Steam Turbine Power Plant: Working, Efficiency
Steam turbine power plants play a vital role in the global power generation sector. These plants are known for their efficiency, reliability, and ability to produce large amounts of electricity. In this article, we will explore the details of a steam turbine power plant, its working principle, cycle, and efficiency, as well as provide an overview of its key components. Let’s dive in!
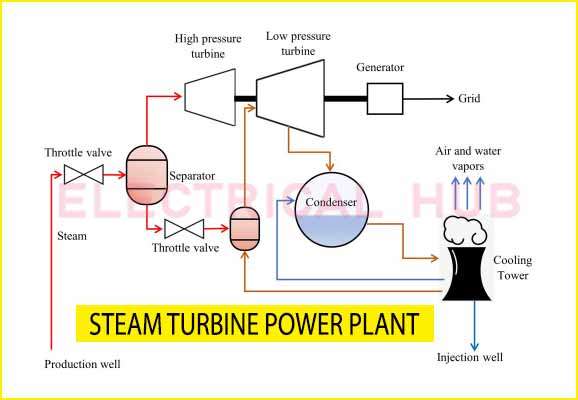
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
What is a Steam Turbine Power Plant?
A steam turbine power plant is a type of thermal power plant where heat energy from fuel combustion is converted into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy using a steam turbine. These power plants are widely used in industries and for large-scale electricity production due to their high power output and efficiency.
Steam turbine plants are designed to handle high-pressure and high-temperature steam, which rotates the turbine blades to generate power.
Key Components of a Steam Turbine Power Plant
To better understand the working of a steam turbine power plant, let’s explore its major components:
1. Boiler
The boiler is where water is heated and converted into steam. This is done by burning fuels such as coal, natural gas, or oil. Some plants also use nuclear energy to heat the water.
2. Steam Turbine
The steam turbine is the heart of the power plant. It converts the high-pressure, high-temperature steam into mechanical energy. Steam turbines are of two main types:
- Impulse turbine and reaction turbine: These designs vary in how they utilize steam to turn the blades. Impulse turbines use high-velocity steam jets, while reaction turbines rely on pressure differences to create motion.
3. Generator
The mechanical energy from the turbine is transferred to the generator, which converts it into electricity. Generators in these plants often include combustion turbine generators as part of the setup.
4. Condenser
The condenser cools and condenses the exhaust steam from the turbine back into water, which is then reused in the cycle.
5. Cooling Tower
This is used to remove excess heat from the system, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
Steam Turbine Power Plant Working Principle
The working principle of a steam turbine plant is based on the Rankine cycle. This cycle involves four main processes:
Heat Addition (in the Boiler)
Water is heated in the boiler to produce high-pressure steam.
Expansion (in the Turbine)
The high-pressure steam expands as it flows through the turbine, causing the turbine blades to rotate. This mechanical energy is then transferred to the generator.
Heat Rejection (in the Condenser)
After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled in the condenser, turning it back into water.
Pump Work
The condensed water is pumped back into the boiler to repeat the cycle.
This continuous process ensures the production of electricity without interruption.
Steam Turbine Power Plant Diagram
Understanding the layout of a steam turbine plant diagram can help visualize how the various components work together. A typical diagram consists of:
- A boiler for steam generation
- A steam turbine for energy conversion
- A generator for electricity production
- A condenser for cooling
- Pumps to maintain the cycle
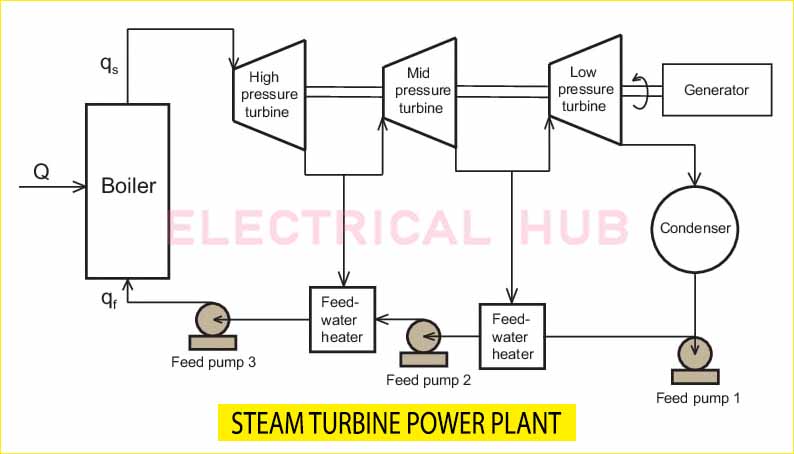
Such diagrams are crucial in understanding the flow of energy in a power plant.
Efficiency of a Steam Turbine Power Plant
The steam turbine plant efficiency depends on several factors, including the temperature and pressure of the steam, the design of the turbine, and the effectiveness of the condenser.
Factors Affecting Efficiency
High Steam Pressure and Temperature
Operating at higher pressure and temperature improves thermal efficiency.
Reheating and Regeneration
Reheating the steam after partial expansion in the turbine and using regeneration techniques can significantly enhance efficiency.
Proper Maintenance
Well-maintained turbines, boilers, and condensers can prevent energy losses and ensure optimal performance.
Steam Turbine Power Plant Cycle
The steam turbine plant cycle is primarily based on the Rankine cycle. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Boiler: Heat energy is added to water, converting it to steam.
Turbine: The steam expands and rotates the turbine blades, producing mechanical energy.
Condenser: The used steam is condensed back into water.
Feed Pump: The water is pumped back to the boiler to restart the cycle.
This cycle is repeated continuously, ensuring a steady power supply.
Advantages of a Steam Turbine Power Plant
Steam turbine plants offer several advantages:
High Efficiency: These plants can achieve high thermal efficiency when properly optimized.
Large-Scale Power Generation: Ideal for industrial and large-scale power needs.
Flexibility: Can operate with various fuel types, including coal, natural gas, and nuclear fuel.
Reliability: Known for their long service life and reliable operation.
Applications of Steam Turbine Power Plants
Steam turbine plants are used in various sectors, including:
Electricity Generation: They are the backbone of power grids worldwide.
Industrial Use: Many industries utilize steam turbines for process heating and power generation.
Nuclear Power Plants: Steam turbines are essential for converting nuclear energy into electricity.
Challenges of Steam Turbine Power Plants
While steam turbine plants are highly efficient, they also face certain challenges:
Environmental Impact: Combustion of fossil fuels produces greenhouse gases.
High Initial Cost: Setting up a steam turbine plant requires significant investment.
Water Requirements: These plants consume large amounts of water for steam generation and cooling.
Conclusion
Steam turbine plants are a cornerstone of modern power generation. Their ability to produce large amounts of electricity efficiently makes them indispensable. One can appreciate the engineering marvel behind these plants by understanding the working principle, cycle, and efficiency factors.
Whether for large-scale power grids or industrial applications, steam turbine plants remain one of the most reliable and effective solutions for meeting the world’s growing energy demands.
For further insights into turbine designs, explore the differences between impulse turbine and reaction turbine, and check how combustion turbine generators are integrated into hybrid systems. These concepts add depth to understanding the versatility and importance of steam turbine power plants.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights to get the latest updates in Electrical Engineering.
#SteamTurbine, #PowerPlant, #EnergyProduction, #RenewableEnergy, #ThermalPower, #TurbineEngineering, #PowerGeneration, #MechanicalEngineering, #CleanEnergy, #EnergyEfficiency, #IndustrialEnergy, #TurbineTechnology, #SteamEnergy, #SustainablePower, #GreenEnergy
