Electrical Panel Heat Load Calculation: Best Guide
Introduction
Electrical panels generate heat due to power losses in electrical components. If this heat is not managed properly, it can lead to overheating, equipment failure, and safety hazards. Electrical panel heat load calculation is essential for designing a safe and efficient electrical system.
This article explains the importance of heat load calculation, the factors affecting heat dissipation, and the correct method to calculate it.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents

Why Electrical Panel Heat Load Calculation is Important
Every electrical component inside a panel generates heat. If the temperature exceeds safe limits, it can cause several issues:
- Reduced Equipment Lifespan: Overheating degrades insulation, circuit breakers, and other components.
- Safety Hazards: Excess heat increases the risk of electrical fires.
- Efficiency Loss: High temperatures reduce the efficiency of electrical devices, leading to energy waste.
- Operational Failures: Overheating can cause tripping, shutdowns, or malfunctioning of electrical systems.
Proper electrical panel heat load calculation ensures a well-designed cooling system that keeps the panel temperature within safe operating limits.
Factors Affecting Heat Load in Electrical Panels
1. Internal Heat Generation
Electrical components inside the panel generate heat. This heat comes from:
- Power loss in transformers, circuit breakers, and contactors.
- Resistance in wires and terminals.
- Electronic devices such as power supplies and PLCs.
2. Ambient Temperature
The surrounding temperature affects the panel’s internal heat level. Panels installed in hot environments require better cooling solutions.
3. Enclosure Material and Size
The material and dimensions of the panel influence heat dissipation. Metal enclosures conduct heat better than plastic ones, reducing internal temperature.
4. Airflow and Ventilation
Panels with proper ventilation allow heat to escape naturally. Enclosures in enclosed spaces or without airflow may experience higher heat buildup.
5. Solar Heat Gain
If the panel is installed outdoors, exposure to sunlight increases heat load. This must be considered in the heat load calculation.
How to Calculate Electrical Panel Heat Load
Step 1: Identify Heat Sources
List all electrical components inside the panel. Find the power loss for each device, usually provided in the manufacturer’s datasheet.
For example, if a device consumes 100W and operates at 90% efficiency, the power loss (heat dissipation) is:

Repeat this for all components and sum up the losses.
Step 2: Calculate External Heat Load
If the panel is in a warm environment, heat transfers from outside to inside. Use this formula to estimate external heat load:

The heat transfer coefficient depends on the enclosure material.
Step 3: Total Heat Load Calculation
The total heat load is the sum of internal and external heat sources:
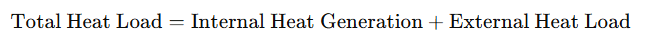
Example Calculation
Consider an electrical panel with the following details:
- Panel Dimensions: 2m (Height) × 1m (Width) × 0.5m (Depth)
- Total Power Loss: 200W
- Ambient Temperature: 40°C
- Desired Internal Temperature: 30°C
Step 1: Surface Area Calculation
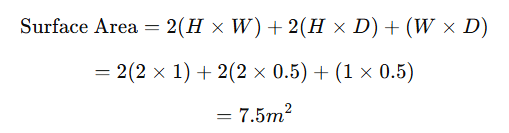
Step 2: External Heat Transfer Calculation
For a 10°C temperature difference, the heat transfer coefficient for a metal enclosure is 5W/m².
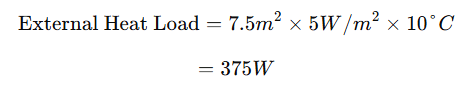
Step 3: Total Heat Load
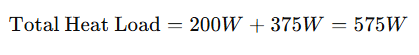
Cooling Solutions for Electrical Panels
Once the total heat load is known, cooling methods can be selected.
1. Natural Ventilation
- Uses vents to allow hot air to escape.
- Suitable for low heat loads.
2. Forced Ventilation
- Uses cooling fans to push hot air out and pull cool air in.
- Effective for moderate heat loads.
3. Air Conditioning or Heat Exchangers
- For high heat loads, an air conditioner or heat exchanger is needed.
- Maintains temperature at desired levels.
Tools for Electrical Panel Heat Load Calculation
Several tools are available for accurate heat load calculations:
- Generator Size Calculator – Helps determine generator size based on load requirements.
- Electrical Service Calculator – Assists in electrical service size selection.
- Electricity Load Calculator in kW for Home – Estimates home energy consumption.
- Solar Power Load Calculator – Calculates load requirements for solar power systems.
- Electrical Load Calculator – Determines total electrical load for a system.
- Electrical Panel Design Calculations – Helps design safe and efficient electrical panels.
Conclusion
Accurate electrical panel heat load calculation is essential for maintaining safe and efficient operations. By considering internal and external heat sources, selecting the right cooling solutions, and using reliable calculation tools, overheating risks can be minimized.
Whether designing new panels or upgrading existing systems, heat load management ensures longevity, efficiency, and safety in electrical installations.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
ElectricalPanel #HeatLoadCalculation #ElectricalEngineering #PowerDistribution #CoolingSystems #HVAC #HeatDissipation #ElectricalDesign #PanelCooling #ThermalManagement #EnergyEfficiency #ElectricalSafety #LoadCalculation #IndustrialAutomation #CoolingSolutions




![Best EV Chargers for Hotels & Guest Accommodations [Commercial Grade] 12 Best EV Chargers for Hotels & Guest Accommodations [Commercial Grade]](https://azadtechhub.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Best-EV-Chargers-for-Hotels-Guest-Accommodations-Commercial-Grade-768x512.jpg)
