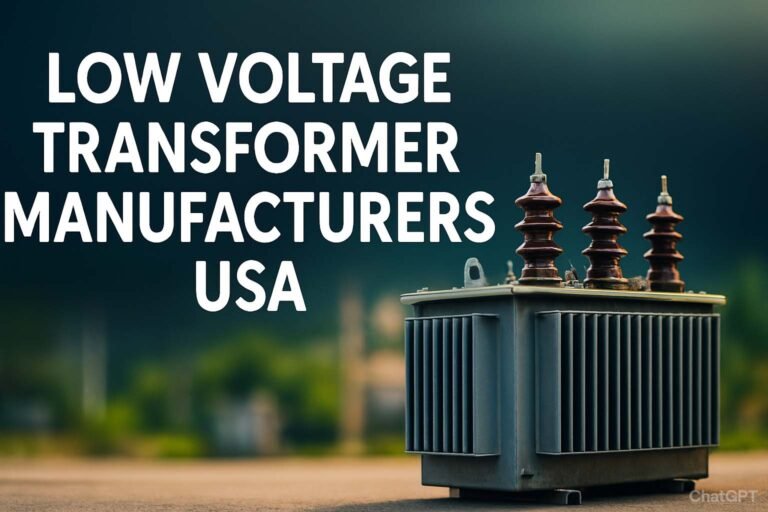
Working Principle of an Earth Fault Relay: How It Protects Electrical Systems
An earth fault relay is an essential component in electrical protection systems. It safeguards equipment and personnel from the dangers of ground faults. Understanding the working principle of an earth fault relay helps engineers, technicians, and electricians ensure safety and reliability in electrical networks.
Table of Contents
Earth faults occur when an unintended connection develops between a phase conductor and the ground. Such faults can damage equipment, cause fire hazards, and even pose risks to human life. An earth fault relay detects these faults and triggers protective actions.
Working Principle of an Earth Fault Relay
The working principle of an earth fault relay is based on detecting the leakage or imbalance in current flowing through a system. In a balanced three-phase system, the sum of the currents in all three phases equals zero. If there is a leakage to the ground, this balance is disturbed. The earth fault relay senses this imbalance.
The relay usually operates in coordination with a current transformer (CT). The CT monitors the current in the system and feeds the data to the relay. When the relay detects a current exceeding a preset threshold, it sends a trip signal to the circuit breaker. This disconnects the faulty section, preventing further damage.
Know more about IEC Standards for Transformer Testing – Complete Guide to IEC 60076 and Testing Procedures
Key Components of an Earth Fault Relay
- Current Transformer (CT) – Senses current and provides proportional signals to the relay.
- Relay Coil – Energized when an earth fault is detected.
- Trip Mechanism – Sends a signal to circuit breakers to isolate the faulty line.
- Time Delay Unit – Provides adjustable delay to prevent nuisance tripping due to transient currents.
These components work together to detect even minor leakage currents. Modern earth fault relays are highly sensitive and can detect currents as low as a few milliamperes. Learn more about is 277 high voltage
Types of Earth Fault Relays
There are mainly three types of earth fault relays based on their operation:
| Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Comparison Type | Compares phase currents and detects imbalance | High-voltage systems |
| Residual Current Type | Uses sum of three-phase currents to detect leakage | Distribution systems |
| Directional Earth Fault Relay | Detects the direction of fault current | Networks with multiple sources |
Each type has specific applications. The residual current type is the most common for low and medium voltage systems.
Know more about IEC Standard for XLPE Cables – Complete Guide to IEC 60502 and Electrical Cable Specifications
Operating Mechanism of an Earth Fault Relay
The relay operates in a simple but effective manner. Let’s understand it step by step:
- Normal Condition: In a healthy system, the sum of the phase currents is zero. The relay remains inactive.
- Fault Condition: If a phase touches the ground or insulation fails, a small leakage current flows through the earth.
- Detection: The current transformer senses this leakage. The relay coil gets energized.
- Time Delay Activation: The relay waits for a preset time to avoid tripping due to short transients.
- Trip Signal: If the fault persists, the relay sends a trip command to the breaker. The faulty line is disconnected.
This process ensures that only genuine faults cause disconnection. It minimizes system downtime and improves safety. Discover everything about Parallel Run for 300Amp 480/277
Advantages of Using Earth Fault Relays
Using an earth fault relay provides multiple benefits. Some of them are:
- Enhanced Safety: Protects humans from electric shocks.
- Equipment Protection: Prevents damage to transformers, generators, and motors.
- Reduced Downtime: Quick isolation of faults helps maintain continuous operation.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces maintenance and repair costs caused by faults.
The correct setting of the relay is crucial. Improper settings may lead to nuisance tripping or delayed fault detection.
Know more about IEC Standard for Vacuum Circuit Breaker – IEC 62271 Guidelines, Ratings & Testing Explained
Sensitivity and Setting of an Earth Fault Relay
Sensitivity refers to the minimum current the relay can detect. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the full load current. High sensitivity ensures early detection of ground faults. Explore details on iec and ieee standards
The setting of the relay depends on:
- Load current
- Fault current level
- System configuration
- Type of relay used
For example, in a distribution system, the relay may be set to detect 10–30% of the rated current. In high voltage systems, directional relays are often preferred to pinpoint the fault location.
Practical Applications
Earth fault relays are widely used in:
- Transformers: To prevent winding damage due to ground faults.
- Motors: To protect from insulation failure.
- Generators: For detecting earth faults in large generators.
- Distribution Lines: Ensures safety in low and medium voltage networks.
They are also integrated with SCADA and protection panels for real-time monitoring. Know more about load factor calculation formula
Common Misconceptions
Many people confuse earth fault relays with overcurrent relays. While both protect electrical systems, their functions differ:
- Overcurrent Relay: Responds to excessive current in the system, irrespective of ground connection.
- Earth Fault Relay: Specifically responds to current leakage to the earth.
Another misconception is that earth fault relays are only needed in high-voltage systems. In reality, they are equally important in low and medium voltage networks. Get complete information about power factor correction calculations
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance ensures that the earth fault relay functions reliably. Recommended practices include:
- Checking CTs for proper connection.
- Testing relay tripping at periodic intervals.
- Verifying time delay settings.
- Inspecting the relay panel for loose connections.
A well-maintained relay increases system reliability and prevents accidents.
Know more about TOP 10 Electrical Contractor Insurance Companies for Saudi Arabia
Summary
The working principle of an earth fault relay is simple yet critical. It monitors the current balance in a system, detects any leakage to the ground, and sends a trip signal to isolate the faulty section. By protecting equipment and personnel, it ensures the safe and efficient operation of electrical networks.
Easily calculate kva for house using our online tool for free
With the use of proper settings, timely maintenance, and understanding of relay types, earth fault relays can significantly enhance electrical safety. Their role in modern power systems cannot be overstated.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#EarthFaultRelay, #ElectricalProtection, #RelayWorkingPrinciple, #PowerSystemSafety, #FaultDetection, #ElectricalEngineering, #CircuitProtection, #IndustrialAutomation, #RelayOperation, #ElectricalSafety