N-channel Enhancement Type MOSFET! A Brief Introduction
N-Channel enhancement type MOSFET normally goes in off condition whenever the voltages across the source and the gate terminals are at zero. So, in order to keep the n-channel enhancement type MOSFET in ON condition we must supply the voltages at the Gate terminal of the MOSFET. The doping of substrate in this type of MOSFET is very light and consists of P-type material. We can also call this substrate the body of the MOSFET.
The doping of the Source and the drain terminals in n-channel enhancement type MOSFET is very heavy. They consist of n-type material and normally connect to the ground terminal. So, the turning on and off procedure for n-channel MOSFET is very easy. We can achieve it by just controlling the “VDD” and the gate voltages.
To keep the MOSFET in the on condition we need to apply sufficient “VDD” (drain voltages). And also apply positive voltages across the gate and the source terminal. To turn off the MOSFET, we can follow two steps either remove the drain voltages or the gate positive voltages. Both will take the n-channel MOSFET in the off condition.
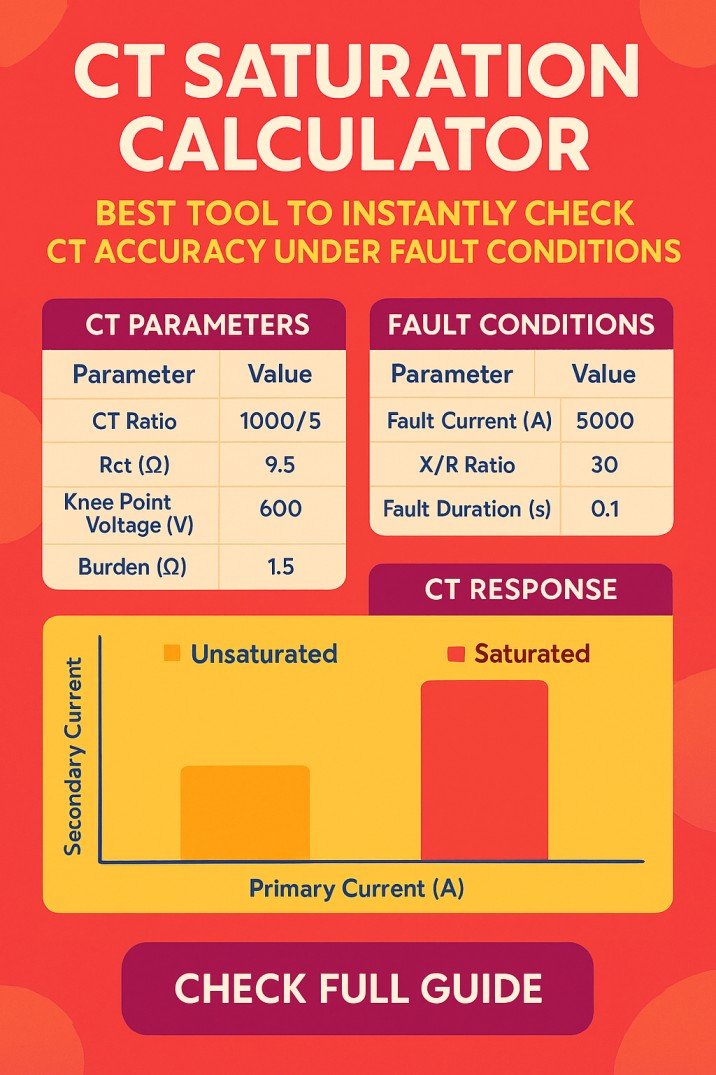
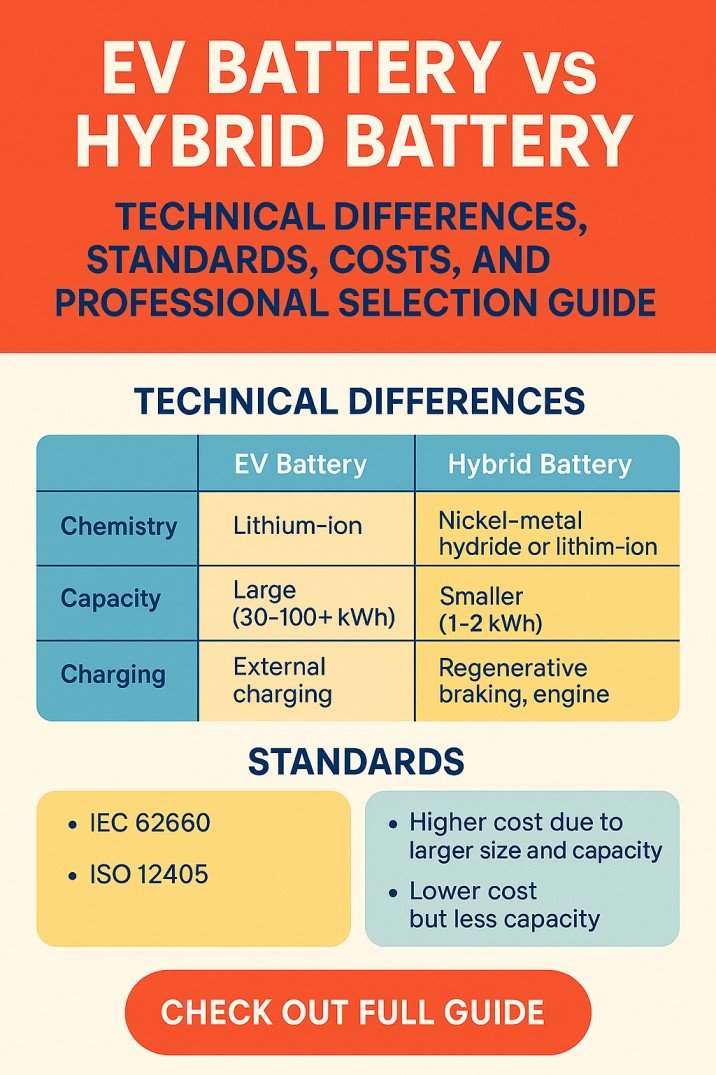
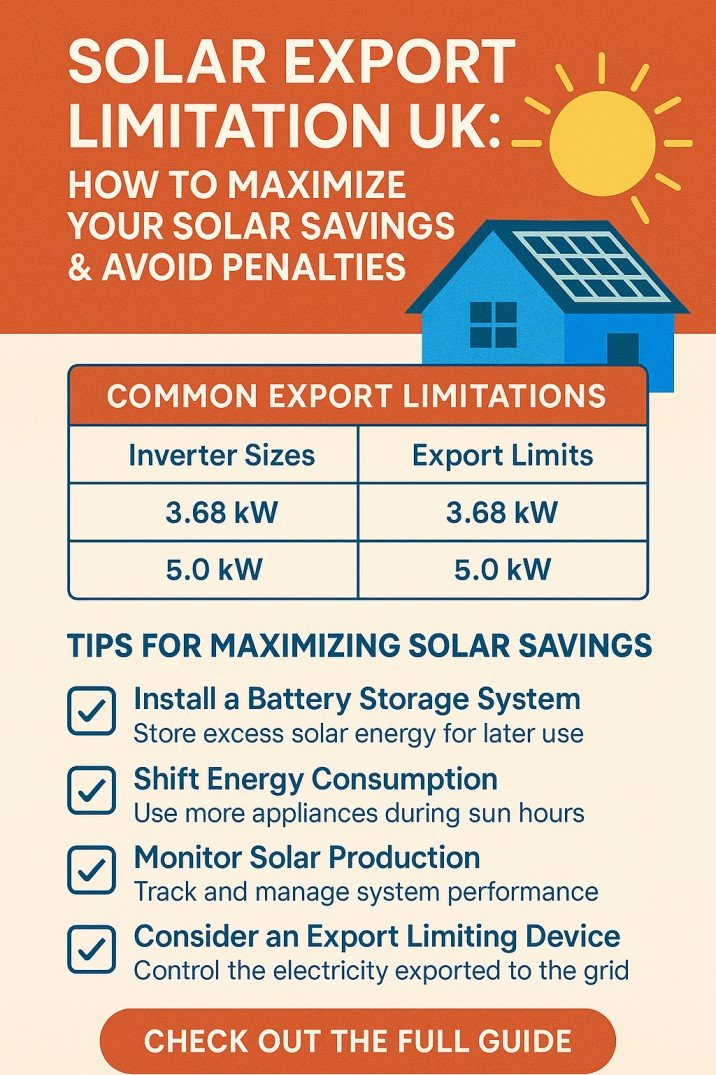
N-channel enhancement type MOSFET
Let’s have a look at the below figure of the n-channel and p-channel MOSFET.
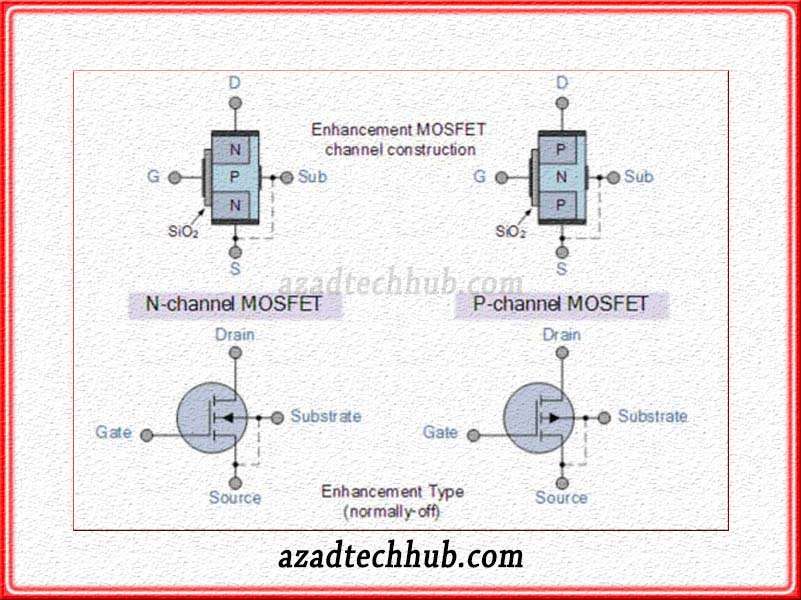
As we can see in the above figure the P-channel and the source connect together. The gate terminal connects itself with the P-channel through a fine layer of silicon dioxide material. In other words, the gate terminal does not connect with the p-channel electrically and isolates itself from the channel. The below figure shows the symbolic representation of the n-channel MOSFET where we can see the substrate connects with the source.
On the other hand, when we look at the P-channel enhancement type MOSFET, the channel consists of n-type material where doping is very light. While the drain and the source terminals are p-type materials and doping is very high.
Topics You might be interested in:
- Transformer Testing Before Commissioning: Important Pre-Commissioning Checklist & Electrical Test Procedures Guide
- Best Megger Insulation Testers 5000V – Top 5kV Megohmmeters for Industrial High-Voltage Testing
- Best Megger Insulation Testers 1000V – Top Rated 1000V Megohmmeters for Accurate Electrical Testing
- Step Down Transformer Sizing Calculator – Accurate kVA Rating & Load Calculation Tool
- Motor Failure Causes: 7 Most Common Reasons Your Motor Stops Working
- Electric Motor Failure Symptoms: 12 Critical Warning Signs Every Engineer Must Identify Early
- Electric Motor Not Starting Reasons – 12 Critical Causes & Proven Troubleshooting Solutions
- Single-Phase Motor Problems and Solutions – Complete Troubleshooting & Repair Guide for Electrical Engineers
- Electric Motor Troubleshooting Chart – Complete Fault Diagnosis & Repair Guide for Engineers
- Transformer OCPD Sizing Chart – Accurate Breaker & Fuse Selection Guide as per NEC
- Transformer Neutral Sizing – Complete Calculation Guide for Accurate Conductor Selection & Compliance
- Demand Factor for Transformer Sizing – Accurate Load Calculation & Optimal kVA Selection Guide