Reverse Polarity Protection Using MOSFET: Efficient Circuit Design for Reliable Power Safety
Reverse polarity is one of the most common issues in electronic circuits, often leading to permanent damage to sensitive components. Whether you are designing a small consumer device or a large industrial system, ensuring that your circuit is safe from accidental polarity reversal is critical.
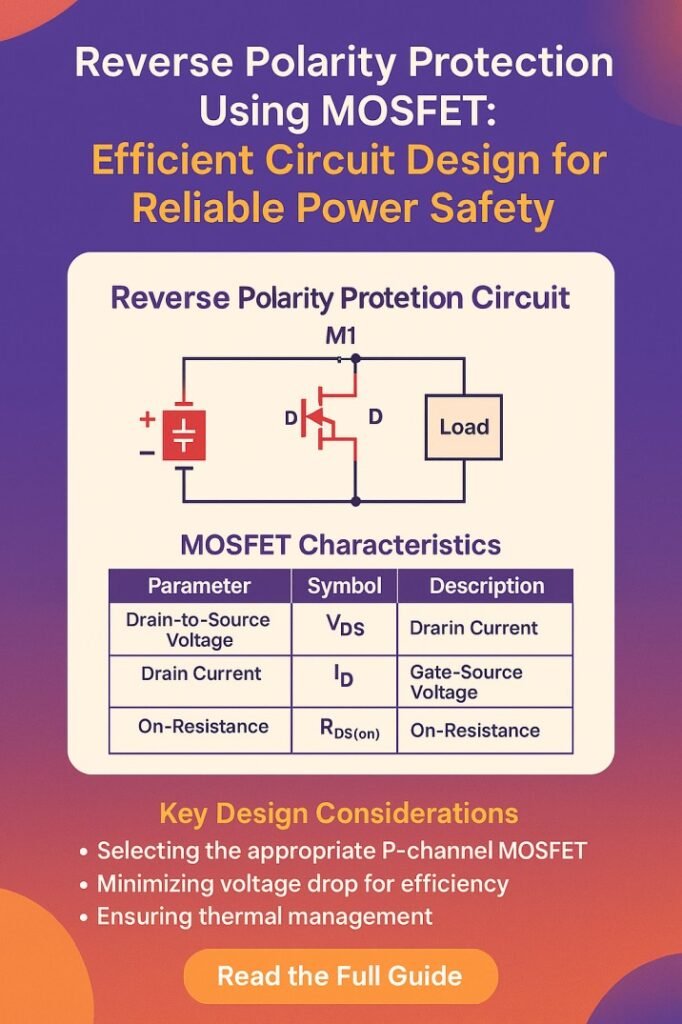
Table of Contents
Reverse polarity protection using MOSFET is an efficient and reliable solution that has become a preferred choice among engineers due to its low voltage drop, fast response, and minimal power loss. In this article, we explore the principles, design considerations, and practical implementations of MOSFET-based reverse polarity protection circuits.
What is Reverse Polarity?
Reverse polarity occurs when the positive and negative connections of a power supply are accidentally swapped. In traditional systems, this can lead to:
- Blown fuses
- Damaged semiconductors
- Short-circuited PCB traces
- Complete device failure
For example, connecting a 12V battery in reverse to a microcontroller board can instantly destroy voltage regulators or other critical ICs. Therefore, designing an effective reverse polarity protection circuit is crucial for reliable device operation.
Know more about Types of Field Effect Transistor
Why Use MOSFET for Reverse Polarity Protection?
MOSFETs, specifically P-channel and N-channel types, have become a preferred method for reverse polarity protection due to several advantages over traditional diode-based solutions:
| Feature | Diode Protection | MOSFET Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Drop | 0.7V (Silicon) or 0.3V (Schottky) | 0.02V–0.05V (typical, depends on Rds(on)) |
| Power Loss | Higher due to forward voltage drop | Significantly lower |
| Efficiency | Reduced efficiency | Higher efficiency |
| Response Time | Instant, but heat generation | Instant, minimal heat |
| Complexity | Simple | Slightly more complex, requires gate control |
MOSFET-based protection circuits are particularly suitable for battery-powered systems and devices where energy efficiency is a priority. The extremely low voltage drop of MOSFETs ensures that almost all the supplied power reaches the load, making them ideal for high-current applications.
Know more about Leakage Current in MOSFET
How MOSFET-Based Reverse Polarity Protection Works
The core idea of reverse polarity protection using MOSFET is to allow current to flow only when the input voltage is correctly polarized. When the polarity is reversed, the MOSFET automatically blocks the current, protecting the downstream circuitry. The mechanism depends on the type and orientation of the MOSFET:
- P-Channel MOSFET: Usually placed in the high side (between power source positive and load). The gate is connected to ground or a negative reference. When voltage is correctly applied, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current flow. When polarity is reversed, it turns off automatically.
- N-Channel MOSFET: Often used in low-side configurations, connected between the load and ground. Reverse voltage prevents the MOSFET from conducting, blocking current flow.
The correct selection of MOSFET parameters, especially Rds(on), maximum drain current, and gate threshold voltage, is critical for efficient operation. A low Rds(on) minimizes voltage drop, while a suitable gate-source voltage ensures proper switching.
Circuit Design Considerations
When designing a reverse polarity protection circuit using MOSFET, engineers should consider the following factors:
| Parameter | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| MOSFET Type | P-Channel for high-side, N-Channel for low-side |
| Maximum Current | Must exceed expected load current by 20–30% |
| Rds(on) | As low as possible to reduce voltage drop |
| Gate Threshold Voltage | Compatible with input supply voltage |
| Power Dissipation | Calculate based on Rds(on) and current |
| Thermal Management | Consider heat sinks for high-power applications |
An efficient design should balance protection, cost, and efficiency. For portable devices, minimizing voltage drop is essential to maximize battery life. In industrial systems, robustness against high-current spikes and thermal reliability becomes more critical.
Know more about Floating Gate MOSFET: A Comprehensive Guide
Advantages of Using MOSFET over Traditional Diodes
While diodes are simple and cost-effective for reverse polarity protection, MOSFETs provide several benefits:
- Lower Voltage Drop: Reduces energy loss, especially in high-current circuits.
- Higher Efficiency: Essential for battery-powered devices.
- Better Thermal Performance: Less heat generation compared to diodes.
- Automatic Switching: No additional control circuitry needed.
- Scalability: Can handle large currents with parallel MOSFETs.
By reducing energy loss and thermal stress, MOSFET-based protection enhances both device reliability and lifespan.
Example Circuit of Reverse Polarity Protection Using MOSFET
Consider a simple high-side P-Channel MOSFET configuration:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| P-Channel MOSFET | Main switch allowing current flow only with correct polarity |
| Resistor (10kΩ) | Pull-down for gate to ensure proper turn-off in reverse polarity |
| Load | Device being protected |
| Input Source | Power supply or battery |
Working Principle: When the input voltage is applied correctly, the MOSFET gate-source voltage turns the device on, allowing current to flow to the load. If the input is reversed, the gate-source voltage is insufficient to turn on the MOSFET, blocking current completely and protecting the load.
Know more about N-channel Enhancement Type MOSFET
Practical Tips for Reliable Design
- Select MOSFETs with Low Rds(on): A lower Rds(on) reduces voltage drop and power loss. For example, a MOSFET with Rds(on) of 0.01Ω at 5A results in only 0.05V drop.
- Consider Current Rating: Always choose a MOSFET with a higher current rating than your maximum load. This ensures safe operation under transient spikes.
- Thermal Management: In high-current applications, MOSFETs can generate heat. Adding a small heat sink or using MOSFETs with low thermal resistance improves longevity.
- Gate Protection: Adding a small resistor or Zener diode to the gate can prevent voltage spikes that may accidentally turn on the MOSFET in reverse polarity situations.
- PCB Layout: Keep traces short and wide to minimize resistance and ensure proper thermal dissipation.
Common Applications
Reverse polarity protection using MOSFET is widely used across multiple sectors:
| Application | Reason for Use |
|---|---|
| Battery-powered devices | Prevents damage from accidental battery reversal |
| Solar panels | Protects inverters and controllers from incorrect connections |
| Automotive electronics | Ensures safety against reversed car battery connections |
| Industrial control systems | Safeguards PLCs, sensors, and relays from wiring errors |
| Consumer electronics | Extends product lifespan by preventing accidental damage |
MOSFET-based circuits are increasingly preferred in modern electronics due to their efficiency and reliability, especially in portable and energy-sensitive applications.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Even with MOSFET-based protection, some issues may arise:
- Excessive Heating: Often caused by undersized MOSFETs or high Rds(on). Check MOSFET specifications and improve cooling.
- Load Not Receiving Power: Ensure correct MOSFET orientation and gate connection.
- Voltage Drop Too High: Select MOSFETs with lower Rds(on) or parallel multiple devices for high-current loads.
- Noise or Transients: Adding small capacitors at the input or gate can stabilize operation.
Know more about How N-Channel MOSFET Works? Important Facts We Must Know
Routine inspection of the MOSFET and connections ensures long-term reliability.
Conclusion
Reverse polarity protection using MOSFET provides an efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solution for safeguarding electronic devices. Its low voltage drop, fast response, and minimal power loss make it superior to traditional diode-based solutions, especially in high-current and battery-operated systems. By carefully selecting MOSFET parameters and designing circuits with proper thermal and electrical considerations, engineers can achieve robust protection that extends device lifespan and ensures operational safety. From consumer electronics to industrial systems, MOSFET-based reverse polarity protection has become a standard practice for reliable power safety.
Adopting this approach not only prevents damage but also improves energy efficiency and enhances overall circuit performance. With the right design and implementation, reverse polarity protection using MOSFET ensures that devices operate safely and reliably under all conditions.
Find all about Types of Transistor
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#ReversePolarityProtection, #MOSFETProtection, #ElectronicCircuits, #CircuitDesign, #PowerElectronics, #MOSFETCircuit, #PCBDesign, #OvervoltageProtection, #ElectronicsEngineering, #PowerSafety