Power Systems & Substations
Traditional systems use simple air rods based on the Franklin principle. These rods intercept lightning and carry the current safely to earth. The concept behind what is early streamer emission builds on this idea but adds an active component intended to improve strike interception.
What Is Early Streamer Emission in Simple Terms
When engineers ask what is early streamer emission, they are referring to a type of lightning air terminal designed to launch an upward leader earlier than a conventional rod. The theory is that by creating an earlier upward discharge, the device can connect with the downward lightning leader sooner, increasing the effective protection area.
In basic terms, what is early streamer emission technology trying to do is extend the “capture radius” of a single air terminal. This means fewer air terminals may be required to protect large structures, depending on the design method and local standards.
An Early Streamer Emission (ESE) air terminal contains an internal triggering system. This system reacts to the electric field that builds up before a lightning strike. When the field reaches a certain level, the device produces an upward streamer slightly earlier than a passive rod.
Know more about Top 10 Lightning Protection Design Softwares: Best Guide
How Early Streamer Emission Devices Work
To better understand what is early streamer emission, it helps to look at the sequence of a lightning strike.
During a thunderstorm, charge separation occurs in the cloud. A stepped leader travels downward toward the ground. At the same time, objects on the ground can launch upward streamers. When one of these streamers connects with the downward leader, the main lightning current flows.
An ESE air terminal is designed to influence this upward streamer process.
Typical working principle includes:
- The ambient electric field increases as a storm approaches
- The ESE device senses this field through its geometry and internal components
- A triggering mechanism generates a high-voltage pulse at the tip
- This pulse initiates an upward streamer earlier than a simple rod
- The earlier connection may allow the ESE terminal to intercept the strike
This earlier emission time is usually expressed as a time advance, often in microseconds. The bigger the time advance, the larger the theoretical protection radius according to the ESE design model.
Know more about IEC Standard for Lightning Arrester – IEC 60099 Guide for Surge and Overvoltage Protection
Comparison Between Conventional Rods and ESE Terminals
Engineers evaluating what is early streamer emission often compare it directly with Franklin rods. The following table highlights key differences.
| Feature | Conventional Air Rod | Early Streamer Emission Terminal |
|---|---|---|
| Operating principle | Passive interception | Active early streamer initiation |
| Internal components | None | Triggering or ionization system |
| Claimed protection radius | Based on rolling sphere method | Based on time advance and ESE model |
| Standards acceptance | Widely accepted worldwide | Accepted in some standards, debated in others |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Periodic inspection recommended |
This comparison helps clarify what is early streamer emission in practical engineering terms. It is not just a different shape of rod, but a device with a specific performance claim.
Design Concepts Used With ESE Systems
When applying what is early streamer emission in a real project, engineers do not use the standard rolling sphere method alone. Instead, they often rely on a protection radius formula derived from the device’s time advance.
Key design factors include:
- Height of the ESE terminal above the protected surface
- Time advance value provided by the manufacturer
- Lightning protection level required for the structure
- Geometry and size of the building
Know more about IEC Standard for Lightning Protection: A Complete Technical Guide
A simplified idea behind the design is that a higher terminal and a greater time advance lead to a larger theoretical protection area. However, the grounding system and down conductors must still be designed to handle full lightning current safely.
Relevant Standards and Codes
One major reason professionals search for what is early streamer emission is to understand its acceptance in standards. The topic is technically and commercially sensitive, and regulations differ across regions.
Some standards and documents associated with ESE include:
| Standard / Document | Region | Approach to ESE |
|---|---|---|
| NFC 17-102 | France and adopted in some countries | Provides a design method for ESE systems |
| UNE 21186 | Spain | Covers ESE lightning protection |
| IEC 62305 series | International | Focuses on conventional systems, does not specifically endorse ESE |
| NFPA 780 | United States | Primarily addresses traditional systems |
Engineers must always check local authority requirements before specifying ESE devices. Understanding what is early streamer emission also means understanding where it is permitted and how it must be designed.
Advantages Often Attributed to ESE Systems
Supporters of ESE technology highlight several practical benefits. These claims are often considered when deciding what is early streamer emission suitable for in a project.
Commonly stated advantages include:
- Larger coverage area with fewer air terminals
- Reduced installation time on large roofs
- Less structural impact due to fewer mounting points
- Potential cost savings in materials and labor
Know more about Leakage Current in Lightning Arrester: Best Guide
These benefits can be attractive for facilities such as warehouses, stadiums, and industrial complexes. However, they must be balanced with compliance, risk analysis, and owner requirements.
Engineering Considerations and Limitations
A responsible discussion of what is early streamer emission must also include engineering limitations. Lightning is a complex natural phenomenon, and no system can guarantee absolute protection.
Important considerations include:
- Proper earthing is still critical, regardless of terminal type
- Down conductor routing must avoid sharp bends and loops
- Equipotential bonding is required to reduce side flashing
- Surge protection is needed for internal electrical systems
ESE terminals do not replace good grounding practice. Even if the interception area is increased, the lightning current magnitude remains the same and must be safely dissipated into the soil.
Typical Applications of ESE Lightning Protection
Understanding what is early streamer emission also involves knowing where it is commonly used. Engineers often consider ESE systems for:
- Industrial plants with wide roof areas
- Telecommunication towers and facilities
- Solar power plants and substations
- Historical or architectural buildings where fewer rods are preferred
In these cases, the reduced number of visible air terminals can be an advantage from both cost and aesthetic perspectives.
Know more about Earth Cable Size for Lightning Protection
Inspection and Maintenance
Like any lightning protection system, ESE installations require periodic inspection. Knowing what is early streamer emission includes understanding that the device contains components that must remain in good condition.
Maintenance practices usually involve:
- Visual inspection of the terminal and mounting
- Checking mechanical tightness of connections
- Verifying continuity of down conductors
- Measuring earth resistance of the grounding system
Regular inspection ensures the system performs as intended over its service life.
Practical Design Tips for Engineers
For engineers working on lightning protection, a clear grasp of what is early streamer emission helps in making balanced decisions. The following practical tips are useful during design.
- Always start with a formal lightning risk assessment
- Confirm local code acceptance before selecting ESE
- Coordinate closely with structural and electrical teams
- Ensure low-impedance grounding with multiple electrodes if needed
- Combine external lightning protection with internal surge protection
These steps ensure that the chosen system, whether ESE or conventional, provides a complete and reliable solution.
Know more about What Is Air Terminal in Lightning Protection? Function, Types & Installation Explained
Final Thoughts on Early Streamer Emission
In summary, what is early streamer emission refers to a lightning protection technology designed to initiate an upward streamer earlier than a standard air rod. Its goal is to increase the effective protection radius and reduce the number of terminals required on a structure. While it is recognized in some national standards, it remains a subject of technical debate in parts of the engineering community.
For practicing engineers, the key is not only knowing what is early streamer emission but also understanding its design method, code acceptance, and integration with grounding and surge protection. When applied correctly and in line with local regulations, it can be a practical option for certain types of structures. Careful engineering judgment and adherence to standards always remain the foundation of safe lightning protection design.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#LightningProtection, #EarlyStreamerEmission, #ESEAirTerminal, #NFPA780, #IEC62305, #UL96A, #ElectricalEngineering, #BuildingSafety, #SurgeProtection, #GroundingSystems