Parallel Run for 300Amp 480/277: A Complete Guide
When designing electrical systems, ensuring a reliable power supply is critical. One important method used in medium-voltage systems is the parallel run for 300amp 480/277. This technique enhances system reliability, ensures load balancing, and allows maintenance without disrupting the power supply.
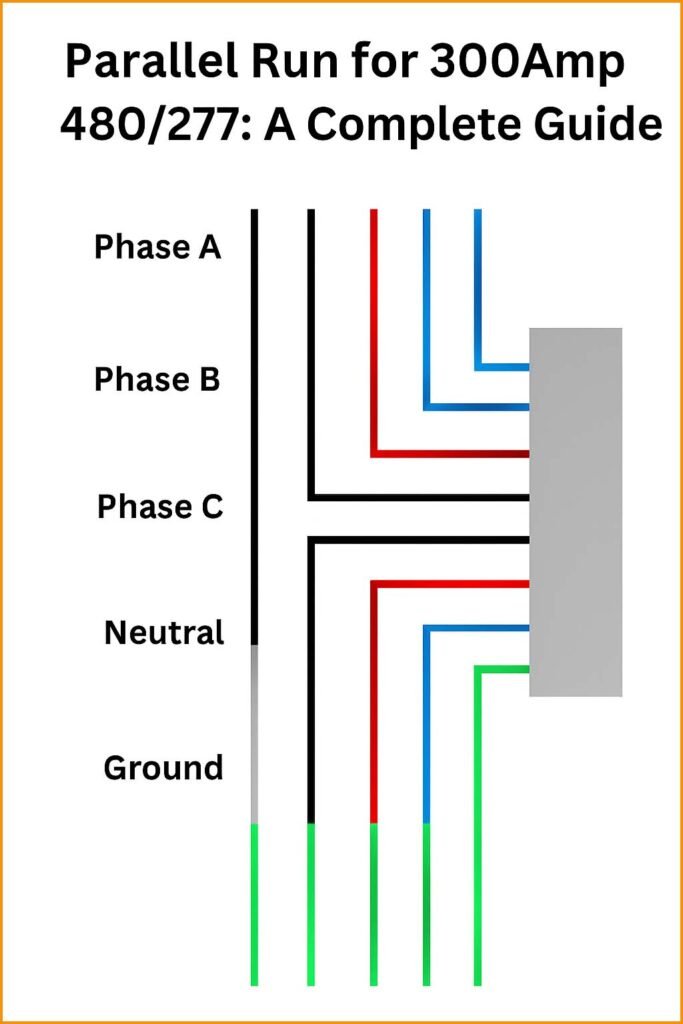
Table of Contents
In this article, we will explore the apparatus used, IEC standards, methods of implementation, and other key aspects of parallel runs. By the end, you will understand how to plan and execute a parallel run efficiently while complying with international standards.
What is a Parallel Run?
A parallel run involves connecting two or more feeders, cables, or busbars in parallel to share the electrical load. For a 300amp 480/277V system, this ensures that current is distributed evenly, reducing overheating risks and minimizing voltage drops.
Parallel runs are widely used in industrial, commercial, and critical facilities where continuous power supply is essential.
Know more about VLF Testing vs Hipot: Best Guide on Key Differences and Applications
Why Use Parallel Runs for 300Amp 480/277 Systems?
Parallel runs offer several benefits:
- Redundancy: If one feeder fails, the other continues to supply power.
- Load balancing: Reduces the risk of overloading a single conductor.
- Maintenance flexibility: Allows one feeder to be isolated for inspection without shutting down the system.
- Reduced voltage drop: By splitting the current, cable heating is minimized.
This method is particularly critical in large buildings, data centers, hospitals, and industrial plants where downtime can be costly.
Know more about IEC Standards for Transformer Testing – Complete Guide to IEC 60076 and Testing Procedures
Apparatus Used in Parallel Runs
Implementing a parallel run for 300amp 480/277 requires careful selection of electrical equipment. Here are the main components:
| Apparatus | Function |
|---|---|
| Circuit Breakers | Protects each feeder from overload and short circuits. Must be rated for 300A at 480/277V. |
| Busbars | Used to connect feeders in parallel. Copper or aluminum busbars are preferred. |
| Cables | Appropriately rated power cables with proper insulation and ampacity. Typically XLPE insulated cables. |
| CTs (Current Transformers) | For monitoring and load balancing in each feeder. |
| Panel Boards | Houses breakers and allows organized parallel connections. |
| Protection Relays | Ensures coordination and prevents circulating currents between parallel feeders. |
| Earthing System | Provides safety and fault current protection. Must comply with earthing cable size as per IEC standards. |
Know more about 277 480 volt 3 phase
IEC Standards Relevant to Parallel Runs
Following IEC standards ensures safety, efficiency, and uniformity in design. Key standards include:
- IEC 60364: Electrical installations of buildings – fundamental for design and safety.
- IEC 60947: Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear – relevant for breakers used in parallel runs.
- IEC 61439: Low-voltage switchgear assemblies – guidelines for busbar and panel construction.
- IEC 60287: Calculates current-carrying capacity of cables – essential to select proper conductor size.
- IEC 60364-5-52: Selection and erection of electrical cables.
- IEC 60364-5-54: Earthing and protection against electric shock.
Following these standards ensures a safe, efficient, and long-lasting parallel run.
Methods for Implementing Parallel Run
There are several ways to set up a parallel run for 300amp 480/277. Proper planning is key to avoid issues like circulating currents or uneven load distribution.
1. Identical Feeder Method
Use two identical feeders connected to the same busbar. Both feeders should have:
- Equal cable lengths.
- Same conductor size.
- Identical breaker ratings.
This method is simple and effective for industrial installations.
Know more about 480v 3-phase 4 wire
2. Load Sharing with CTs
Install CTs on each feeder to monitor current. Use a control system to adjust breaker settings or introduce series reactors if needed. This method ensures precise load sharing and avoids feeder overloading.
3. Parallel Busbar Connection
Two or more busbars are connected in parallel, and feeders are distributed among them. This approach reduces voltage drop and allows easier expansion of the system in the future.
4. Redundant Supply Method
One feeder acts as the main supply while the second is normally open. It only comes into operation when the main feeder trips. This method is common in critical facilities like hospitals or data centers.
Steps to Design a Parallel Run
- Load Analysis: Determine total load and distribution across feeders.
- Cable Selection: Choose cable size based on ampacity, voltage drop, and thermal limits. Follow IEC 60287 and earthing cable size as per IEC.
- Breaker Selection: Choose breakers rated for 300A and coordination with protective devices.
- Busbar Design: Ensure busbars can handle combined current of parallel feeders.
- Protection Coordination: Set up relays and CTs to prevent circulating currents.
- Testing & Commissioning: Perform tests for insulation, continuity, and load sharing before energizing the system.
Know more about IEC Standard for XLPE Cables – Complete Guide to IEC 60502 and Electrical Cable Specifications
Cable Size Selection for Parallel Run
Correct cable sizing is critical to avoid overheating and voltage drops. For a 300amp 480/277V system, the following table provides guidance:
| Cable Type | Conductor Material | Current Rating (A) | Recommended Size (mm²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| XLPE/SWA/LSZH | Copper | 300 | 120 |
| XLPE/SWA | Aluminum | 300 | 185 |
| Flexible XLPE | Copper | 300 | 150 |
Note: Always check local regulations and IEC standards for exact sizing. Include proper earthing conductor following earthing cable size as per IEC.
Safety Considerations
When working on a parallel run, safety is paramount:
- Ensure all breakers are isolated before maintenance.
- Verify earthing system is intact.
- Avoid mismatch in feeder lengths or sizes to prevent circulating currents.
- Regularly inspect cable insulation and busbars.
- Follow IEC 60364 and 60947 standards strictly.
Common Challenges in Parallel Runs
Even experienced engineers face challenges with parallel runs:
- Unequal load distribution: Can cause overheating in one feeder.
- Circulating currents: Occur if feeders are not identical or if breaker settings are misaligned.
- Voltage drop issues: Longer feeders can create imbalance.
- Maintenance coordination: Requires careful planning to avoid system downtime.
Proper design, adherence to IEC standards, and periodic testing can eliminate most of these challenges.
Know more about IEC Standard for Vacuum Circuit Breaker – IEC 62271 Guidelines, Ratings & Testing Explained
Advantages of Properly Designed Parallel Runs
- Increased system reliability and uptime.
- Reduced thermal stress on cables and equipment.
- Simplified maintenance without shutting down the system.
- Flexibility for future expansion.
- Compliance with international standards ensures safety.
Conclusion
A parallel run for 300amp 480/277 is a reliable way to enhance electrical system performance. By carefully selecting apparatus like breakers, busbars, and cables, and following IEC standards, engineers can ensure load balancing, safety, and redundancy. Implementing proper methods such as identical feeders, load sharing, or redundant supply ensures the system operates efficiently.
Always consider correct earthing cable size as per IEC for fault protection and safety. With meticulous planning, a parallel run can provide uninterrupted power, long-term reliability, and compliance with global electrical standards.
Know more about IEC Standard for Voltage Drop Calculation: Best Guide
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#ParallelRun, #300Amp, #480277Voltage, #ElectricalEngineering, #PowerDistribution, #IECStandards, #ElectricalInstallation, #HighCurrentCables, #FeederDesign, #IndustrialElectricity