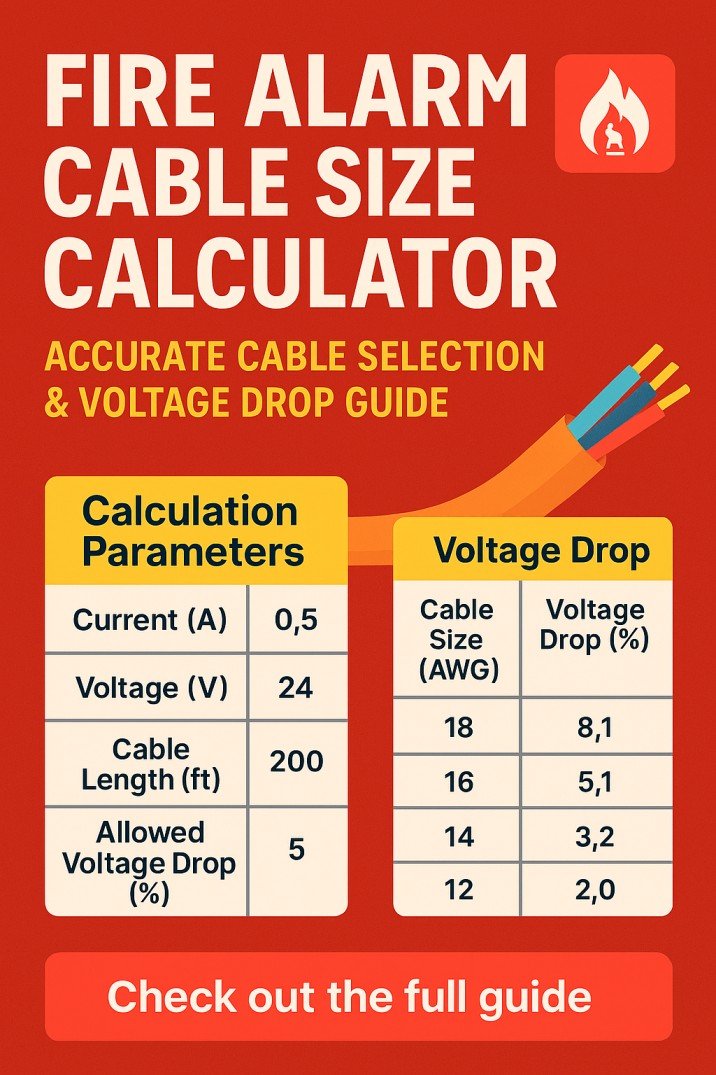
Motor Starter Size Chart: 7 Essential Insights for Better Selection
Choosing the right motor starter is one of the simplest ways to protect your equipment and improve system performance. A starter that is too small can overheat, cause tripping, or fail early. A starter that is too large adds unnecessary cost. This is why a clear and reliable Motor Starter Size Chart becomes so important. It helps match the motor horsepower, full load current, and starter size so your system runs smoothly and safely.
This detailed guide explains everything you need to know before choosing a starter. You will find seven essential insights that make selection easier.
Table of Contents
Why Motor Starter Size Charts Matter
Every motor has its own torque demand, start-up current, and operating characteristics. Motor starters manage this stress. They handle inrush current and protect motors from overloads. Because of this responsibility, the starter size must match the motor rating.
A Motor Starter Size Chart allows you to compare horsepower, current, and recommended sizes without guesswork. This increases equipment life, reduces maintenance cost, and improves overall safety. Charts also help standardize motor control selections across industries.
Know more about IEC Standards for Transformer Testing – Complete Guide to IEC 60076 and Testing Procedures
Understanding the Basics Before Using a Motor Starter Size Chart
Before you check the chart, it helps to understand the two main rating systems used in the industry. These are NEMA and IEC. Both standards serve the same purpose but follow different rating classifications.
NEMA uses size levels such as 00, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. These sizes remain consistent across manufacturers. IEC, however, rates starters based on operational current and duty category like AC-1 or AC-3. When you compare horsepower with these sizes, the chart helps you see how each level matches the current a motor requires.
This foundation makes the chart easier to understand and apply.
Starter Ratings and Motor Horsepower
Motor horsepower directly affects starter size. A higher horsepower motor requires more starting current. The table below gives a clear example of how horsepower and NEMA starter sizes commonly match in many industrial applications.
Example Motor Starter Size Comparison Table
| Motor HP | Full Load Current (A) | Typical NEMA Starter Size |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.8 – 4 | 0 |
| 3 | 7 – 10 | 1 |
| 5 | 15 – 17 | 1 |
| 7.5 | 22 – 25 | 2 |
| 10 | 28 – 32 | 2 |
| 15 | 42 – 46 | 3 |
| 20 | 54 – 59 | 3 |
| 25 | 68 – 75 | 4 |
| 30 | 80 – 88 | 4 |
| 40 | 104 – 112 | 5 |
| 50 | 130 – 150 | 5 |
This table offers a quick and helpful reference for understanding starter combinations.
Know more about IEC Standard for Vacuum Circuit Breaker – IEC 62271 Guidelines, Ratings & Testing Explained

Insight 1: Voltage Affects Starter Selection
Horsepower alone is not enough for accurate selection. A motor running at lower voltage draws higher current. This increased current may require a larger starter. Always verify the voltage rating presented in the Motor Starter Size Chart. If the voltage is different from your system, select the starter using full load current instead of horsepower.
Insight 2: Duty Cycle and Load Type Matter
Different load types demand different starter strengths. A fan with light load characteristics will require less torque compared to a loaded conveyor or compressor. Hard-starting loads need higher-rated starters. When using the chart, identify whether your load type is light, medium, or heavy. This helps you choose a size that maintains reliability under continuous or demanding duty cycles.
Know more about IEC Standard for Voltage Drop Calculation: Best Guide
Insight 3: Environmental Conditions Influence Selection
Temperature, dust, humidity, and vibration all affect starter performance. In hot or dusty environments, a starter may need a higher rating for stable performance. When you see borderline readings in the chart, choose the higher size for harsh operating conditions. This reduces breakdowns and improves long-term reliability.
Insight 4: Overload Relay Settings Must Match the Starter
The motor starter works hand-in-hand with overload protection. Incorrect overload relay settings can cause nuisance trips or fail to protect the motor. When using the Motor Starter Size Chart, review the overload current range for each starter size. If the relay range does not match your motor’s current, select the next higher starter size.
Insight 5: Consider the Starting Method
Direct-on-line (DOL) starting produces a high inrush current. Soft starters, VFDs, and star-delta starters significantly reduce this current. Because of this, some charts list special ratings for reduced-voltage starters. Always confirm whether your system uses DOL or reduced-voltage starting before finalizing the starter size.
Insight 6: Check Manufacturer Differences
Even though most brands follow NEMA or IEC standards, starter ratings differ slightly among manufacturers. This difference may affect your selection. Always compare your results with the brand-specific Motor Starter Size Chart for the most accurate match. The example tables here help guide your decision but do not replace official manufacturer data.
Know more about VLF Testing vs Hipot: Best Guide on Key Differences and Applications
Insight 7: Using Tables Improves Faster Decision Making
Tables help improve comparison, reduce reading time, and boost engagement. Below is another helpful table that aligns horsepower with estimated current. This allows you to double-check your selection even when you do not have the chart available.
Motor HP vs Estimated Full Load Current (400V)
| Motor HP | Estimated Current (A) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 7 |
| 5 | 14 |
| 7.5 | 22 |
| 10 | 28 |
| 15 | 42 |
| 20 | 54 |
| 25 | 68 |
| 30 | 80 |
| 40 | 104 |
| 50 | 130 |
These values make it easier to verify whether your chosen starter fits the motor rating.
Conclusion
A Motor Starter Size Chart is an essential tool for selecting the correct starter based on horsepower, full load current, voltage, load type, and environmental conditions. Understanding the seven insights in this guide helps you make better decisions, reduce downtime, extend motor life, and improve system safety.
Know more about Cable VLF Testing Procedure: Step-by-Step Guide for Safe High Voltage Cable Testing
Whether you are designing a system, upgrading equipment, or troubleshooting, using the right chart and the right method ensures long-term performance and reliability.
Follow Us on Social:
Subscribe our Newsletter on Electrical Insights for latest updates from Electrical Engineering Hub
#motorstartersizechart, #motorstarterguide, #electricalengineeringbasics, #motorcontroltips, #starterselection, #industrialmotors, #motortechnology, #motorprotection, #electricaldesign, #engineeringresources