Single Phase Motor Cable Size Calculator
Choosing the right cable size for a single-phase motor is crucial for ensuring the motor operates efficiently and safely. An undersized cable can result in voltage drops, overheating, and potential damage to the motor, while an oversized cable may be costly and unnecessary. A single-phase motor cable size calculator simplifies this process, helping engineers and electricians determine the correct cable size based on motor specifications, current ratings, and distance.
This article explains how to use a single-phase motor cable size calculator, outlines the factors that influence cable size selection, and provides technical insights, formulas, and standards for proper cable sizing.
Understanding Cable Sizing for Single-Phase Motors
Cable sizing for motors is a critical aspect of electrical installation. A motor’s performance depends heavily on the correct cable size, as too small a cable can lead to excessive heat generation and reduced efficiency. Conversely, using a cable that’s too large can be more expensive than necessary.
The cable’s purpose is to carry the electrical current from the power source to the motor. For a single-phase motor, several factors must be considered, including:
- Current Rating: The motor’s full-load current rating is used to determine the current the cable must safely carry.
- Voltage Drop: The acceptable voltage drop across the cable, which depends on the distance between the motor and the power supply.
- Motor Power: The rated power of the motor, usually measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW), helps in calculating the current drawn.
- Conductor Material: Copper or aluminum conductors are typically used for electrical cables, with copper offering better conductivity but being more expensive.
Formula for Calculating Cable Size
The basic formula used for calculating cable size for single-phase motors is derived from Ohm’s law and the power formula:
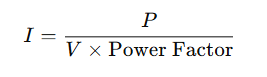
Where:
- I is the current (Amps)
- P is the power (Watts or VA)
- V is the voltage (Volts)
- Power Factor is typically around 0.8 for most motors.
Once the current is known, the next step is to determine the cable size by using the following general formula:
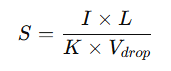
Where:
- S is the cable cross-sectional area in square millimeters (mm²)
- I is the current in amperes
- L is the length of the cable in meters
- K is a constant (depending on the cable material: for copper, it’s 56, and for aluminum, it’s 35)
- V_{drop} is the permissible voltage drop (usually 3% of the supply voltage)
This formula can help you calculate the optimal cable size for your motor, considering the factors mentioned.
Using a Single Phase Motor Cable Size Calculator
A single-phase motor cable size calculator typically requires the following inputs:
- Motor Power: The rated power of the motor, in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
- Voltage: The system voltage, typically 230V for residential and small commercial installations.
- Current: If available, the full-load current rating of the motor (can be obtained from the motor nameplate).
- Distance: The length of the cable run, from the power supply to the motor.
- Conductor Material: Copper or aluminum, as the conductivity of these materials differs.
- Voltage Drop: The maximum allowable voltage drop across the cable.
Once these values are entered into the calculator, it will compute the cable size that ensures the motor operates efficiently and safely. These calculators often use the formulas mentioned above to provide accurate results quickly.
Important Considerations When Using the Calculator
While the single-phase motor cable size calculator provides an easy and quick solution, certain factors should still be considered:
- Cable Type: There are various types of cables designed for different environments (e.g., indoor, outdoor, underground). The calculator might also factor in the type of insulation, which affects the cable’s current-carrying capacity.
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the environment where the cable is installed impacts its capacity. Higher temperatures can reduce the cable’s ability to carry current.
- Safety Margins: Always allow for a safety margin, especially if the motor may be subjected to fluctuating loads. Oversizing the cable slightly ensures reliable performance.
Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage drop is an important factor when selecting the correct cable size. The voltage drop depends on the cable length, conductor material, current, and cable size. To calculate the voltage drop for a single-phase circuit, the formula is:
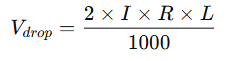
Where:
- V_{drop} is the voltage drop (Volts)
- I is the current (Amps)
- R is the resistance of the cable per meter (Ohms)
- L is the length of the cable in meters
In general, a voltage drop of 3% is considered acceptable for most residential and commercial installations. If the voltage drop exceeds this, it could result in motor inefficiency and potential damage.
Choosing Between Copper and Aluminum Conductors
When selecting a conductor material, you will typically choose between copper and aluminum. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Copper: Copper cables have better conductivity, which means that for the same current, a smaller copper cable is required compared to an aluminum cable. However, copper cables are more expensive than aluminum cables.
- Aluminum: Aluminum cables are cheaper but require a larger cross-sectional area to carry the same current as copper cables. This makes them more cost-effective for long cable runs but less efficient than copper for short distances.
Industry Standards and References
When choosing the appropriate cable size for a single-phase motor, it’s essential to refer to industry standards and regulations. Some of the widely used standards are:
- IEC 60228: This standard provides the general specifications for conductors of insulated cables.
- NEC (National Electrical Code): The NEC specifies the minimum requirements for electrical installations in the United States, including motor cable sizing.
- BS 7671: The British Standard for electrical installations, which includes cable sizing recommendations.
- IEEE 142 (Green Book): Provides guidelines for grounding and protection of electrical systems, including motor circuits.
Cable Size Chart for Single-Phase Motors
To give you an idea of the typical cable sizes, here is a table showing the recommended cable sizes for single-phase motors based on different motor power ratings:
| Motor Power (kW) | Full Load Current (A) | Recommended Cable Size (mm²) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 kW | 2.17 A | 1.5 mm² |
| 1 kW | 4.35 A | 2.5 mm² |
| 2.2 kW | 9.52 A | 4 mm² |
| 4 kW | 17.39 A | 6 mm² |
| 7.5 kW | 30.43 A | 10 mm² |
| 11 kW | 45.65 A | 16 mm² |
Note: These values are approximate and should be verified using a single-phase motor cable size calculator based on specific installation conditions.
Conclusion
Using the right cable size for a single-phase motor is vital for ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of the motor. The single-phase motor cable size calculator simplifies this process, providing quick, reliable results based on motor power, current, distance, and material. By understanding the underlying principles and using the calculator correctly, you can make informed decisions that optimize both cost and performance.
For accurate results, always refer to relevant standards like IEC 60228, NEC, and BS 7671, and ensure that safety margins are considered in the final cable sizing.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#SinglePhaseMotor, #CableSizeCalculator, #MotorWiring, #ElectricalEngineering, #CableSelection, #MotorCableSize, #SinglePhaseMotorWiring, #ElectricalSafety, #WireGauge, #VoltageDrop, #ElectricMotor, #CableSizing, #MotorInstallation, #Ampacity, #WiringStandards


