Voltage Regulator LM317, LM317S: Types and Applications
Voltage regulator is an electronic device that is used to regulate the output voltage of a power supply or battery to a stable and reliable level. They are essential components in electronic circuits that require a constant and reliable power supply. Such as microprocessors, sensors, and other electronic components.
Voltage regulators work by detecting the input voltage and adjusting the output voltage to a specific level. Regardless of any fluctuations in the input voltage or load current. They ensure that the output voltage remains constant and within a specified range. Even when the input voltage or load current changes.
There are several types of voltage regulators available, including linear voltage regulators, switching voltage regulators, and Zener diode voltage regulators. Each type of voltage regulator has its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of a voltage regulator depends on the specific application requirements. Such as input and output voltage range, current capacity, efficiency, and cost.
Overall, voltage regulators play a critical role in ensuring that electronic circuits operate reliably and efficiently. By providing a constant and stable power supply.
types of voltage regulators
Voltage regulators are electronic devices. That are used to regulate the output voltage of a power supply or battery to a stable and reliable level. There are several types of voltage regulators available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this answer, we will discuss the most common types of voltage regulators in detail.
Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear Voltage Regulators: Linear voltage regulators are the most common type of voltage regulators. They work by dissipating the excess voltage as heat, which makes them simple and easy to use. However, they are less efficient than other types of voltage regulators and generate more heat. Linear voltage regulators can be further classified into two types:
a. Fixed Voltage Regulators: Fixed voltage regulators have a fixed output voltage, which cannot be adjusted. Examples of fixed voltage regulators include LM7805 and LM7812.
b. Adjustable Voltage Regulators: Adjustable voltage regulators allow the user to adjust the output voltage within a specified range. By using external components such as resistors. Examples of adjustable voltage regulators include LM317 and LM337.
Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching Voltage Regulators: Switching voltage regulators are more efficient than linear voltage regulators and generate less heat. They work by converting the excess voltage into a different form of energy. Such as a magnetic field or stored energy in a capacitor. However, they are more complex and expensive than linear voltage regulators. Switching voltage regulators can be further classified into two types:
a. Buck Regulators: Buck regulators are used to step down the input voltage to a lower output voltage. They work by turning the input voltage on and off at a high frequency. And then filtering the output to obtain a stable DC voltage. Examples of buck regulators include LM2675 and LM2677.
b. Boost Regulators: Boost regulators are used to step up the input voltage to a higher output voltage. They work by storing energy in an inductor and then releasing it to the output when required. Examples of boost regulators include LM2734 and LM2736.
Switched-Capacitor Voltage Regulators
Switched-Capacitor Voltage Regulators: Switched-capacitor voltage regulators work by charging and discharging capacitors to step up or step down the input voltage to the desired output voltage. They are relatively simple and inexpensive compared to other types of voltage regulators. However, they have a limited input and output voltage range and are not suitable for high-power applications.
Zener Diode Voltage Regulators
Zener Diode Voltage Regulators: Zener diode voltage regulators are simple and inexpensive voltage regulators. That use a Zener diode to regulate the output voltage. They work by maintaining a constant voltage across the Zener diode, which ensures that the output voltage remains constant. However, they have a limited current capacity and are not suitable for high-power applications.
There are several types of voltage regulators available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of a voltage regulator depends on the specific application requirements. Such as input and output voltage range, current capacity, efficiency, and cost.
applications of voltage regulator
Voltage regulators have a wide range of applications in various electronic systems. Where a stable and reliable power supply is essential. Some of the most common applications of voltage regulators are:
Microprocessors and microcontrollers: Microprocessors and microcontrollers are the core components of many electronic systems. Including computers, smartphones, and home automation systems. Voltage regulators are used to provide a stable power supply to these devices, ensuring that they operate reliably and efficiently.
Sensors and transducers: Sensors and transducers are used to detect physical and environmental changes and convert them into electrical signals. Voltage regulators are used to provide a stable power supply to these devices, ensuring that the signals they produce are accurate and reliable.
Power supplies: Voltage regulators are used in power supplies to ensure that the output voltage remains constant and within a specified range, regardless of fluctuations in the input voltage or load current.
Audio amplifiers: Audio amplifiers require a stable and clean power supply to produce high-quality audio output. Voltage regulators are used to provide a stable and noise-free power supply to audio amplifiers, ensuring that the audio output is clear and distortion-free.
LED lighting: LED lighting requires a stable power supply to operate efficiently and produce consistent light output. Voltage regulators are used to provide a stable power supply to LED lighting systems, ensuring that they operate reliably and efficiently.
Battery charging: Voltage regulators are used in battery charging circuits to ensure that the battery is charged to the correct voltage and current, preventing overcharging or undercharging, which can damage the battery.
Overall, voltage regulators play a critical role in ensuring that electronic systems and devices operate reliably and efficiently, by providing a stable and reliable power supply.
Voltage Regulator LM317
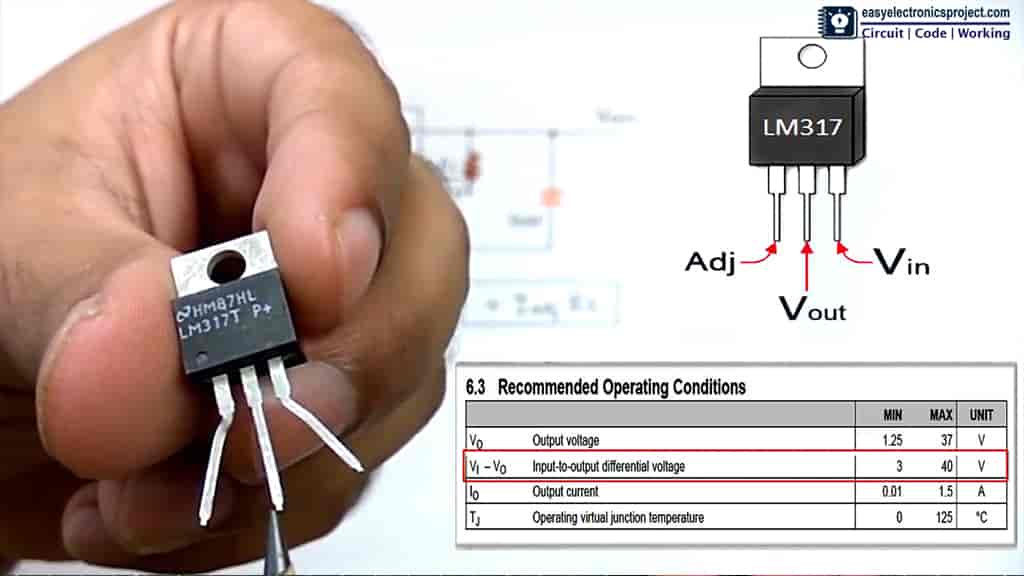
LM317 is a popular voltage regulator that has been widely used in various electronic circuits for several decades. It is a three-terminal device that is capable of regulating the output voltage to a precise level, regardless of variations in the input voltage and load current.

The LM317 voltage regulator is an integrated circuit that belongs to the 78xx series of linear regulators. It has an adjustable output voltage that can be set anywhere between 1.25V to 37V, making it a versatile device for a wide range of applications. It is a positive voltage regulator, which means that it regulates the output voltage to a voltage that is higher than the input voltage.
The LM317 voltage regulator has several features that make it a popular choice among electronic circuit designers. It has a low dropout voltage, which means that the output voltage can be very close to the input voltage. This is particularly useful in applications where the input voltage is only slightly higher than the desired output voltage.
Furthermore, the LM317 has a built-in thermal overload protection, which protects the device from damage due to excessive heat. It also has a current limiting feature that protects the device from damage due to excessive current.
Voltage regulator lM317s
LM317S is a variant of the popular LM317 voltage regulator, which is widely used in electronic circuits to regulate the output voltage to a precise level. The LM317S is a three-terminal device that is capable of regulating the output voltage to a range of voltages, regardless of variations in the input voltage and load current.

The LM317S voltage regulator is an adjustable voltage regulator, which means that the output voltage can be set to a desired level by using two external resistors. It has a wide input voltage range of 4.2V to 40V, making it suitable for a variety of applications. The output voltage of LM317S can be adjusted between 1.2V to 37V, making it a versatile device for many electronic circuits.
Features of Voltage regulator lM317s
One of the key features of LM317S is its low dropout voltage, which means that it can regulate the output voltage even when the input voltage is close to the desired output voltage. This feature makes it an ideal choice for battery-powered applications where the input voltage may fluctuate.
The LM317S voltage regulator also has a built-in thermal overload protection, which prevents the device from overheating and getting damaged due to excessive heat. It also has a current limiting feature that protects the device from damage due to excessive current.
LM317S is available in various packages, such as TO-263, TO-220, and SOT-223, and can handle a maximum output current of 1.5A. This makes it suitable for a variety of applications, including power supplies, battery chargers, and voltage regulators.
To use LM317S in a circuit, two external resistors are required to set the output voltage. The formula for calculating the output voltage is Vout = 1.25V x (1 + R2/R1). The value of R1 is typically 240 ohms, and the value of R2 can be calculated based on the desired output voltage.
LM317S is a versatile and reliable voltage regulator that is widely used in electronic circuits. Its adjustable output voltage, low dropout voltage, and built-in protection features make it an ideal choice for a variety of applications.
voltage regulator 12v
Voltage regulator 12V is a type of electronic device that is used to regulate the output voltage to a stable 12 volts. It is a crucial component in electronic circuits that require a stable and reliable power supply.
The voltage regulator 12V can be either a linear or a switching regulator. Linear regulators are simple and easy to use, but they are less efficient and generate more heat than switching regulators. Switching regulators, on the other hand, are more efficient and generate less heat, but they are more complex and expensive than linear regulators.
Applications of voltage regulator 12V
In electronic circuits, a voltage regulator 12V is typically used to power microcontrollers, sensors, and other electronic components that require a stable power supply. It is also commonly used in automotive and marine applications to regulate the voltage of the battery or alternator to a stable 12 volts.
The voltage regulator 12V is available in various packages, such as TO-220, TO-92, and SOT-223, and can be found in different configurations, including adjustable and fixed output voltage. Some of the popular voltage regulator 12V ICs include LM7812, LM2940, and LM2937.
The working principle of a voltage regulator 12V is based on a feedback mechanism. The output voltage is compared to a reference voltage, and the difference between the two is used to adjust the output voltage. In a linear regulator, the excess voltage is dissipated as heat, while in a switching regulator, the excess voltage is converted into a different form of energy.
To use a voltage regulator 12V in a circuit, it is important to choose the right type of regulator based on the application requirements. The input voltage, output voltage, and load current are important parameters that must be considered while selecting a voltage regulator 12V.
A voltage regulator 12V is an essential component in electronic circuits that require a stable and reliable power supply. It is available in different configurations and packages, and its selection depends on the specific application requirements.
Topics You might be interested in:
- Step Down Transformer Sizing Calculator – Accurate kVA Rating & Load Calculation Tool
- Motor Failure Causes: 7 Most Common Reasons Your Motor Stops Working
- Electric Motor Failure Symptoms: 12 Critical Warning Signs Every Engineer Must Identify Early
- Electric Motor Not Starting Reasons – 12 Critical Causes & Proven Troubleshooting Solutions
- Single-Phase Motor Problems and Solutions – Complete Troubleshooting & Repair Guide for Electrical Engineers
- Electric Motor Troubleshooting Chart – Complete Fault Diagnosis & Repair Guide for Engineers
- Transformer OCPD Sizing Chart – Accurate Breaker & Fuse Selection Guide as per NEC
- Transformer Neutral Sizing – Complete Calculation Guide for Accurate Conductor Selection & Compliance
- Demand Factor for Transformer Sizing – Accurate Load Calculation & Optimal kVA Selection Guide
- Distribution Transformer Sizing – Accurate Load Calculation, kVA Selection & Design Guide
- Diversity Factor for Transformer Sizing – Accurate Load Calculation & kVA Selection Guide
- Buck and Boost Transformer Sizing: Complete Calculation Guide for Accurate Voltage Correction
- Dry Type Transformer Sizing Chart – Accurate kVA Selection Guide for Electrical Engineers
- Auxiliary Transformer Sizing Calculation – Complete Engineering Guide for Accurate Load & Capacity Selection
- Transformer Secondary Protection Sizing – Complete Engineering Guide for Accurate Relay & Breaker Selection