Transformer Disconnect Sizing Guide: Accurate Selection for Optimal Power Safety
Choosing the right transformer disconnect is critical for the safety and efficiency of any electrical system. Transformer disconnect sizing ensures that your system is protected against overloads, short circuits, and other electrical hazards. Selecting an improper disconnect not only compromises safety but also can lead to equipment damage, unnecessary downtime, and increased maintenance costs. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of transformer disconnect sizing, its importance, and a step-by-step approach to ensure optimal protection.
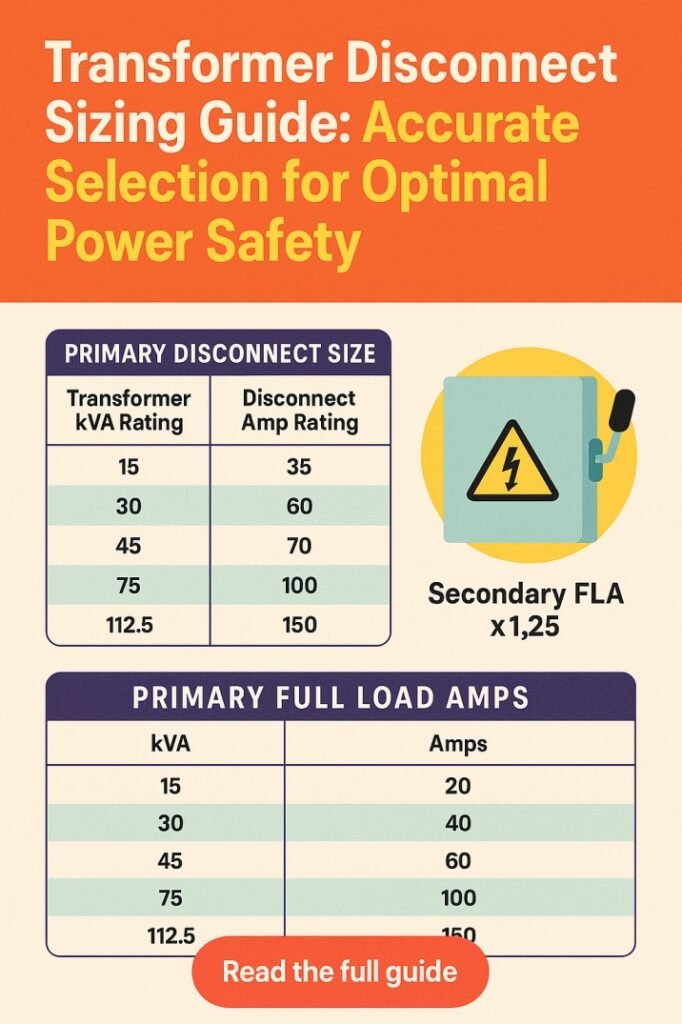
Table of Contents
Understanding Transformer Disconnects
A transformer disconnect is a switch that isolates the transformer from the power source or load for maintenance, repair, or emergency purposes. It allows electricians to safely work on the transformer without the risk of electrical shock or fire. Disconnects are designed to handle the transformer’s full load current and withstand short-circuit conditions.
Start using our online tool today — it’s free Transformer Short Circuit Calculator – Accurate Fault Current & Transformer Protection Tool
Correct transformer disconnect sizing involves evaluating the transformer’s voltage, rated current, and environmental conditions. This process ensures that the disconnect can safely interrupt fault currents without damage or hazard.
Why Proper Sizing is Crucial
The correct sizing of a transformer disconnect affects the following aspects:
- Safety: Prevents electrical accidents caused by overcurrent or short circuits.
- Reliability: Reduces the risk of transformer downtime due to fuse or switch failure.
- Compliance: Meets local electrical codes and standards, such as NEC and IEC.
- Longevity: Protects both the transformer and downstream equipment from stress.
Improper sizing can result in nuisance tripping, equipment overheating, or even catastrophic failure.
Test our online tool for free Transformer Full Load Current Calculator – Accurate Load & Current Calculation Tool for Transformers
Key Parameters for Transformer Disconnect Sizing
When sizing a transformer disconnect, the following parameters must be considered:
- Transformer Rating (kVA): The transformer’s rated capacity directly influences the required disconnect current rating.
- Primary and Secondary Voltage: Determines the voltage rating of the disconnect. Voltage mismatches can lead to arcing or insulation failure.
- Full Load Current (FLC): Calculated using the formula:
FLC = (Transformer kVA × 1000) / (√3 × Voltage)This is essential for selecting a disconnect capable of handling continuous load. - Short-Circuit Current Rating: The disconnect must safely interrupt the maximum available fault current without damage.
- Ambient Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and installation environment affect the current carrying capacity of the disconnect.
Enjoy free access to our online tool Step-Down Transformer Calculator – Accurate Voltage & Power Conversion Tool
Step-by-Step Transformer Disconnect Sizing Process
Step 1: Determine Transformer Full Load Current
Calculating the full load current is the first and most critical step. For a three-phase transformer, the full load current on the primary side is:
I_primary = (Transformer kVA × 1000) / (√3 × Primary Voltage)
For the secondary side:
I_secondary = (Transformer kVA × 1000) / (√3 × Secondary Voltage)
This current is the baseline for selecting a disconnect switch rated for continuous operation.
Step 2: Select Disconnect Voltage Rating
The disconnect voltage rating should equal or exceed the transformer’s rated voltage. For example, a 480V transformer requires a disconnect rated at 600V AC to provide a safety margin and comply with NEC standards.
Use our online tool without paying anything Transformer Impedance Calculation Tool – Accurate Transformer Impedance Calculator for Engineers
Step 3: Choose Current Rating
Once the full load current is calculated, select a disconnect with a current rating 125% of the FLC. This margin ensures the disconnect can handle temporary surges without tripping unnecessarily.
| Transformer Rating (kVA) | Primary Voltage (V) | Full Load Current (A) | Recommended Disconnect Rating (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 480 | 30 | 40 |
| 50 | 480 | 60 | 75 |
| 100 | 480 | 120 | 150 |
| 150 | 480 | 180 | 225 |
| 200 | 480 | 240 | 300 |
Step 4: Verify Short-Circuit Rating
The disconnect must have an interrupting capacity equal to or higher than the maximum fault current at the transformer location. This rating is often provided in kiloamperes (kA) and ensures the disconnect can safely open the circuit during a fault.
Get started with our free online tool Transformer Efficiency Calculator – Calculate Power, Losses & Performance Instantly
Step 5: Consider Environmental Factors
Ambient temperature, installation altitude, and enclosure type affect the disconnect performance. For example, higher temperatures reduce current carrying capacity. Outdoor installations require NEMA-rated enclosures to protect against moisture and dust.
Step 6: Compliance with Standards
Always select disconnects that comply with NEC, IEC, or local electrical codes. This ensures not only safety but also legal and insurance compliance.
Types of Transformer Disconnects
Transformer disconnects come in several types, each suited for specific applications:
- Fused Disconnects: Provide overcurrent protection using integrated fuses. Ideal for small to medium transformers.
- Non-Fused Disconnects: Rely on external protection devices such as circuit breakers. Suitable for larger transformers or when selective coordination is required.
- Load Break Switches: Allow switching under load conditions safely. Common in industrial applications.
- Air Circuit Breakers (ACB): Provide high interrupting capacity for large transformers with high fault current potential.
Access our online tool completely free Transformer Vector Group Calculation Tool | Easy & Accurate Vector Group Calculator
Practical Tips for Selection
- Always size the disconnect based on the higher of primary or secondary FLC.
- Include a safety margin to account for transformer inrush currents.
- Ensure enclosure type matches the installation environment (indoor, outdoor, corrosive, dusty).
- Consider future expansion when selecting the disconnect size.
Example Calculation
Consider a 100 kVA, 480V/208V transformer.
- Primary Full Load Current:
I_primary = (100 × 1000) / (√3 × 480) ≈ 120 A
- Recommended Disconnect Rating: 125% × 120 ≈ 150 A
- Secondary Full Load Current:
I_secondary = (100 × 1000) / (√3 × 208) ≈ 277 A
- Recommended Disconnect Rating: 125% × 277 ≈ 350 A
Use our online tool for free Transformer Neutral Current Calculator – Accurate Neutral Current Estimation
This shows that the disconnect on the secondary side needs to be significantly larger than the primary to handle the current safely.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Undersizing: Choosing a disconnect below the FLC can cause nuisance tripping and overheating.
- Ignoring Short-Circuit Rating: Disconnect may fail to interrupt fault current, leading to fire hazards.
- Neglecting Environmental Conditions: High temperature, dust, or moisture can reduce disconnect life if not considered.
- Overlooking Code Compliance: Non-compliant installations can result in penalties and insurance issues.
Maintenance and Testing
Even properly sized disconnects require periodic inspection and maintenance:
- Check for loose connections that can cause arcing.
- Inspect for corrosion or dust accumulation, especially in outdoor environments.
- Test the operation of switches under load periodically to ensure reliability.
- Verify that fuses or breakers are properly rated and intact.
Know more about Transformer Oil Testing: 9 Important Tests for Healthiness
Regular maintenance extends the service life of the transformer disconnect and ensures continuous protection.
Conclusion
Transformer disconnect sizing is a crucial step in designing safe and reliable electrical systems. By carefully calculating full load current, selecting the appropriate voltage and current ratings, verifying short-circuit capacity, and considering environmental factors, you can ensure optimal protection for your transformers and downstream equipment. Using the correct disconnect enhances safety, improves reliability, and ensures compliance with electrical standards. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial installations, following a systematic approach to transformer disconnect sizing is essential for long-term operational safety and efficiency.
Know more about HVDC Transformer Working Principle Explained – How Converter Transformers Handle Extreme DC Power
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#TransformerDisconnectSizing, #ElectricalEngineering, #PowerSystems, #IndustrialElectrical, #ElectricalSafety, #TransformerProtection, #LoadCalculation, #Switchgear, #ElectricalDesign, #Energymanagement


