CT Saturation Calculator: Best Tool to Instantly Check CT Accuracy Under Fault Conditions
Introduction
The CT saturation calculator is designed to help electrical professionals evaluate whether a current transformer will operate within its linear region under specific fault and load conditions. In power systems, current transformers are critical for protection relays, metering accuracy, and overall system reliability. When a CT saturates, it can no longer reproduce the primary current accurately on the secondary side, leading to protection maloperation or delayed fault clearing.
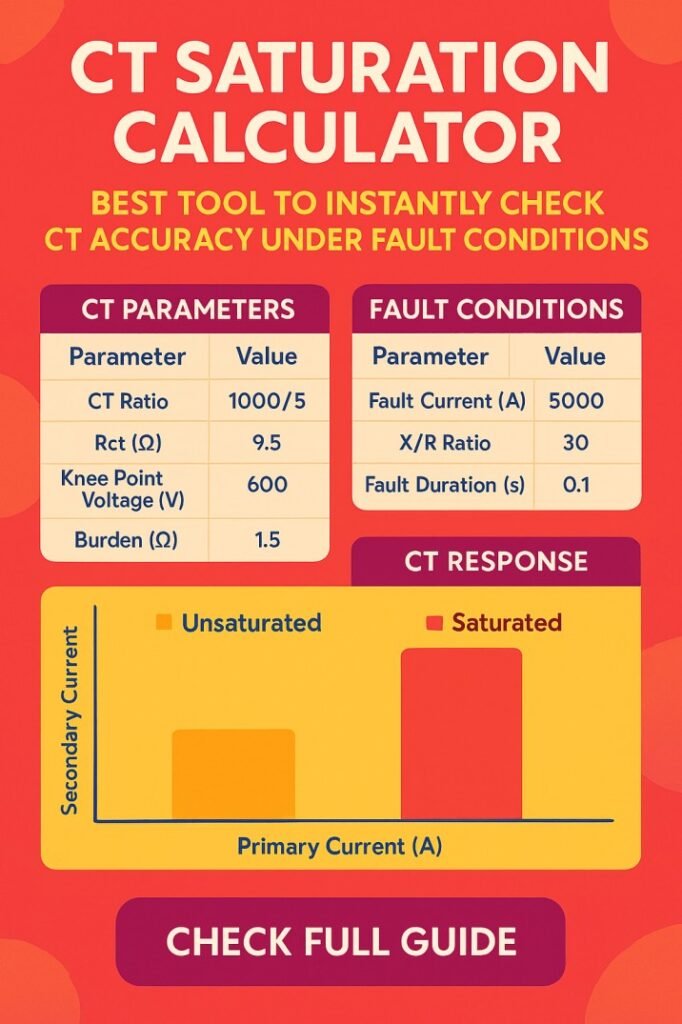
Table of Contents
This calculator is commonly used during protection design, relay coordination studies, and commissioning of substations, switchgear, and industrial power systems. Engineers rely on the CT saturation calculator to assess performance during high fault currents, long secondary cable runs, or when multiple relays are connected to a single CT core.
Accurate electrical calculation is essential because CT saturation directly affects safety, equipment protection, and compliance. A small misjudgment can result in false trips, failure to trip, or damaged protection equipment. This page provides both the calculator and the technical guidance needed to interpret the results correctly.
Use our online tool for free Sub Panel Sizing Calculator: Best Tool to Use
CT Saturation Calculator
Use the CT saturation calculator below by entering the required current transformer and system values. Once the inputs are filled, calculate to instantly assess saturation risk under the selected conditions.
Ensure that all values are taken from verified drawings, CT nameplates, or protection study data for reliable results.
CT Saturation Calculator
Evaluate CT saturation risk with IEC & NEC context
Inputs
How to use
- Enter CT rated current, secondary current, burden VA, knee‑point voltage, and fault current.
- Select accuracy class or enter a custom class.
- Click Calculate to see burden resistance, required voltage, and saturation check.
- Adjust inputs to reflect your CT application, installation, and compliance requirements.
Technical notes
- Burden resistance is derived from burden VA and secondary current.
- Required voltage is based on fault current, CT ratio, and burden resistance.
- Saturation check compares required voltage with knee‑point voltage to assess CT performance.
Find more Electrical Engineering Tools for easy electrical calculations and estimations.
How to Use CT Saturation Calculator (Step-by-Step)
- Enter the rated primary current of the current transformer as specified on the CT nameplate.
- Input the rated secondary current, typically 1 A or 5 A depending on the CT design.
- Provide the burden connected to the CT secondary, including relay impedance and lead resistance.
- Enter the expected fault current level at the installation point.
- Select any additional parameters requested by the calculator related to system voltage or application.
- Click calculate to obtain the saturation assessment and interpretation.
Each step is designed to guide even first-time users through the evaluation process without requiring advanced protection engineering knowledge.
How the Calculation Works
The CT saturation calculator works by comparing the magnetic capability of the CT core with the electrical demand imposed by the connected burden during fault conditions. When fault current flows, the CT must generate sufficient secondary voltage to drive current through the connected burden.
If the required voltage exceeds what the CT core can produce without entering saturation, the output current becomes distorted. The calculator evaluates this balance by considering CT rating, burden magnitude, and fault current level. The output indicates whether the CT operates within acceptable limits or if saturation is likely.
Rather than focusing on mathematical expressions, the logic is based on real-world transformer behavior. Higher fault currents, longer cable runs, or heavier burdens increase the likelihood of saturation, which the calculator highlights clearly.
Use our online tool for free Sub Panel Breaker Size Calculator – Find the Right Breaker for Your Electrical Sub Panel
Practical Electrical Example
Consider a medium-voltage switchgear panel feeding a large motor group in an industrial plant. The protection scheme includes overcurrent and earth fault relays connected to a single set of protection-class CTs.
The CT primary rating is selected based on normal load current, while the secondary circuit includes multiple relays and long cable runs to a control room. During a short-circuit study, the maximum fault current at the panel is identified.
Using the CT saturation calculator, the engineer enters the CT ratings, total secondary burden, and fault current. The calculated result shows that under maximum fault conditions, the CT core approaches saturation early in the fault cycle.
This result allows the engineer to reconsider CT class selection, reduce secondary burden, or modify relay settings before installation, avoiding future protection issues.
Key Factors That Affect the Result
Several electrical and operational factors influence the outcome of a CT saturation calculator assessment:
- System voltage level, which affects fault current magnitude
- Type of load connected, such as motors or transformers with high inrush currents
- Power factor, especially in industrial systems with inductive loads
- CT core material and accuracy class
- Total secondary burden, including relay impedance and cable resistance
- Ambient temperature and installation conditions that affect resistance values
Use our online tool Creepage Distance Calculator – Calculate Safe Insulation & Clearance for PCB and High Voltage Design
Understanding these factors helps users interpret the calculator output beyond a simple pass or fail indication.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrect use of a CT saturation calculator often stems from incomplete or inaccurate input data. Common issues include:
- Ignoring secondary cable resistance, especially for long runs
- Using nominal load current instead of maximum fault current
- Mixing metering and protection CT data
- Assuming all CTs with the same ratio behave the same under fault conditions
- Overlooking future expansion that adds extra burden to the secondary circuit
These mistakes can lead to underestimating saturation risk, which has serious implications for protection reliability and safety compliance.
Why Use This CT Saturation Calculator
The CT saturation calculator provides a structured way to evaluate transformer performance without relying on assumptions or rough estimates. It supports accurate engineering decisions during design, review, and troubleshooting stages.
By using this calculator, professionals can save time during protection studies, reduce rework during commissioning, and improve confidence in relay performance. It also helps align design decisions with utility and industrial best practices, ensuring dependable fault detection and isolation.
We recommend this tool for anyone struggling with the sizing of subpanels. Try here Wire Size Calculator for Subpanels and Feeders – NEC Guidelines Included
Electrical Standards & Practical Considerations
Current transformer performance is guided by internationally recognized electrical standards and utility practices. These standards define accuracy classes, knee-point characteristics, and testing requirements to ensure predictable behavior under fault conditions.
Using a CT saturation calculator alongside standard guidelines improves coordination between CT selection, relay settings, and system fault levels. This approach enhances system stability, protects equipment, and reduces the risk of non-compliance during audits or inspections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is CT saturation and why is it important?
CT saturation occurs when a current transformer cannot accurately reproduce primary current, which can cause protection relays to malfunction.
When should I use a CT saturation calculator?
It should be used during protection design, fault analysis, relay coordination studies, and before commissioning new electrical systems.
Does CT saturation affect metering accuracy?
Yes, but it is more critical for protection circuits, where inaccurate current measurement can delay or prevent fault clearing.
Can reducing burden prevent CT saturation?
Lowering secondary burden often improves CT performance and reduces the risk of saturation under fault conditions.
Is CT saturation only a problem during faults?
It mainly occurs during high-current events such as short circuits, but severe inrush conditions can also contribute in some systems.
Explore this tool here to simplify your work instantly Neutral Conductor Sizing Calculator – Accurate Neutral Wire Size for Electrical Circuits
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#CTSaturationCalculator, #CTSizingGuide, #CurrentTransformer, #ProtectionEngineering, #RelayProtection, #CTAccuracy, #SubstationDesign, #FaultCurrentAnalysis, #PowerSystemStudies, #ElectricalCalculations