Types of Transmission Lines Explained: Overhead vs Underground with Important Applications
Electrical power systems depend heavily on transmission networks to deliver electricity from generating stations to substations and distribution grids. Understanding the types of transmission lines is essential for electrical engineers, planners, students, and even policymakers involved in energy infrastructure. Each transmission method has its own design philosophy, cost structure, performance limits, and application areas.
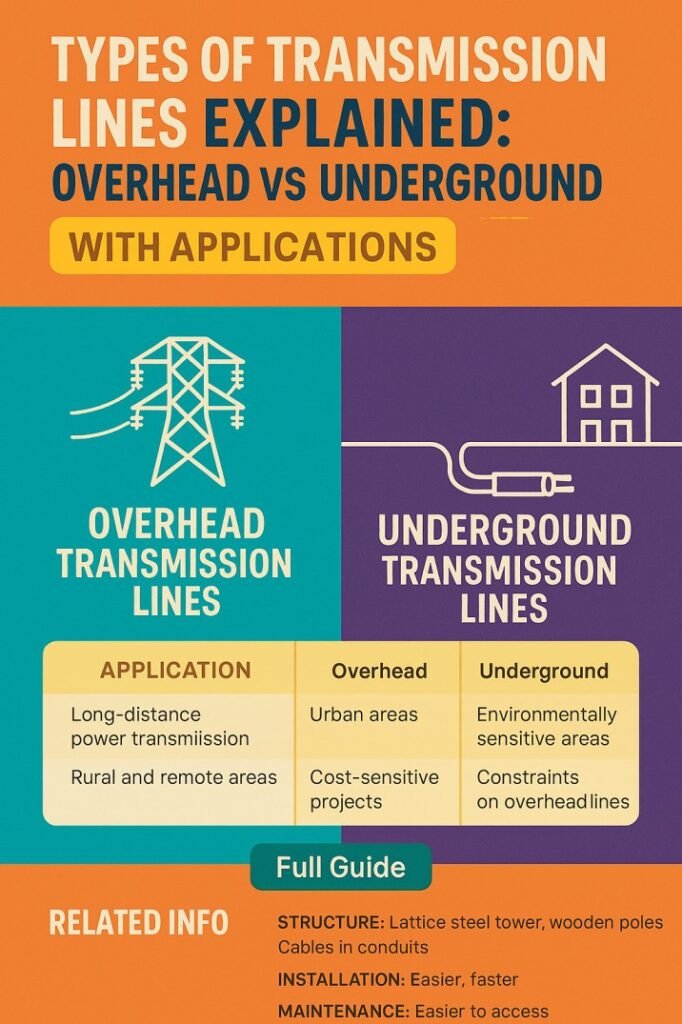
Table of Contents
This article explains the major types of transmission lines, with a clear comparison between overhead and underground transmission systems. Practical applications, advantages, limitations, and selection criteria are discussed in a simple, human-written style to ensure clarity and strong readability.
What Are Transmission Lines in Power Systems
Transmission lines are conductors that carry high-voltage electrical power over long distances. They operate at voltage levels typically above 33 kV and are designed to minimize losses while maintaining system stability. Among the different types of transmission lines, the choice depends on voltage level, distance, terrain, environmental conditions, and economic factors.
Know more about types of faults in transmission lines
From a structural perspective, transmission lines are broadly classified into overhead transmission lines and underground transmission lines. Both are essential parts of modern power networks and often coexist within the same grid.
Overview of Types of Transmission Lines
The most common types of transmission lines used in power systems can be grouped based on their physical installation and electrical behavior.
Table 1: Basic Classification of Transmission Lines
| Classification Basis | Types |
|---|---|
| Installation method | Overhead transmission lines, Underground transmission lines |
| Length | Short, Medium, Long transmission lines |
| Voltage level | High voltage, Extra high voltage, Ultra high voltage |
| Current type | AC transmission lines, DC transmission lines |
Among these, overhead and underground systems are the most widely discussed because they differ significantly in construction, performance, and applications.
Know more about bus differential protection
Overhead Transmission Lines Explained
Overhead transmission lines are the most commonly used among all types of transmission lines. They consist of bare conductors supported by poles or towers and insulated from the ground using insulators.
These lines are usually installed in open areas, rural regions, highways, and long-distance corridors where space is available.
Construction and Components
An overhead transmission line typically includes the following components:
- Conductors made of aluminum, copper, or ACSR
- Insulators such as porcelain, glass, or composite
- Supporting structures like steel lattice towers or concrete poles
- Ground wire or shield wire for lightning protection
Advantages of Overhead Transmission Lines
Overhead systems dominate most power grids due to several practical benefits:
- Lower installation cost compared to underground systems
- Easier fault detection and maintenance
- Efficient heat dissipation to surrounding air
- Suitable for very high and ultra-high voltage levels
These advantages make overhead lines the preferred option for long-distance bulk power transmission.
Know more about hvdc transmission
Limitations of Overhead Transmission Lines
Despite their benefits, overhead lines have certain drawbacks:
- Visual impact on landscapes
- Exposure to weather conditions like storms and lightning
- Higher right-of-way requirements
- Risk of outages due to falling trees or accidents
Even with these limitations, overhead systems remain one of the most economical types of transmission lines for large-scale power transfer.
Underground Transmission Lines Explained
Underground transmission lines are installed below the earth’s surface, usually within ducts or trenches. They are increasingly used in urban areas where space is limited and visual impact must be minimized.
These types of transmission lines use insulated cables rather than bare conductors, which significantly changes their thermal and electrical behavior.
Know more about High Voltage Testing Procedures for Electrical Panels: Step by Step
Construction and Components
An underground transmission system generally includes:
- Power cables with XLPE or oil-impregnated insulation
- Metallic sheath for grounding and protection
- Protective outer jacket
- Cable ducts or tunnels
Advantages of Underground Transmission Lines
Underground systems offer several important benefits:
- Minimal visual impact and improved aesthetics
- Higher reliability in extreme weather conditions
- Reduced risk of accidental contact
- Lower electromagnetic exposure at the surface
Because of these features, underground systems are often selected in densely populated areas.
Limitations of Underground Transmission Lines
The limitations of underground lines are mainly related to cost and maintenance:
- High initial installation cost
- Complex fault location and repair
- Limited current-carrying capacity due to heat dissipation
- Difficult upgrades once installed
For these reasons, underground systems are selectively used among the various types of transmission lines, rather than replacing overhead networks entirely.
Know more about Power Quality Analyzer Buying Guide for Engineers
Overhead vs Underground Transmission Lines Comparison
Understanding the differences between these two major types of transmission lines helps engineers choose the right option for specific applications.
Table 2: Comparison of Overhead and Underground Transmission Lines
| Parameter | Overhead Transmission Lines | Underground Transmission Lines |
|---|---|---|
| Installation cost | Low | Very high |
| Maintenance | Easy and quick | Difficult and time-consuming |
| Visual impact | High | Negligible |
| Fault detection | Simple | Complex |
| Weather impact | High | Very low |
| Typical application | Long-distance, rural | Urban, congested areas |
This comparison clearly shows that neither system is universally better. Instead, each serves a specific purpose within the power grid.
Explore details on iec standard for underground cable laying
Applications of Different Types of Transmission Lines
The practical use of different types of transmission lines depends on voltage level, location, and power demand.
Applications of Overhead Transmission Lines
Overhead lines are widely used in:
- Interconnection of power plants and substations
- Cross-country transmission corridors
- Renewable energy evacuation from wind and solar farms
- Rural and semi-urban power networks
Their ability to handle extra high voltage makes them ideal for bulk power transfer.
Applications of Underground Transmission Lines
Underground systems are commonly applied in:
- Urban city centers
- Airports and railway corridors
- Industrial zones with space constraints
- Environmentally sensitive areas
These types of transmission lines improve reliability and safety where overhead construction is impractical.
Use our online tool Creepage Distance Calculator – Calculate Safe Insulation & Clearance for PCB and High Voltage Design
Factors Affecting the Choice of Transmission Line Type
Selecting among different types of transmission lines involves technical and economic analysis. Key decision factors include:
- Voltage and power level
- Distance of transmission
- Land availability and right-of-way
- Environmental and aesthetic requirements
- Maintenance strategy and reliability targets
A balanced evaluation ensures optimal system performance and lifecycle cost.
Use this tool if you are trying to calculate cable size for underground cables. Try here Underground Cable Size Calculator – Find Correct Wire Size for Long Distance Runs
Future Trends in Transmission Line Technologies
Modern power systems are evolving rapidly, and so are the types of transmission lines used within them. High-voltage direct current systems, gas-insulated lines, and underground cable tunnels are gaining popularity.
Smart monitoring systems are also being integrated to improve fault detection, thermal management, and predictive maintenance for both overhead and underground networks.
Conclusion
The types of transmission lines used in electrical power systems play a critical role in ensuring reliable and efficient energy delivery. Overhead transmission lines remain the backbone of long-distance power transfer due to their low cost and high capacity. Underground transmission lines, while expensive, provide unmatched advantages in urban and sensitive environments.
Understanding the differences, applications, and limitations of these systems allows engineers and planners to design robust power networks that meet modern energy demands. A well-balanced mix of overhead and underground transmission lines is essential for a resilient and future-ready electrical grid.
Designing electrical system? Use this clearance and creepage calculator for accurate distances
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#TypesOfTransmissionLines, #PowerTransmission, #ElectricalEngineering, #OverheadTransmission, #UndergroundCables, #HVTransmission, #PowerSystems, #ElectricGrid, #TransmissionLineDesign, #HighVoltage