Types of Lightning Arrester Explained: Important Guide for Power Systems & Substations
Lightning is one of the most dangerous natural threats to electrical power systems. A single lightning strike can cause insulation failure, equipment damage, outages, and even fire hazards. To protect power networks, engineers rely on lightning arresters. Understanding the types of lightning arrester used in power systems and substations is essential for proper selection, installation, and maintenance.

Table of Contents
This guide explains all major lightning arrester types in a clear and practical way, focusing on real-world power system applications. Whether you work in utilities, substations, or industrial power distribution, this article will help you make informed decisions.
What Is a Lightning Arrester?
A lightning arrester is a protective device installed between a live conductor and ground. Its purpose is to divert high-voltage surges caused by lightning or switching operations safely to earth. Under normal operating voltage, the arrester remains inactive. When a surge appears, it conducts and limits the overvoltage to a safe level.
The selection of correct types of lightning arrester depends on system voltage, insulation level, environmental conditions, and equipment sensitivity.
Know more about 7 Common Mistakes in Electrical Outlet Height
Why Lightning Arresters Are Critical in Power Systems
Lightning arresters play a vital role in maintaining system reliability and safety. Without them, transient overvoltages can destroy transformers, circuit breakers, and control equipment.
Key reasons for using lightning arresters include:
- Protection of insulation from flashover
- Reduction in transformer and switchgear failures
- Improved system reliability and uptime
- Lower maintenance and replacement costs
- Compliance with power system protection standards
Know more about IEC Standard for Busbar Clearance
Classification of Lightning Arresters
Engineers classify lightning arresters based on construction, operating principle, and voltage level. The following sections explain the commonly used types of lightning arrester found in substations and power networks.
Rod Gap Lightning Arrester
Rod gap arresters are one of the simplest and earliest forms of surge protection. They consist of two rods separated by an air gap, connected between the line and earth.
When a high-voltage surge occurs, the air gap breaks down and allows the surge to pass to ground.
Advantages of rod gap arresters:
- Simple design
- Low cost
- Easy installation
Limitations:
- Poor voltage control
- Not suitable for modern substations
- Affected by weather conditions
Because of these limitations, rod gap arresters are rarely used in modern systems but still appear in rural or temporary installations.
Know more about IEC Standard for MV Cable Testing: Complete Acceptance, Routine & Type Test Guide
Horn Gap Lightning Arrester
Horn gap arresters use two horn-shaped electrodes with a narrow gap at the bottom. When a surge occurs, an arc forms and rises upward due to thermal effects, eventually extinguishing.
This design offers better arc control than simple rod gaps.
Key features:
- Self-extinguishing arc
- Improved reliability over rod gaps
- Moderate cost
Horn gap arresters were once popular in medium-voltage systems, but today they are largely replaced by advanced designs.
Multi-Gap Lightning Arrester
Multi-gap arresters consist of several spark gaps connected in series with grading resistors. These resistors help distribute voltage evenly across the gaps.
During normal operation, the gaps remain non-conductive. During a surge, the combined gaps break down and discharge energy safely.
Benefits of multi-gap arresters:
- Better voltage distribution
- Improved surge handling
- Reduced follow current
These types of lightning arrester were widely used in older substations but have limited application in modern high-performance systems.
Know more about IEC Standard for Insulation Resistance Test – Procedures, Limits & Best Practices Explained
Expulsion Type Lightning Arrester
Expulsion arresters use a fiber tube with an internal spark gap. When a surge occurs, an arc forms inside the tube, producing gases that expel the arc and interrupt current flow.
Common applications include:
- Distribution lines
- Rural substations
- Pole-mounted transformers
Advantages:
- Simple and robust
- Low cost
- Suitable for outdoor use
Disadvantages:
- Limited life expectancy
- Requires regular inspection
- Less precise voltage control
Valve Type Lightning Arrester
Valve type arresters were a major advancement in surge protection. They use nonlinear resistors, typically silicon carbide, in series with spark gaps.
At normal voltage, resistance is high. During a surge, resistance drops sharply, allowing current to flow to ground.
Key advantages:
- Better voltage limiting
- Improved protection for transformers
- Higher reliability than gap-only designs
Limitations include aging of components and larger physical size compared to modern alternatives.
Use our online tool Creepage Distance Calculator – Calculate Safe Insulation & Clearance for PCB and High Voltage Design
Metal Oxide Lightning Arrester
Metal oxide arresters are the most widely used solution today. They use zinc oxide varistors without spark gaps, offering fast response and excellent voltage control.
These arresters react almost instantly to surges and return to high resistance after the event.
Advantages of metal oxide arresters:
- Gapless design
- Superior protection levels
- Long service life
- Compact size
Because of these benefits, metal oxide designs dominate modern types of lightning arrester used in substations and industrial power systems.
Comparison of Common Lightning Arrester Types
The table below summarizes the main differences between commonly used lightning arresters.
| Lightning Arrester Type | Voltage Control | Maintenance | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rod Gap | Poor | Low | Temporary systems |
| Horn Gap | Moderate | Medium | Medium voltage lines |
| Multi-Gap | Good | Medium | Older substations |
| Expulsion Type | Moderate | High | Distribution lines |
| Valve Type | Good | Medium | Power transformers |
| Metal Oxide | Excellent | Low | Modern substations |
Explore details on Electrical Compliance Testing – Safety Regulations | Best Electrical Services in USA
Selection Criteria for Lightning Arresters
Choosing the right lightning arrester requires careful evaluation of system parameters. Engineers consider several factors before finalizing the types of lightning arrester.
Important selection factors:
- System rated voltage
- Maximum continuous operating voltage
- Lightning impulse withstand level
- Short-circuit current capability
- Environmental conditions
- Installation location
Proper coordination with insulation levels ensures effective protection without unnecessary operation.
Know more about What Is Early Streamer Emission A Practical Guide for Engineers, Standards, and Lightning Protection Design
Installation Practices in Substations
Correct installation is as important as correct selection. Poor installation can reduce the effectiveness of even the best arrester.
Best practices include:
- Keep ground leads as short as possible
- Use low-resistance earthing systems
- Install close to protected equipment
- Avoid sharp bends in conductors
Following these guidelines improves surge discharge performance and system safety.
Learn more about Arc Flash Risk Assessment According to NFPA 70E
Maintenance and Testing Considerations
Modern metal oxide arresters require minimal maintenance, but periodic inspection is still recommended.
Common checks include:
- Visual inspection for cracks or contamination
- Leakage current measurement
- Ground resistance testing
Routine maintenance extends service life and ensures reliable performance during lightning events.
Applications Across Power System Levels
Different types of lightning arrester serve different voltage levels and applications.
| Application Area | Recommended Arrester Type |
|---|---|
| Transmission lines | Metal oxide |
| Power transformers | Metal oxide or valve type |
| Distribution networks | Expulsion or metal oxide |
| Industrial substations | Metal oxide |
Matching the arrester type with application needs improves protection efficiency.
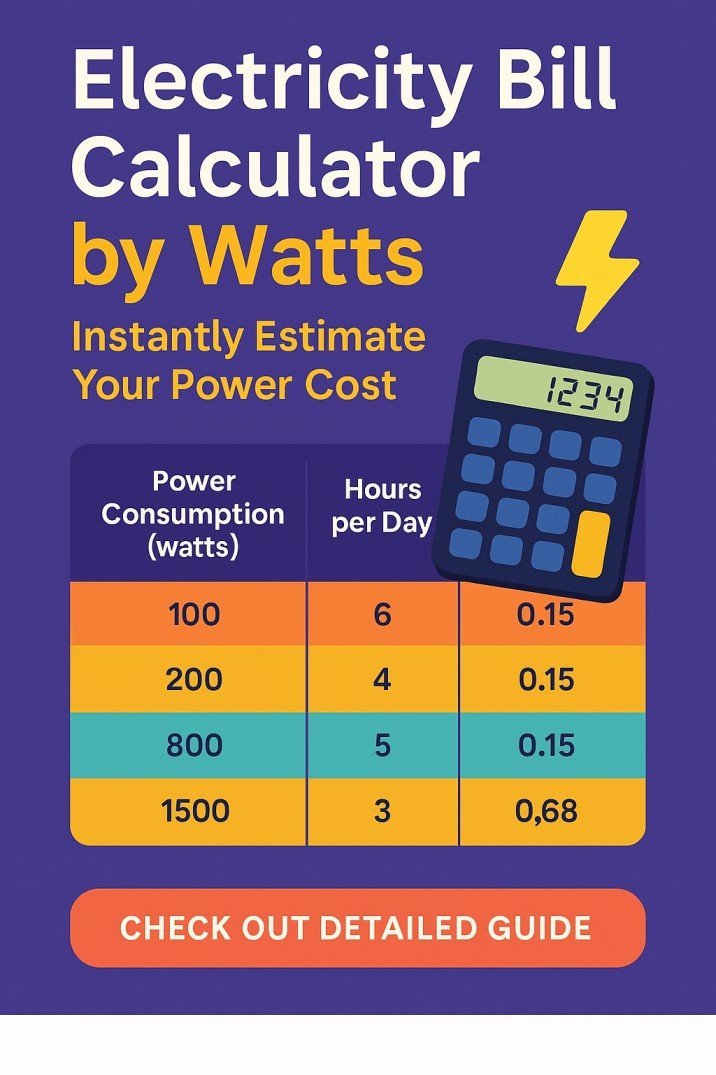
Use our online tool electricity load calculator in kw for home
Final Thoughts
Lightning arresters are a fundamental part of power system protection. Understanding the types of lightning arrester helps engineers design safer, more reliable electrical networks. While older designs laid the foundation, modern metal oxide arresters now provide superior performance for substations and industrial systems.
By selecting the right arrester, installing it correctly, and maintaining it properly, power utilities can significantly reduce equipment damage, outages, and operational risks. This knowledge is essential for anyone involved in electrical engineering, power system design, or substation operation.
Use our online tool for free Wire Size Calculator for Subpanels and Feeders – NEC Guidelines Included
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#TypesOfLightningArrester, #LightningArresterTypes, #SurgeProtection, #ElectricalSafety, #PowerSystemProtection, #LightningProtectionSystem, #HighVoltageEngineering, #ElectricalDesign, #SubstationEquipment, #OvervoltageProtection