Steam Turbine Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Steam turbines are a vital part of the power generation industry and are extensively used in various industrial applications. This article delves into the various steam turbine types, their working principles, advantages, and applications. Whether you’re looking to understand how they function or to decide which one suits your needs, this guide covers it all.
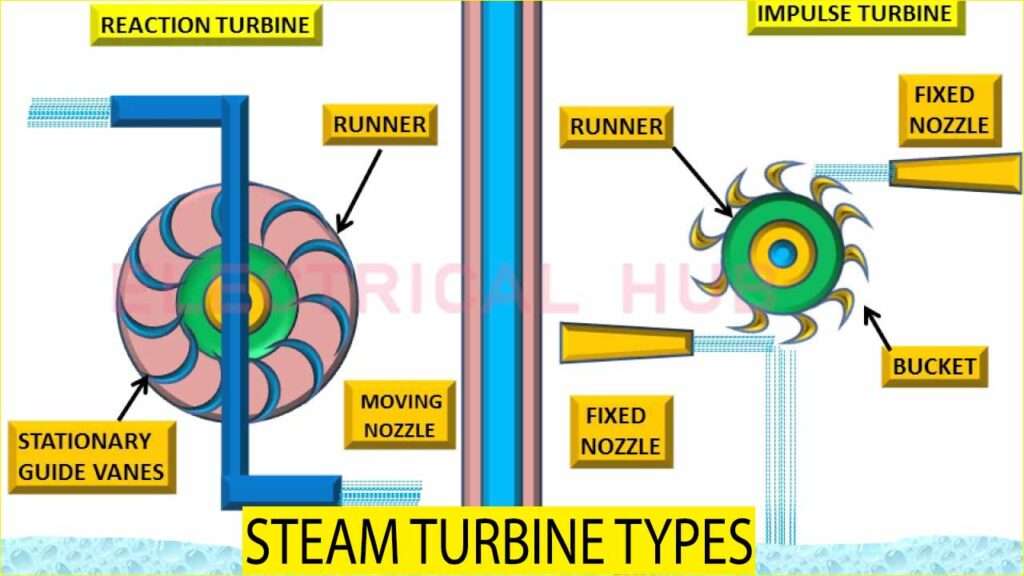
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
What are Steam Turbines?
A steam turbine is a mechanical device that converts thermal energy from pressurized steam into rotational motion. This rotational motion is then used to generate electricity or power mechanical processes. Steam turbines are widely used in power plants, industrial processes, and propulsion systems due to their efficiency and reliability.
Steam Turbine Types: Overview
There are two primary types of steam turbines based on their working principles:
- Impulse Turbine
- Reaction Turbine
Apart from these, there are other classifications based on steam flow direction, stages, and operational purposes. Below, we will explore these steam turbine types in detail.
Impulse Turbine
Working Principle
The impulse turbine works on Newton’s second law of motion. In this type, high-pressure steam is directed through nozzles to create high-velocity jets. These jets strike the turbine blades, causing them to rotate. The pressure of the steam remains constant during this process, and only its velocity changes.
Key Features
- Operates with high steam velocity.
- Pressure drops occur in the nozzles, not in the turbine blades.
- Suitable for high-speed operations.
Applications
- Power generation in Steam Turbine Power Plants.
- Industrial applications requiring high-speed operations.
Reaction Turbine
Working Principle
The reaction turbine operates on the principle of Newton’s third law of motion. In this turbine, steam expands continuously as it flows over the blades, creating a reaction force that drives the rotor. Both pressure and velocity change within the turbine blades.
Key Features
- Operates with moderate steam velocity.
- Pressure drops occur in both nozzles and turbine blades.
- Requires precise blade design for efficient operation.
Applications
- Common in industrial Steam Turbine Power Plants.
- Used in applications with varying load requirements.
Other Types of Steam Turbines
1. Axial Flow and Radial Flow Turbines
These classifications are based on the direction of steam flow.
- Axial Flow Turbines: Steam flows parallel to the axis of the rotor. They are common in large power plants.
- Radial Flow Turbines: Steam flows perpendicular to the axis. These are smaller and used in compact setups.
2. Condensing and Non-Condensing Turbines
This classification depends on how steam exits the turbine.
- Condensing Turbines: Steam exhausts into a condenser, ensuring maximum energy extraction.
- Non-Condensing Turbines: Steam exits at a higher pressure for use in other processes.
3. Single-Stage and Multi-Stage Turbines
These depend on the number of stages used to extract energy from the steam.
- Single-Stage Turbines: Steam expands in one stage, making them suitable for small-scale applications.
- Multi-Stage Turbines: Steam expands over multiple stages, maximizing efficiency in large-scale applications like power plants.
Comparison of Steam Turbine Types
The table below compares key characteristics of impulse and reaction turbines.
| Feature | Impulse Turbine | Reaction Turbine |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | High-velocity steam jet strikes blades | Continuous steam expansion over blades |
| Pressure Drop | In nozzles only | In both nozzles and blades |
| Steam Velocity | High | Moderate |
| Applications | High-speed operations | Varying load conditions |
| Blade Design | Simple | Complex |
Steam Turbine Power Plant and Applications
Steam turbines are integral to power plants, particularly in producing electricity. A steam turbine power plant works by boiling water to produce steam, which then drives the turbine to generate electricity. These plants are widely used because of their efficiency and ability to handle large power demands.
In industrial applications, steam turbines are also paired with combustion turbine generators to create combined cycle systems, further enhancing efficiency.
Which Steam Turbine Type is Right for You?
Choosing the right steam turbine depends on your specific needs:
- For high-speed operations and simplicity, an impulse turbine is ideal.
- For applications requiring efficiency under varying loads, a reaction turbine is better.
If you’re considering setting up a steam turbine power plant, understanding these turbine types is crucial to optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
Steam turbines are the backbone of power generation and industrial applications worldwide. By understanding the steam turbine types, their working principles, and applications, you can make informed decisions to meet your energy needs. Whether it’s an impulse turbine and reaction turbine or a setup with combustion turbine generators, each type has its unique strengths.
Choosing the right turbine type ensures efficient energy conversion, reduces costs, and meets the specific demands of your operation. So, whether you’re building a power plant or looking for industrial solutions, steam turbines will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the energy landscape.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering.
#SteamTurbines, #TurbineTypes, #Engineering, #PowerGeneration, #SteamPower, #MechanicalEngineering, #EnergyEfficiency, #TurbineTechnology, #IndustrialMachinery, #ThermalEnergy, #EnergySolutions, #SteamTurbineDesign, #RenewableEnergy, #EnergyEngineering, #PowerPlants
