NEC Wire Size Chart Explained: Important Concepts
The NEC Wire Size Chart is one of the most trusted tools for safe electrical design. It helps electricians, engineers, and site owners select the correct conductor size for any load. Accurate wire sizing matters more than ever. Power demand is rising. Equipment is sensitive. Codes are strict. Using the NEC Wire Size Chart reduces overheating, voltage drop, and fire risk. It also improves system efficiency and long-term reliability. This guide explains the chart in a simple and practical way, with examples, tables, and clear rules you can apply on real projects.
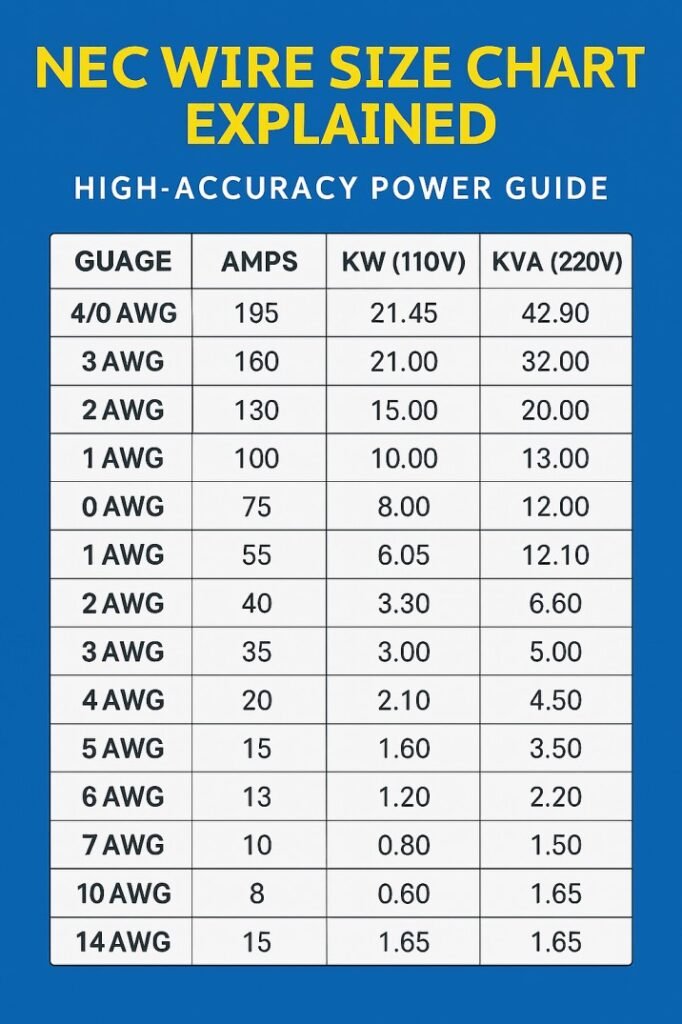
Table of Contents
What the NEC Wire Size Chart Really Means
The NEC Wire Size Chart links wire gauge to allowable ampacity. Ampacity is the maximum current a conductor can carry without exceeding its temperature rating. The chart is based on the National Electrical Code. It considers conductor material, insulation type, ambient temperature, and installation method. When you read the NEC Wire Size Chart correctly, you are not guessing. You are following tested limits that protect people and equipment.
Many electrical failures come from undersized conductors. Heat builds up slowly. Insulation degrades. Terminals loosen. The chart exists to prevent this chain of problems. That is why inspectors rely on it. That is also why professionals should never ignore it.
Explore our professional online tool for quick calculations kw to cable size calculator
How Wire Gauge and Ampacity Are Connected
Wire size in the chart is usually shown in AWG or kcmil. A lower AWG number means a thicker wire. Thicker wire carries more current with less resistance. Resistance creates heat. Heat limits ampacity. The NEC Wire Size Chart balances all of these factors in one place.
Copper and aluminum behave differently. Copper has lower resistance. Aluminum needs a larger size for the same load. The chart shows separate ampacity values for each material. Always check that detail before selecting a conductor. Use our online tool Conduit Fill Calculator for Multi Conductor Cable which measures accurate NEC Based Cable conduit Sizing
Standard NEC Wire Size Chart for Copper Conductors
The table below shows common copper wire sizes used in residential and commercial work. Values are based on typical 75°C insulation, which is common for breakers and terminals.
| AWG Size | Ampacity (A) | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 14 AWG | 15 A | Lighting circuits, outlets |
| 12 AWG | 20 A | General receptacles |
| 10 AWG | 30 A | Water heaters, dryers |
| 8 AWG | 40 A | Ranges, subpanels |
| 6 AWG | 55 A | Feeders, large motors |
| 4 AWG | 70 A | Service feeders |
| 2 AWG | 95 A | Main distribution |
This table is a simplified view. The full NEC Wire Size Chart includes many more sizes and temperature ratings. Still, this overview helps you understand everyday selections. Make your task simple with our online tool electrical cable size calculator
Aluminum Wire Sizes and Their Limits
Aluminum is lighter and often cheaper. It is widely used in feeders and service entrances. However, it carries less current than copper of the same size. The NEC Wire Size Chart clearly reflects this difference.
| AWG Size | Aluminum Ampacity (A) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| 12 AWG | 15 A | Limited branch circuits |
| 10 AWG | 25 A | Small appliances |
| 8 AWG | 35 A | AC units |
| 6 AWG | 40 A | Subpanel feeders |
| 4 AWG | 55 A | Main feeders |
| 2 AWG | 75 A | Service conductors |
When using aluminum, proper terminations are critical. Use rated lugs. Apply antioxidant compound. Torque connections correctly. Access our powerful online calculator now Conduit Fill Calculator (NEC Standard): Best Tool
Temperature Rating and Why It Changes the Chart
Insulation temperature rating has a major impact on ampacity. The NEC Wire Size Chart provides values for 60°C, 75°C, and 90°C conductors. Higher temperature ratings allow higher current. But there is a catch. Terminations often limit the usable rating.
Access our powerful online calculator now Electrical Diversity Calculator for accurate Load Estimation and efficient electrical Design.
Most breakers and lugs are rated at 75°C. Even if the wire is rated 90°C, you may still need to use the 75°C column. This is a common mistake. Always size the conductor to the weakest point in the circuit.
Voltage Drop and Long Cable Runs
Ampacity alone is not enough. Long distances cause voltage drop. Excessive voltage drop reduces motor torque and damages electronics. Best practice is to keep voltage drop under three percent for branch circuits.
The NEC Wire Size Chart does not directly show voltage drop. But it helps you upsize conductors when distance increases. For example, a 20-amp circuit may need 10 AWG instead of 12 AWG if the run is very long. This improves performance and efficiency.
Motor Loads and Continuous Circuits
Motors draw higher current during startup. Continuous loads run for three hours or more. The NEC requires additional capacity for these cases. Typically, you size conductors at 125 percent of the continuous load.
Using the NEC Wire Size Chart after applying this factor ensures compliance. It also reduces nuisance tripping and thermal stress. Industrial panels rely heavily on this rule. Experience fast and accurate results using our online tool cable size calculator uk
Conduit Fill and Installation Method
Wires installed in conduit retain more heat. Bundled conductors also reduce heat dissipation. The NEC Wire Size Chart includes adjustment factors for these conditions. When many current-carrying conductors share a conduit, ampacity must be reduced.
Ignoring this rule leads to silent overheating. Always consider conduit size, number of conductors, and spacing.
Residential vs Commercial Applications
Homes usually use smaller gauges. Commercial sites often use feeders, panels, and three-phase systems. The NEC Wire Size Chart applies to both. The difference is how carefully each factor is applied.
Commercial designs often require detailed calculations. Ambient temperature. Load diversity. Future expansion. The chart remains the foundation for all of it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many people misuse the chart. Some assume one size fits all. Others ignore aluminum differences. Another common error is matching breaker size without checking insulation rating.
The NEC Wire Size Chart is not optional guidance. It is code-backed safety data. Treat it with respect.
Start using our easy-to-use online tool earthing cable size calculator
Practical Selection Checklist
Use this short checklist before finalizing any conductor size.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify load current |
| 2 | Check continuous load factor |
| 3 | Select material type |
| 4 | Verify insulation rating |
| 5 | Adjust for temperature |
| 6 | Check voltage drop |
| 7 | Confirm termination rating |
Following these steps keeps your design compliant and efficient.
Why Accurate Wire Sizing Improves ROI
Correct sizing reduces energy loss. It extends equipment life. It lowers maintenance costs. It also improves safety ratings, which matters for insurance and inspections. Content that explains the NEC Wire Size Chart clearly attracts high-intent readers. These readers often convert on tools, services, and professional products.
Use our online tool 3 phase cable size calculator
Final Thoughts
Electrical systems are becoming more demanding. EV chargers, solar inverters, and automation loads are common. The NEC Wire Size Chart remains the most reliable reference for handling these changes. Learn it well. Apply it carefully. When in doubt, size up. Safety and performance always come first.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#NECWireSizeChart,#ElectricalCode,#WireGaugeSizing,#ElectricalEngineering,#PowerDistribution,#NECCompliance,#ElectricalSafety,#ConductorSizing,#LoadCalculation,#IndustrialElectrical