Partial Discharge vs Tan Delta Cable Testing: Important Key Differences Every Engineer Must Know
In the field of electrical engineering, ensuring the reliability and safety of high voltage cables is critical. Two widely used diagnostic techniques for assessing cable insulation are Partial Discharge (PD) testing and Tan Delta (TD) testing. While both are essential for preventive maintenance and fault detection, understanding the differences between them can significantly improve decision-making in cable condition assessment. This article explores partial discharge vs tan delta cable testing, their principles, applications, advantages, and limitations, providing engineers with a clear understanding of when to use each method.
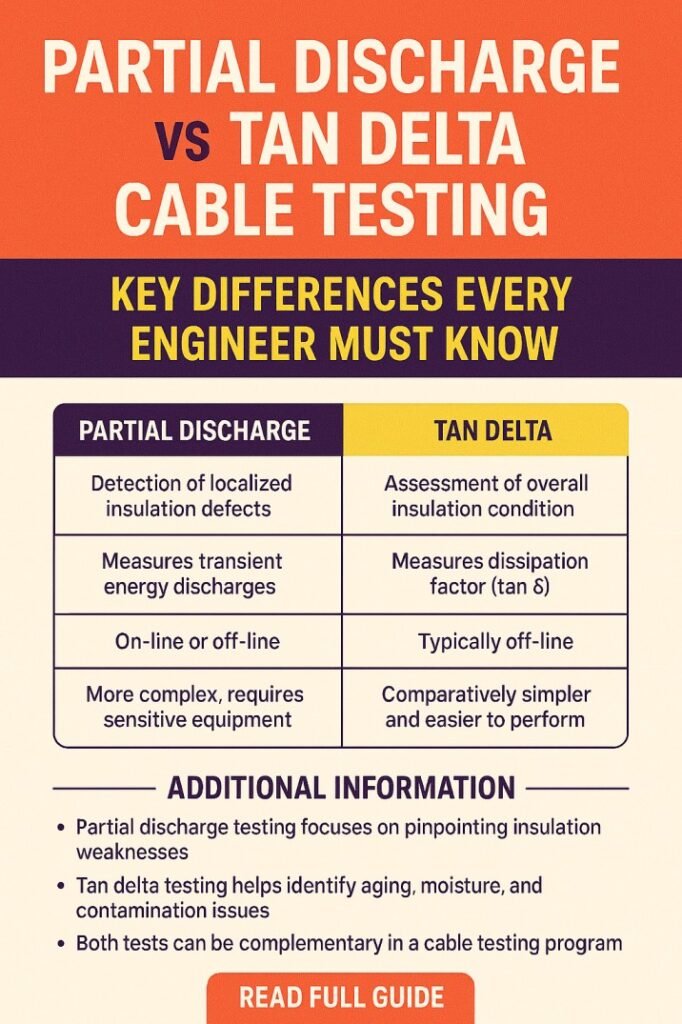
Table of Contents
Partial Discharge vs Tan Delta Cable Testing
Understanding Partial Discharge Testing
Partial discharge testing is a non-destructive diagnostic method that detects localized electrical discharges within cable insulation. PD occurs when insulation imperfections, such as voids, cracks, or contamination, allow small discharges to occur without causing complete insulation failure. These discharges can gradually deteriorate the insulation, eventually leading to catastrophic cable failure if left undetected.
Key Features of Partial Discharge Testing
- Sensitivity to localized defects: PD testing can detect minute defects that may not immediately impact the cable’s performance but could cause long-term degradation.
- Early fault detection: Engineers can identify potential failure points before they escalate, allowing timely maintenance.
- Applicable to various insulation types: PD testing works for XLPE, EPR, and paper-insulated cables.
PD testing requires specialized equipment such as PD detectors, coupling capacitors, and sensors to capture the high-frequency pulses generated during discharge. Measurements are often performed at operating voltage or slightly above to simulate real conditions. The results are typically represented as phase-resolved partial discharge (PRPD) patterns, which help in identifying the type and location of the defect.
Explore details on High Voltage Cable Testing Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide for Safe & Accurate HV Cable Testing
Understanding Tan Delta Testing
Tan Delta testing, also known as dissipation factor or loss angle measurement, evaluates the overall condition of cable insulation by measuring dielectric losses. It provides a quantitative assessment of insulation deterioration, which increases with aging, moisture ingress, and contamination.
Key Features of Tan Delta Testing
- Global insulation assessment: Unlike PD, which detects localized defects, TD measures the overall insulation health.
- Indicates aging and moisture: Higher tan delta values usually indicate insulation deterioration or water trees in polymeric cables.
- Simple measurement procedure: Tan delta testing involves applying an AC voltage and measuring the phase angle between current and voltage.
The tan delta value is the ratio of resistive current to capacitive current, reflecting the insulation’s dielectric losses. Engineers use TD testing to monitor insulation aging trends over time, making it an excellent tool for preventive maintenance programs.
Partial Discharge vs Tan Delta Cable Testing: Core Differences
While both partial discharge vs tan delta cable testing are diagnostic tools for high voltage cables, their objectives, measurement principles, and results differ significantly. Understanding these differences helps engineers select the right method based on cable type, age, and operational conditions.
| Feature | Partial Discharge Testing | Tan Delta Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detects localized insulation defects | Measures overall insulation health |
| Sensitivity | High for small defects | Low sensitivity to localized defects |
| Detection Type | Localized electrical discharges | Dielectric losses (global insulation condition) |
| Equipment | PD detectors, coupling capacitors, HF sensors | AC voltage source, measurement bridge, phase angle meter |
| Voltage Requirement | Operating or slightly higher than operating voltage | Typically rated voltage of cable |
| Interpretation | Phase-resolved patterns indicate defect type & location | Tan delta value indicates insulation deterioration level |
| Best Use | Identifying manufacturing defects, moisture voids, or cracks | Assessing aging, contamination, or water treeing over entire cable length |
| Complexity | High, requires expertise | Moderate, easier to perform |
| Result Representation | PRPD patterns and pulse magnitude | Tan delta value, usually plotted vs voltage |
Explore all about vlf testing procedure
Applications and Selection Criteria
Selecting between PD and TD testing depends on the specific maintenance objectives and cable conditions.
When to Use Partial Discharge Testing
Partial discharge testing is ideal for detecting hidden defects that could lead to premature failure. It is particularly useful for:
- Newly installed cables to detect manufacturing defects.
- Critical circuits where early detection of faults is necessary.
- Periodic condition monitoring in high voltage substations.
PD testing provides actionable insights into defect type and severity, allowing engineers to schedule targeted repairs or replacements.
When to Use Tan Delta Testing
Tan delta testing is better suited for evaluating insulation aging and overall cable condition. Common applications include:
- Monitoring insulation deterioration in service-aged cables.
- Detecting moisture ingress in XLPE and paper-insulated cables.
- Assessing long cable runs where localized defects may not be the primary concern.
TD testing is highly effective for preventive maintenance programs, especially when combined with historical data to track insulation degradation over time.
Find all about High Voltage Cable Testing Standards: Complete Guide for Engineers
Advantages and Limitations
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each testing method ensures accurate diagnosis and reduces unnecessary downtime.
Partial Discharge Testing
Advantages:
- Detects critical defects early.
- Helps in fault location and prioritization.
- Applicable to multiple insulation types.
Limitations:
- Requires experienced operators for accurate interpretation.
- Sensitive to electromagnetic interference, requiring noise-free environments.
- Equipment cost can be high.
Tan Delta Testing
Advantages:
- Provides clear indication of insulation aging.
- Easier to perform and interpret compared to PD testing.
- Useful for trend monitoring and preventive maintenance.
Limitations:
- Cannot detect small localized defects.
- May not provide exact defect location.
- Less effective for newly installed cables with potential hidden faults.
Know more about VLF Testing vs Hipot: Best Guide on Key Differences and Applications
Complementary Use for Maximum Reliability
In practice, many engineers use partial discharge vs tan delta cable testing in combination to obtain a comprehensive understanding of cable condition. PD testing identifies critical localized defects, while TD testing monitors the overall insulation health. Together, they form a robust diagnostic approach, reducing unexpected failures and extending cable life.
| Test Combination | Benefits |
|---|---|
| PD + TD on new cables | Detects manufacturing defects and establishes baseline insulation condition |
| PD + TD on aged cables | Identifies existing defects while monitoring insulation deterioration trends |
| TD for routine monitoring | Simple tracking of insulation health over time |
| PD for high-risk circuits | Early detection of localized faults in critical installations |
Know more about High Voltage Testing Procedures for Electrical Panels: Step by Step
Conclusion
Choosing between partial discharge vs tan delta cable testing is not about which method is superior but about understanding their complementary roles. Partial discharge testing excels at detecting localized defects that could cause sudden failures, while tan delta testing provides an overall measure of insulation aging and dielectric losses. By leveraging both techniques appropriately, engineers can implement proactive maintenance strategies, improve cable reliability, and avoid costly outages.
For every electrical engineer dealing with high voltage systems, mastering these testing methods is essential. Proper implementation ensures safety, reduces downtime, and maximizes the operational life of critical cable infrastructure. Whether you are dealing with newly installed cables, aging circuits, or critical high voltage lines, understanding the nuances of PD and TD testing is key to effective electrical asset management.
Know more about Power Quality Analyzer Buying Guide for Engineers
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#PartialDischarge, #TanDeltaTesting, #CableTesting, #ElectricalTesting, #HVTesting, #PowerCables, #PDvsTanDelta, #InsulationTesting, #HighVoltageCables, #ElectricalEngineering


