VLF Testing vs Hipot: Best Guide on Key Differences and Applications
When it comes to testing high-voltage cables and electrical insulation systems, two common methods stand out — VLF testing and Hipot testing. Many engineers, technicians, and electrical contractors often ask which one is better or when to use each. This article explores VLF testing vs Hipot in detail, helping you understand their principles, advantages, and best applications.
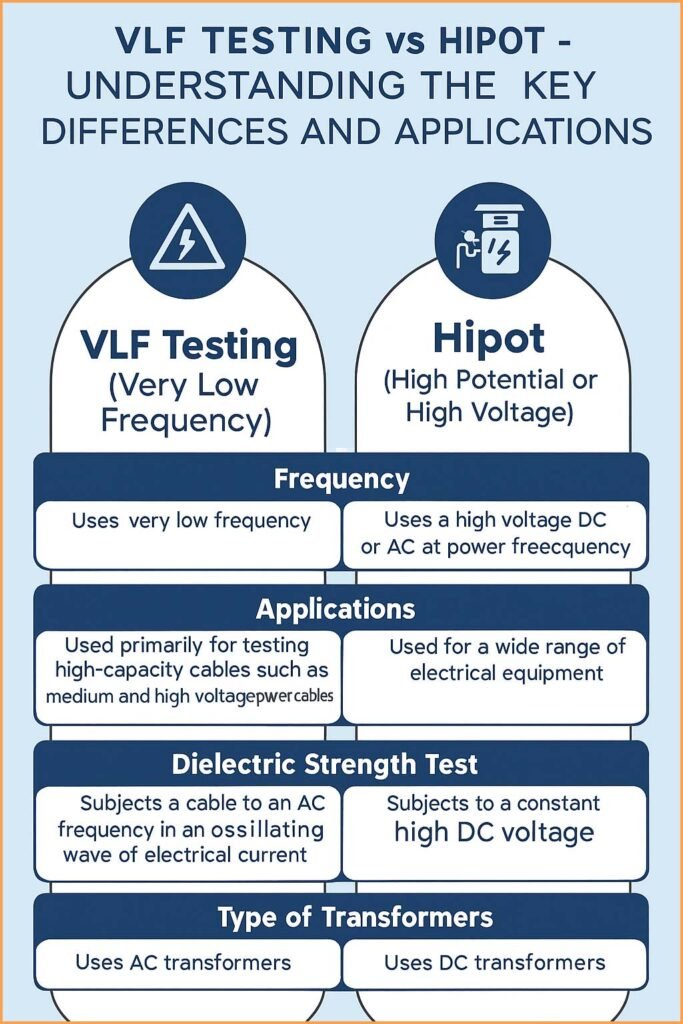
Table of Contents
What is VLF Testing?
VLF stands for Very Low Frequency. It is a type of high-voltage AC testing used to check the integrity of medium and high-voltage power cables, generators, and transformers. The frequency used in VLF testing is typically between 0.01 Hz and 0.1 Hz, much lower than the standard 50 or 60 Hz power frequency.
In VLF testing, a high AC voltage is applied at a very low frequency to the insulation system. Because of the low frequency, the reactive power demand is significantly reduced, allowing for the testing of long cables with smaller and more portable equipment.
VLF tests help identify insulation deterioration, moisture ingress, partial discharge activity, and other defects before they lead to costly failures in service.
Know more about High Voltage Cable Testing Standards: Complete Guide for Engineers
What is Hipot Testing?
Hipot stands for “High Potential.” It is a dielectric withstand test used to verify the insulation strength between electrical conductors and ground. The test applies a high voltage (AC or DC) across the insulation for a specific duration to see if it can withstand the voltage without breaking down.
Hipot testing is commonly used for quality control during manufacturing and maintenance inspections. It ensures that insulation can handle normal operating voltages and temporary overvoltages without failure.
Hipot tests can be performed using either AC or DC voltage, depending on the equipment type and insulation characteristics. AC Hipot tests are dynamic and simulate actual service conditions, while DC Hipot tests are simpler and commonly used for factory tests.
VLF Testing vs Hipot – Comparison Overview
The following table highlights the major differences between VLF testing and Hipot testing to help you choose the right method for your application.
| Parameter | VLF Testing | Hipot Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Very Low Frequency Test | High Potential Test |
| Voltage Type | AC (low frequency 0.01–0.1 Hz) | AC or DC |
| Purpose | Detects insulation degradation and defects | Checks insulation withstand capability |
| Frequency | Very low (0.01–0.1 Hz) | Power frequency (50/60 Hz) or DC |
| Equipment Size | Compact and portable | Varies with test type |
| Typical Applications | Field testing of MV/HV cables, motors, transformers | Factory tests, insulation quality checks |
| Test Duration | Several minutes per cycle | Short duration (seconds to minutes) |
| Stress on Insulation | Low and controlled | High, may cause stress on insulation |
| Detection of Partial Discharge | Yes | Limited or No |
| Suitability for Aged Cables | Excellent | Limited due to possible damage risk |
How VLF Testing Works
In VLF testing, the test voltage alternates slowly between positive and negative peaks. This allows the insulation system to charge and discharge over time, simulating actual AC stress but without the high reactive current associated with standard AC tests.
The test equipment applies the desired test voltage based on the cable’s rated voltage. For example, a 15 kV-rated cable might be tested at 22 kV peak during VLF testing. The test is usually maintained for 15 to 30 minutes while monitoring leakage current, insulation resistance, and any discharge activity.
If the insulation withstands the test without breakdown or abnormal leakage, it passes. If not, the location of failure can be pinpointed and repaired.
Know more about Cable VLF Testing Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide for Safe High Voltage Cable Testing
VLF testing is especially useful for long power cables and underground distribution systems, where DC Hipot testing could over-stress the insulation and cause premature failures.
How Hipot Testing Works
Hipot testing involves applying a high voltage between the conductors and insulation barrier (usually ground). The idea is to ensure that the insulation can withstand voltages higher than its normal operating level.
For example, a 480 V cable might be tested at 2,000 V DC or AC to check for insulation integrity. The current flow is measured during the test — if it remains below the acceptable limit and no breakdown occurs, the cable passes.
In AC Hipot tests, the polarity alternates just like in service conditions, providing a more realistic assessment. However, because AC Hipot tests require higher current capacity, the equipment tends to be larger and more expensive.
DC Hipot tests, on the other hand, use a constant polarity voltage. These tests are easier to conduct and require smaller equipment, but they can sometimes cause dielectric charging effects in aged insulation.
VLF Testing vs Hipot – Which is Better for Cable Testing?
When comparing VLF testing vs Hipot, the best method depends on the condition and type of cable being tested.
For new cables, both VLF and Hipot can verify insulation quality. However, VLF provides a more realistic simulation of AC operating stress, making it preferable for modern polymeric cables (like XLPE).
For aged cables, VLF is much safer. DC Hipot testing can cause polarization and charge buildup in older insulation, potentially leading to failure during or after testing. VLF testing applies stress similar to actual service without overstressing the insulation, helping detect weak spots before they fail in the field.
In short, VLF testing is the modern standard for field acceptance and maintenance testing of medium- and high-voltage cables, while Hipot remains valuable for manufacturing and short-term insulation verification.
Advantages of VLF Testing
VLF testing offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in today’s power industry:
- Portable and lightweight test equipment
- Safe for aged polymeric insulation
- Detects partial discharge and insulation defects early
- Reduces risk of insulation damage
- Complies with IEEE 400.2 and IEC 60502 testing standards
Know more about IEC Standard for VRLA Battery – Complete Guide to Design, Testing, and Performance
Advantages of Hipot Testing
Despite its limitations for aged cables, Hipot testing still holds importance in many applications:
- Simple to perform and widely understood
- Effective for factory acceptance testing
- Useful for switchgear, transformers, and short cable assemblies
- Provides clear pass/fail insulation verification
Know more about Capacity Factor vs Load Factor – Key Differences, Formula, and Examples Explained
Summary Table – VLF vs Hipot Key Differences
| Aspect | VLF Testing | Hipot Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Best Use | Field testing of power cables | Factory testing and QC |
| Frequency Range | 0.01–0.1 Hz | 50/60 Hz AC or DC |
| Test Voltage Stress | Lower, gradual | High, direct |
| Risk to Old Insulation | Minimal | Higher |
| Partial Discharge Detection | Possible | Limited |
| Equipment Portability | High | Moderate |
| Compliance Standards | IEEE 400.2, IEC 60060 | IEC 60243, ASTM D149 |
Conclusion
Understanding VLF testing vs Hipot is essential for every electrical engineer and maintenance professional. While both methods serve the same purpose — verifying insulation integrity — their principles and impacts differ greatly.
VLF testing uses a low-frequency AC voltage to simulate real operating conditions safely, making it ideal for aged or field cables. Hipot testing applies high potential (AC or DC) voltage to confirm insulation withstand strength, commonly used for new equipment and quality checks.
Know more about IEC Standard for Generator Protection – Key Guidelines and Compliance Requirements
Choosing the right method ensures accurate results, extended equipment life, and reduced failure risks. In most modern applications, VLF testing is considered the safer and more reliable choice for medium and high-voltage cable testing, while Hipot remains valuable for controlled factory environments.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#VLFTesting, #HipotTesting, #CableTesting, #HighVoltageTesting, #ElectricalTesting, #PowerCableMaintenance, #DielectricTest, #HVTesting, #InsulationTesting, #ElectricalEngineering, #SubstationMaintenance, #TestingAndCommissioning, #PowerSystemTesting, #VLFvsHipot, #ElectricalSafety