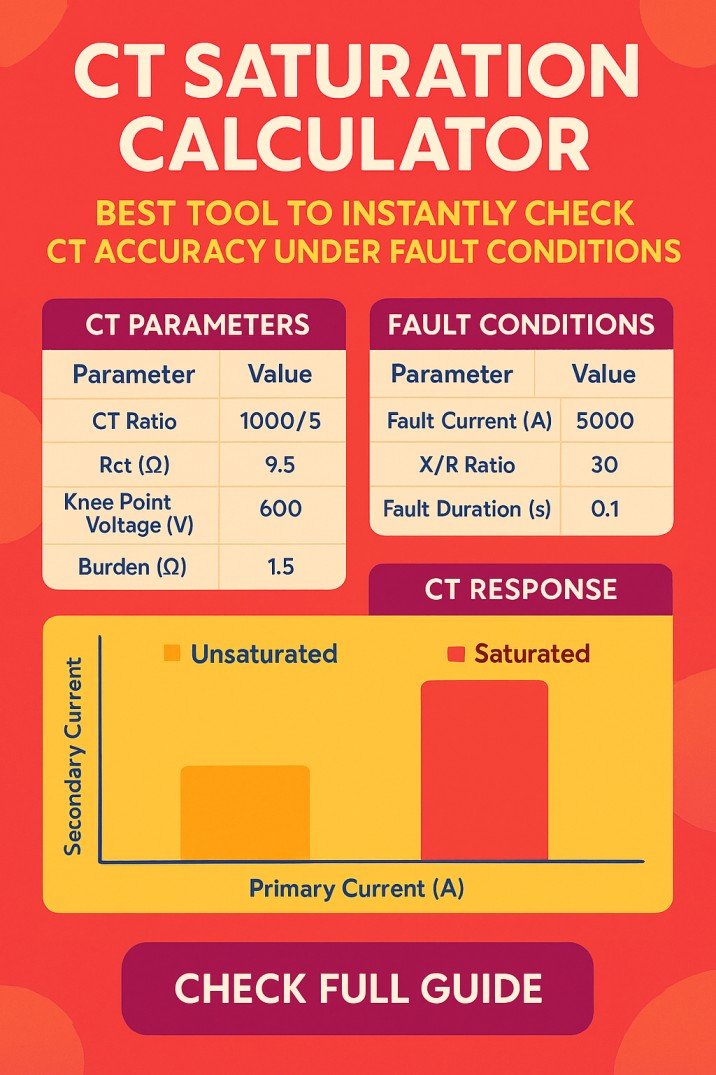
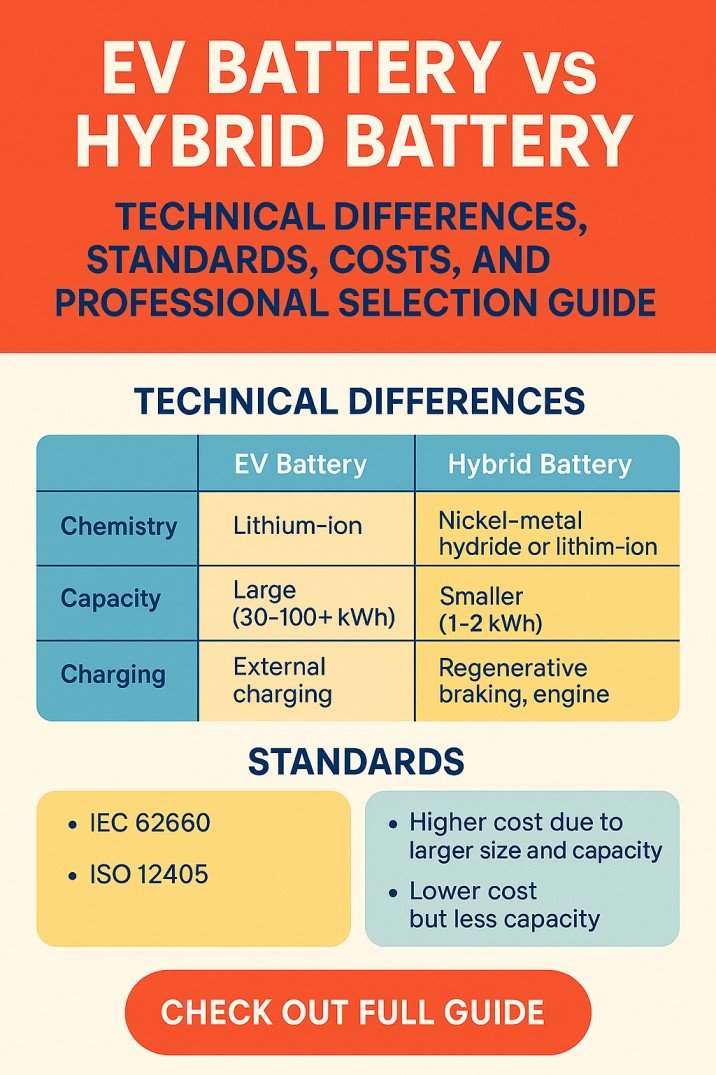
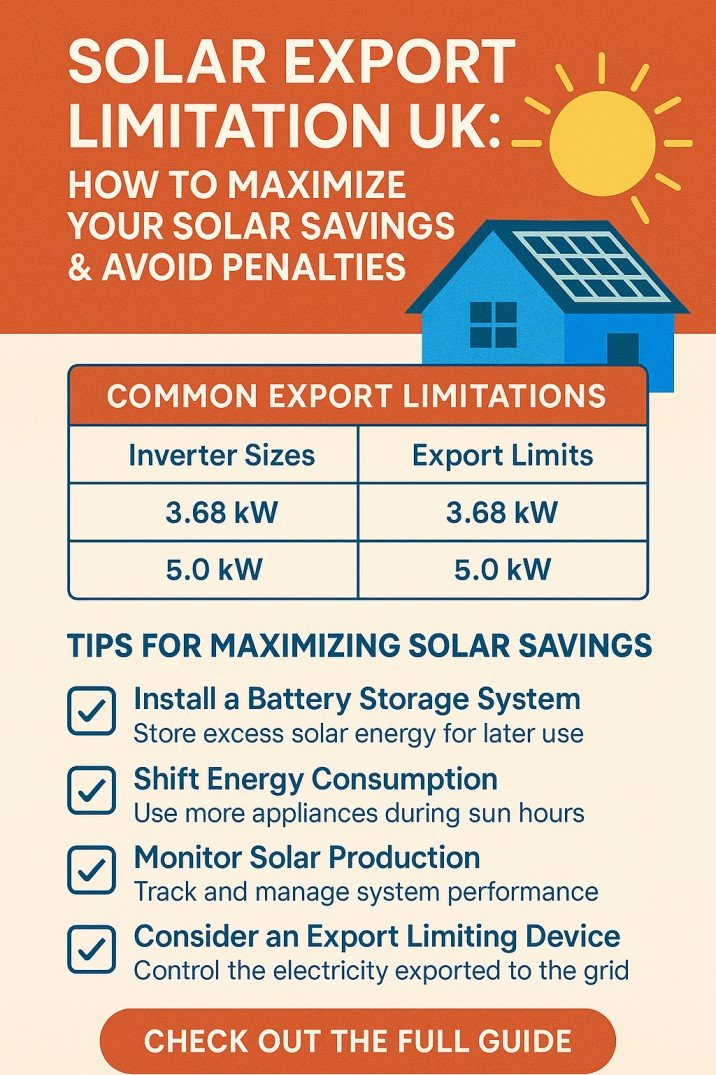
Smart Grid and Microgrid: Modern Energy Solutions
Understanding Smart Grid and Microgrid
The smart grid and microgrid are transforming the way electricity is generated, distributed, and consumed. While a smart grid is a large-scale, intelligent electrical network integrating digital communication for efficiency and reliability, a microgrid is a localized energy system that can operate independently or in connection with the main grid. Both play crucial roles in modern power infrastructure, improving energy resilience and integrating renewable energy sources.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
How Smart Grid and Microgrid Work
A smart grid incorporates advanced sensors, automation, and real-time data analytics to optimize electricity flow. It ensures better demand-side management, reduces power outages, and enables renewable energy integration. On the other hand, a microgrid consists of distributed energy resources (DERs) such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage, allowing for self-sustained operation even during grid failures.
Components of a Smart Grid
- Smart Meters – Provide real-time energy usage data.
- Advanced Sensors – Detect faults and optimize power distribution.
- Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) – Solar, wind, and battery storage.
- Automated Control Systems – Enable demand response and self-healing mechanisms.
- Two-Way Communication – Ensures seamless data exchange between consumers and utilities.
Key Elements of a Microgrid
- Generation Units – Solar, wind, biomass, or small-scale thermal plants.
- Energy Storage – Batteries and supercapacitors for backup power.
- Microgrid Controller – Manages power distribution and islanding operations.
- Grid-Tied and Islanded Modes – Can operate with or without the main grid.
The Role of Smart Grid and Microgrid in Renewable Energy
Both smart grids and microgrids facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources. A smart grid for renewable energy optimizes power generation and consumption, ensuring that clean energy is used efficiently. Microgrids, particularly in remote areas, enhance energy independence by utilizing local renewable resources.
Benefits of Smart Grid and Microgrid in Renewable Energy
- Higher Grid Stability – Reduces the risk of power outages.
- Optimized Energy Usage – Smart meters and analytics improve efficiency.
- Decentralized Power Generation – Increases resilience against natural disasters.
- Cost Reduction – Reduces dependency on fossil fuels and peak-hour pricing.
For more details, check out Smart Grid for Renewable Energy.
Smart Grid and Microgrid Architecture
The smart grid architecture model consists of multiple layers:
- Physical Layer – Includes power plants, transmission lines, and substations.
- Communication Layer – Uses IoT, cloud computing, and AI for data transfer.
- Control Layer – Implements automation and decision-making systems.
- Application Layer – Includes smart grid applications for billing, security, and analytics.
A microgrid architecture follows a decentralized structure, allowing local generation and distribution within a defined geographical area.
For an in-depth guide, read Smart Grid Fundamentals of Design.
Smart Grid Analytics and Blockchain Integration
Smart Grid Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is at the core of smart grid analytics. Real-time monitoring helps utilities detect faults, forecast demand, and optimize energy distribution. Companies like Smart Grid Analytics Private Limited specialize in advanced data solutions for predictive maintenance and demand forecasting.
Blockchain in Smart Grids
The use of smart grid blockchain ensures secure transactions and transparency in energy trading. Decentralized ledgers help in peer-to-peer energy trading and prevent electricity theft.
Smart Grid Billing and Applications
Smart Grid Billing System
A smart grid billing system enhances the accuracy of electricity consumption tracking. With smart meters, consumers can monitor their energy usage in real time, leading to more efficient billing and lower costs.
Applications of Smart Grid and Microgrid
- Smart Homes – Enables automation of energy consumption.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging – Optimizes charging during off-peak hours.
- Industrial Efficiency – Reduces energy wastage in factories.
- Disaster Recovery – Microgrids provide backup power in emergencies.
For more insights, check out Smart Grid Functions.
Challenges in Implementing Smart Grid and Microgrid
Despite their advantages, the smart grid and microgrid face several challenges:
- High Initial Costs – Infrastructure upgrades require significant investment.
- Cybersecurity Risks – Digital networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Regulatory Barriers – Policies differ across regions, slowing adoption.
- Interoperability Issues – Integrating old and new technologies can be complex.
Smart Grid Books and Resources
For a deeper understanding of smart grid and microgrid, you can explore various smart grid books available in the market. Some resources offer smart grid books free download pdf, making technical knowledge more accessible.
For expert discussions, visit Smart Grid Forum 2025.
Future of Smart Grid and Microgrid
The future of smart grids and microgrids is driven by technological advancements, such as AI-powered grid management, blockchain-based energy trading, and improved battery storage solutions. The concept of smart grid bed, which integrates power-saving technologies in residential settings, is also gaining traction.
As more nations commit to sustainability, the demand for smart grid architecture and microgrid applications will continue to grow, ensuring a cleaner and more resilient energy future.
For fundamental knowledge, visit What is a Smart Grid?.
Conclusion
The smart grid and microgrid represent the next generation of energy infrastructure, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. With continuous innovation in smart grid analytics, blockchain, billing, and architecture, the power sector is set for a significant transformation. Investing in these technologies today will pave the way for a smarter, more resilient grid tomorrow.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
SmartGrid #Microgrid #SmartGridTechnology #RenewableEnergy #EnergyEfficiency #GridModernization #SmartGridSolutions #MicrogridSystem #PowerGrid #SmartEnergy #SustainableGrid #EnergyStorage #DecentralizedEnergy #ElectricGrid #FutureEnergy